Dive into the fascinating world of alkaline acid food charts, where you’ll discover the secrets to achieving optimal health and well-being. This comprehensive guide will empower you with the knowledge to make informed choices about the foods you eat, ensuring a harmonious balance in your body.
Embark on a journey of understanding the pH levels of various foods and their profound impact on your body’s chemistry. Learn how alkaline foods can neutralize acids, promoting a healthy internal environment, while acidic foods can potentially lead to inflammation and other ailments.
Alkaline and Acidic Foods: Alkaline Acid Food Chart
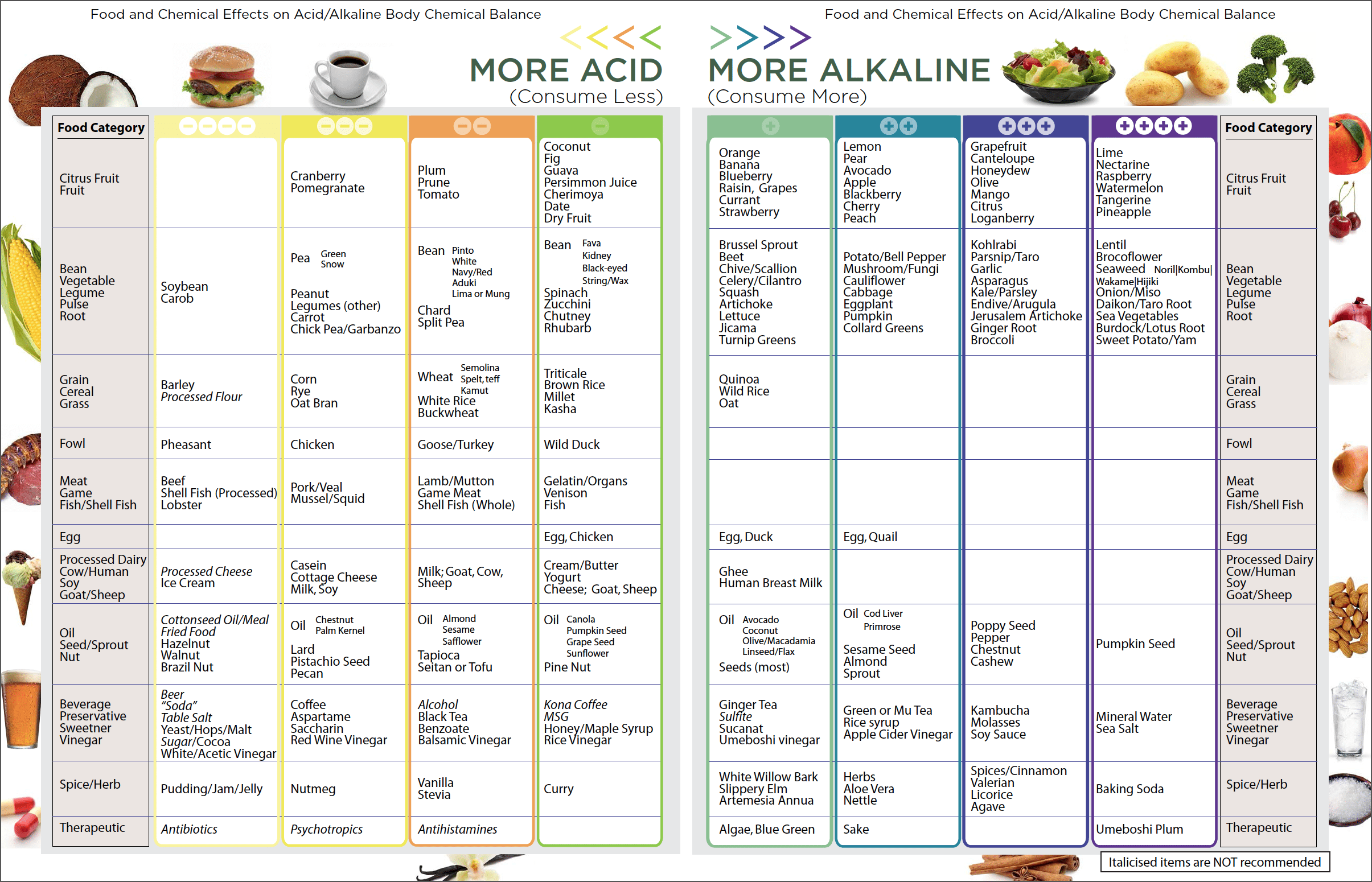
The pH level of a food measures its acidity or alkalinity on a scale of 0 to 14. Foods with a pH below 7 are considered acidic, while those with a pH above 7 are alkaline. The pH of our body is slightly alkaline, and it is important to maintain this balance for optimal health.
Consuming too many acidic foods can lead to acidosis, a condition in which the body becomes too acidic. This can cause a range of health problems, including fatigue, headaches, and digestive issues.To maintain a healthy pH balance, it is important to consume a diet that includes both alkaline and acidic foods.
Some common alkaline foods include:
- Fruits: Most fruits are alkaline, including bananas, apples, oranges, and melons.
- Vegetables: Many vegetables are also alkaline, such as broccoli, spinach, and carrots.
- Legumes: Legumes, such as beans and lentils, are good sources of alkaline.
- Nuts and seeds: Nuts and seeds are generally alkaline, including almonds, walnuts, and sunflower seeds.
Some common acidic foods include:
- Meat: Meat is generally acidic, including beef, pork, and chicken.
- Dairy products: Dairy products are also acidic, such as milk, cheese, and yogurt.
- Grains: Grains are typically acidic, including wheat, rice, and corn.
- Sugary foods: Sugary foods, such as candy and soda, are very acidic.
It is important to note that the pH of a food can change depending on how it is prepared. For example, cooking vegetables can make them more alkaline, while adding lemon juice to a salad can make it more acidic.It
is also important to note that the pH of a food is not the only factor that affects its impact on the body. Other factors, such as the presence of antioxidants and minerals, can also play a role.
The pH Levels of Various Foods and Their Impact on the Body
The pH level of a food can have a significant impact on its health effects. Acidic foods can contribute to inflammation, while alkaline foods can help to reduce inflammation. Inflammation is a major risk factor for a number of chronic diseases, including heart disease, cancer, and diabetes.Consuming
a diet that is high in alkaline foods can help to reduce inflammation and improve overall health. However, it is important to note that it is not necessary to avoid acidic foods altogether. A healthy diet includes a balance of both alkaline and acidic foods.
The ideal pH level for the human body is slightly alkaline, between 7.35 and 7.45. When the pH level falls below 7.35, the body becomes acidic, which can lead to a number of health problems.
Benefits of an Alkaline Diet
Adopting an alkaline diet offers a range of potential health benefits. By consuming alkaline-rich foods, individuals can help neutralize excess acids in the body, promoting a more balanced internal environment.
An alkaline diet can assist in maintaining a healthy pH level, reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as osteoporosis, kidney stones, and gout. Additionally, it can improve digestion, boost energy levels, and enhance overall well-being.
Improved Digestion
An alkaline diet supports healthy digestion by neutralizing stomach acid, reducing bloating, gas, and other digestive discomfort. Alkaline foods, such as fruits and vegetables, provide fiber, which aids in regulating bowel movements and promoting a healthy gut microbiome.
Enhanced Energy Levels
Consuming an alkaline diet can contribute to increased energy levels. By reducing acidity in the body, an alkaline diet helps prevent fatigue and sluggishness. Alkaline foods are rich in nutrients and antioxidants, providing sustained energy throughout the day.
Improved Overall Well-being, Alkaline acid food chart
An alkaline diet promotes overall well-being by reducing inflammation and supporting detoxification. Alkaline foods contain antioxidants that combat free radicals, protecting cells from damage and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. Additionally, an alkaline diet can improve skin health, reduce headaches, and enhance sleep quality.
Dangers of an Acidic Diet
An overly acidic diet can lead to a range of health issues due to the imbalance it creates in the body’s pH levels. Consuming excessive acidic foods can disrupt the body’s natural equilibrium, resulting in inflammation and various ailments.
Acidic Diet and Inflammation
An acidic diet promotes an inflammatory environment within the body. Acidic substances, when present in high levels, can trigger the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are chemical messengers that signal the immune system to initiate an inflammatory response. Chronic inflammation is linked to numerous health conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, arthritis, and certain types of cancer.
Bone Health and Acidic Diet
The consumption of acidic foods can contribute to bone loss. When the body attempts to neutralize the acidity in the bloodstream, it may draw upon alkaline minerals, such as calcium, from the bones. Over time, this can lead to a decrease in bone density, increasing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
Digestive Issues and Acidic Diet
An acidic diet can disrupt the digestive system. The stomach naturally produces hydrochloric acid to aid in the breakdown of food, but excessive acidity can irritate the stomach lining, causing heartburn, indigestion, and acid reflux.
Practical Implementation

Integrating more alkaline foods into your diet is crucial for maintaining an alkaline balance. Here’s how to do it:
Start by consuming more fruits and vegetables, which are naturally alkaline. Focus on leafy greens, such as spinach, kale, and broccoli, as well as fruits like bananas, apples, and berries.
Meal Plans and Recipes
Incorporate alkaline-promoting foods into your meals through balanced meal plans and recipes. Consider the following:
- Breakfast:Oatmeal with berries and nuts, or a smoothie made with spinach, banana, and almond milk.
- Lunch:Salad with grilled chicken, quinoa, and vegetables, or a lentil soup with whole-wheat bread.
- Dinner:Salmon with roasted vegetables, or a tofu stir-fry with brown rice.
Considerations and Exceptions

While the alkaline-acidic food chart provides a general guideline, there are exceptions and considerations to keep in mind.
Some foods may exhibit both alkaline and acidic properties depending on their preparation or consumption.
pH of Food and Urine
It’s important to note that the pH of food does not directly determine the pH of urine. The body’s metabolic processes can alter the pH of ingested substances.
Mixed Foods
Many meals consist of a combination of alkaline and acidic foods. The overall pH of the meal depends on the proportions and interactions of the ingredients.
Preparation and Processing
Cooking methods and food processing can affect the pH of foods. For example, boiling vegetables may increase their alkalinity, while grilling or roasting may decrease it.
Popular Questions
What is an alkaline acid food chart?
An alkaline acid food chart categorizes foods based on their pH levels, indicating whether they have an alkalizing or acidifying effect on the body.
Why is maintaining an alkaline balance important?
An alkaline balance helps neutralize acids in the body, reducing inflammation and promoting overall well-being.
Are there any risks associated with an overly acidic diet?
Yes, an overly acidic diet can lead to inflammation, bone loss, and other health issues.
How can I incorporate more alkaline foods into my diet?
Focus on consuming fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, which are typically alkaline-forming.
