Natural food coloring, a symphony of vibrant hues derived from nature’s bounty, paints a delectable canvas upon our culinary creations. Embark on a gastronomic journey where color meets nourishment, as we delve into the world of these natural pigments, their origins, applications, and the tantalizing possibilities they hold.
From the deep reds of anthocyanins to the sunny yellows of carotenoids, natural food coloring unveils a vibrant palette that not only enhances the visual appeal of our food but also offers a treasure trove of health benefits.
Types of Natural Food Coloring
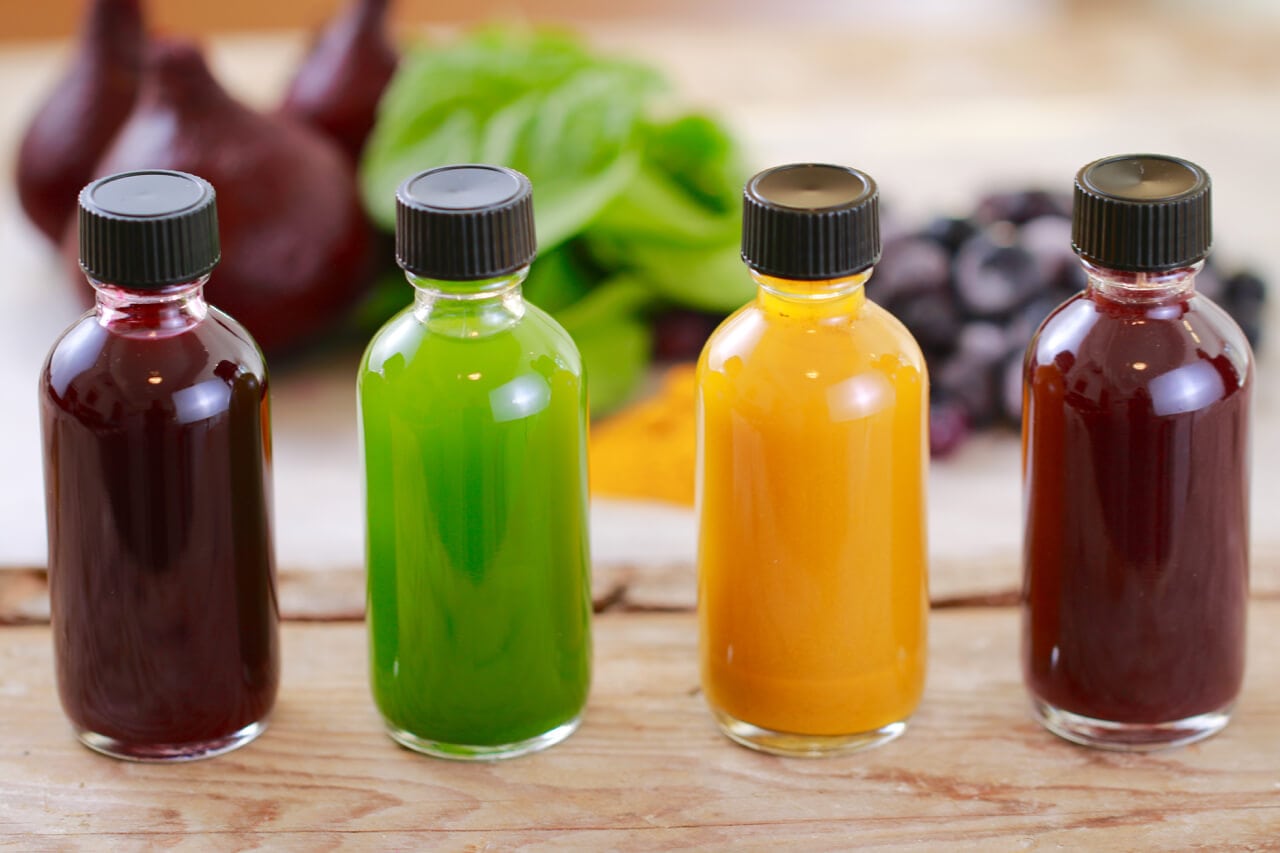

Natural food coloring is derived from plants, minerals, or animals and provides color to food and beverages without the use of synthetic dyes. These colorings are often preferred due to their perceived health benefits and consumer demand for natural ingredients.
Anthocyanins
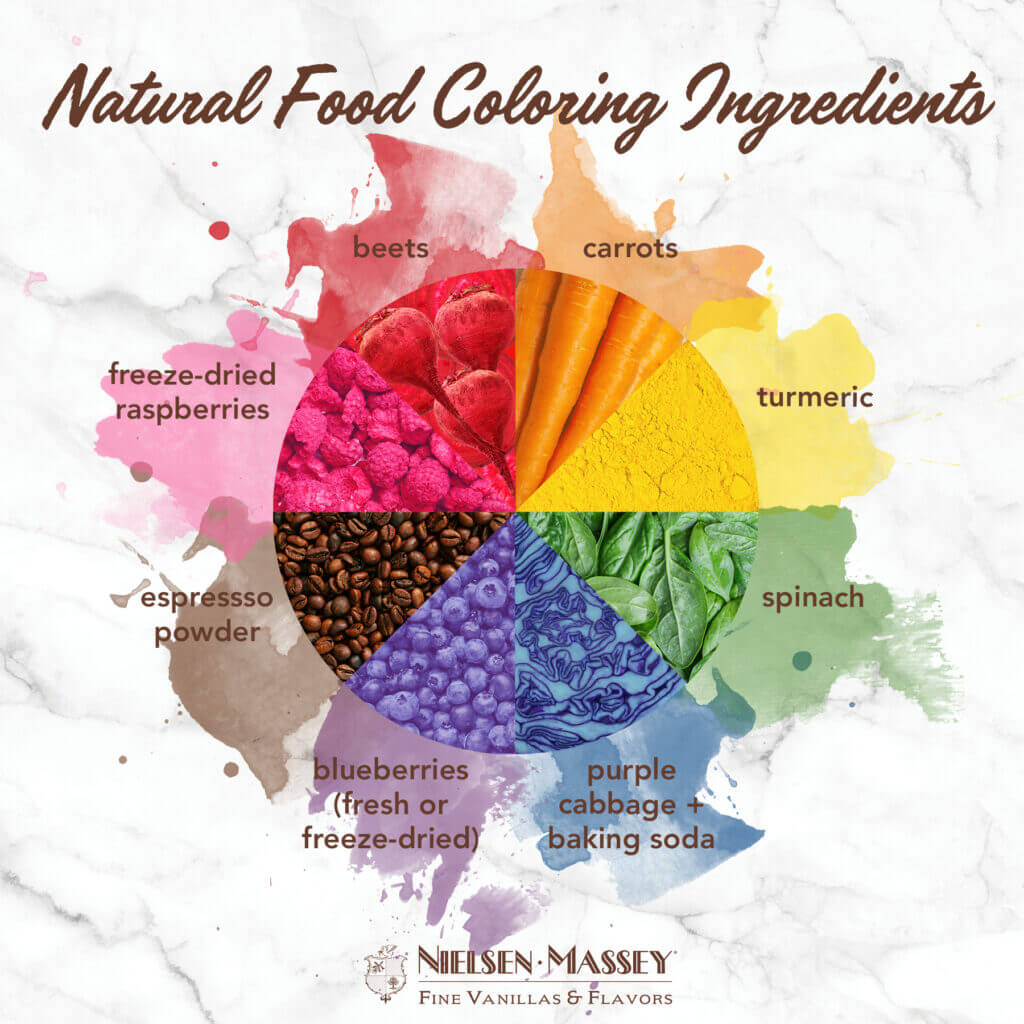
Anthocyanins are water-soluble pigments that give fruits, vegetables, and flowers their red, blue, and purple hues. They are powerful antioxidants and have been linked to several health benefits, including improved heart health, reduced inflammation, and protection against certain types of cancer.
- Foods containing anthocyanins: blueberries, cranberries, blackberries, cherries, red cabbage, eggplant
Carotenoids, Natural food coloring
Carotenoids are fat-soluble pigments that give fruits, vegetables, and algae their yellow, orange, and red colors. They are also powerful antioxidants and have been linked to several health benefits, including improved eye health, reduced risk of heart disease, and protection against certain types of cancer.
- Foods containing carotenoids: carrots, sweet potatoes, pumpkin, tomatoes, mangoes, apricots
Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is a green pigment found in plants that is essential for photosynthesis. It is also a powerful antioxidant and has been linked to several health benefits, including improved blood sugar control, reduced inflammation, and protection against certain types of cancer.
- Foods containing chlorophyll: spinach, kale, broccoli, green beans, parsley
Applications of Natural Food Coloring
Natural food coloring has gained immense popularity in various industries due to its safety, vibrant hues, and ability to enhance the visual appeal of products.
Food and Beverage Industry
Natural food coloring plays a crucial role in the food and beverage industry, where it adds color and vibrancy to a wide range of products, including:
- Soft drinks
- Candies
- Ice creams
- Baked goods
- Processed foods
By incorporating natural food coloring, manufacturers can create visually appealing products that stimulate consumers’ appetite and enhance their overall eating experience.
Cosmetics Industry
Natural food coloring is also widely used in the cosmetics industry to add color to products such as:
- Lipsticks
- Eyeshadows
- Blush
- Hair dyes
The use of natural food coloring in cosmetics ensures that products are safe for topical application, reducing the risk of allergic reactions or skin irritation.
Pharmaceutical Industry
In the pharmaceutical industry, natural food coloring is employed to enhance the appearance of medications, making them more palatable and appealing to patients. It is particularly beneficial for pediatric medications, as it can help disguise unpleasant flavors or colors.By incorporating natural food coloring into products, manufacturers can create visually appealing and appealing products that meet the needs of consumers across various industries.
Safety and Regulation of Natural Food Coloring
Natural food coloring, derived from plant, animal, or mineral sources, generally poses fewer safety concerns compared to synthetic counterparts. However, it is essential to ensure its safety and adherence to regulations for responsible use.
Regulatory bodies play a crucial role in evaluating the safety of natural food coloring and establishing guidelines for its use. These bodies assess the potential risks associated with specific colorants, including toxicity, allergenicity, and stability under various conditions.
Regulatory Bodies and Their Role
- US Food and Drug Administration (FDA):Regulates the use of food additives, including natural food coloring, in the United States. It evaluates safety data, sets limits for usage, and monitors compliance.
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA):Responsible for assessing the safety of food additives, including natural food coloring, in the European Union. It conducts risk assessments and provides scientific advice to policymakers.
- Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC):Develops international food safety standards, including guidelines for the use of food additives and natural food coloring. Its recommendations are adopted by many countries worldwide.
These regulatory bodies ensure that natural food coloring meets safety standards and is used responsibly in the food industry. They provide guidance to manufacturers and consumers, promoting transparency and protecting public health.
Trends and Innovations in Natural Food Coloring
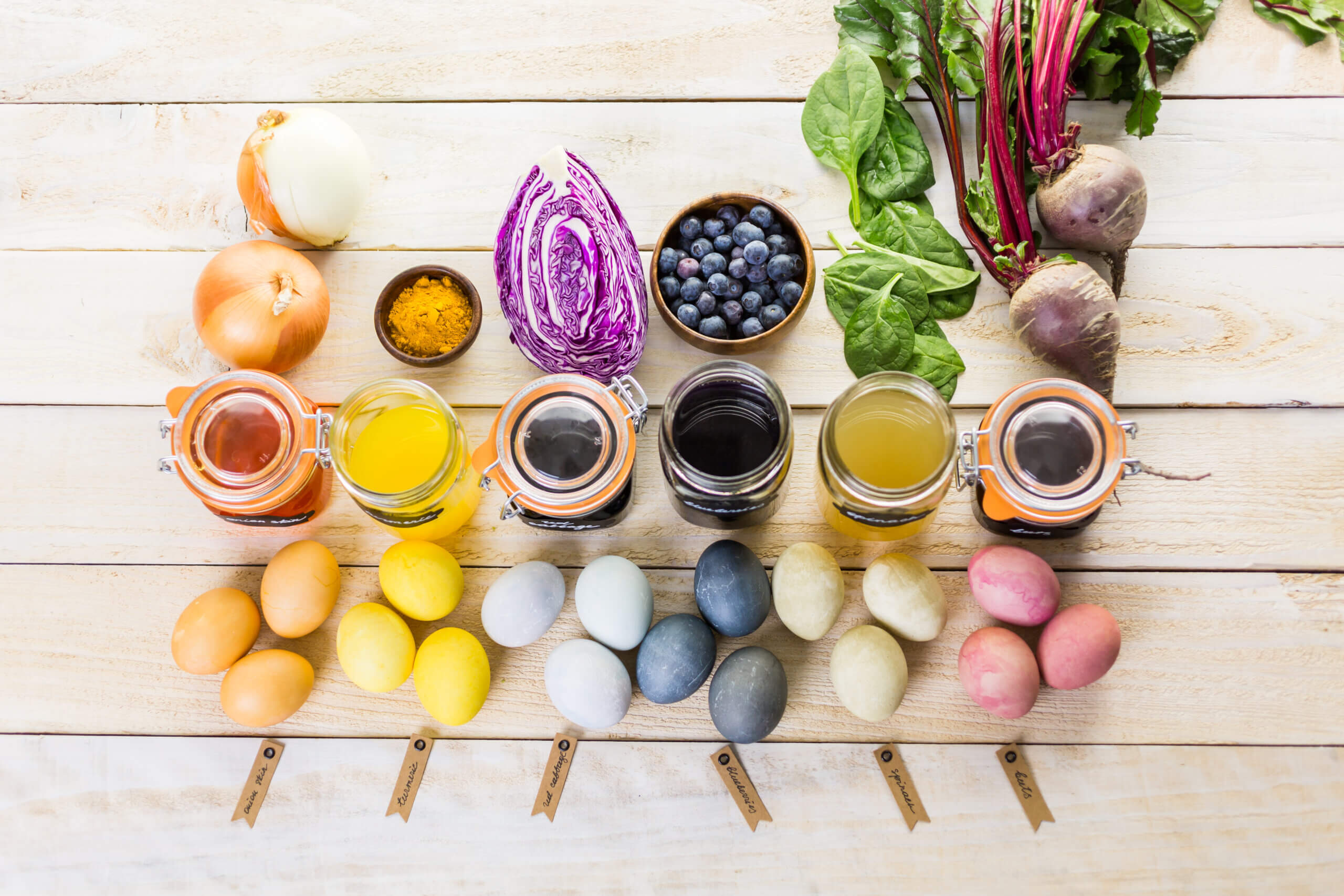

The use of natural food coloring is rapidly growing as consumers become more aware of the potential health risks associated with artificial colors. This trend is expected to continue in the coming years, as food manufacturers seek to meet consumer demand for healthier and more natural products.
One of the most significant trends in the natural food coloring industry is the development of new and innovative technologies for extracting and purifying colorants from natural sources. These technologies allow manufacturers to produce natural colors that are more vibrant, stable, and cost-effective than ever before.
Emerging Sources
Another trend is the exploration of new sources of natural food coloring. Traditionally, natural colors have been derived from fruits, vegetables, and spices. However, researchers are now investigating the potential of other sources, such as algae, fungi, and bacteria.
Future Potential
The future of natural food coloring is bright. As consumers continue to demand healthier and more natural products, food manufacturers will increasingly turn to natural colors to meet this demand. The development of new technologies and the exploration of new sources will continue to drive innovation in this industry, making natural food coloring an essential part of the food industry.
Common Queries
Is natural food coloring safe to consume?
Yes, natural food coloring is generally considered safe for consumption. It is derived from natural sources, such as fruits, vegetables, and minerals, and does not pose the same health risks as artificial food coloring.
What are the benefits of using natural food coloring?
Natural food coloring offers several benefits over artificial food coloring. It is free from synthetic chemicals, provides antioxidant and nutritional value, and is often preferred by consumers who seek natural and healthier options.
How can I incorporate natural food coloring into my cooking?
Incorporating natural food coloring into your cooking is easy. You can use fruit juices, vegetable powders, or natural food coloring extracts to add vibrant hues to your dishes. Experiment with different sources to achieve the desired colors and flavors.
