Food combining chart – Welcome to the world of food combining! This comprehensive guide will delve into the principles, benefits, and practical applications of this dietary approach. From understanding the basics to creating balanced meals, we’ll explore how food combining can revolutionize your digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall well-being.
Food combining is a holistic approach to nutrition that focuses on the compatibility of different food groups. By understanding which foods work well together and which ones don’t, we can optimize our digestive system, reduce inflammation, and maximize nutrient absorption.
This guide will provide you with a comprehensive food combining chart, scientific evidence, and practical tips to help you incorporate this approach into your daily life.
Food Combining Basics
Food combining is a dietary practice that involves eating certain foods together while avoiding others, based on the belief that different food groups require different digestive processes and can interfere with each other’s digestion if consumed simultaneously.
The basic principles of food combining include:
- Consuming protein-rich foods (e.g., meat, fish, eggs) with non-starchy vegetables.
- Eating starchy foods (e.g., bread, pasta, rice) with non-protein vegetables and avoiding combining them with protein-rich foods.
- Avoiding mixing acidic fruits (e.g., citrus fruits, tomatoes) with other foods.
Proponents of food combining argue that it can improve digestion, reduce gas and bloating, and increase nutrient absorption. However, scientific evidence supporting these claims is limited, and the practice is generally considered pseudoscience.
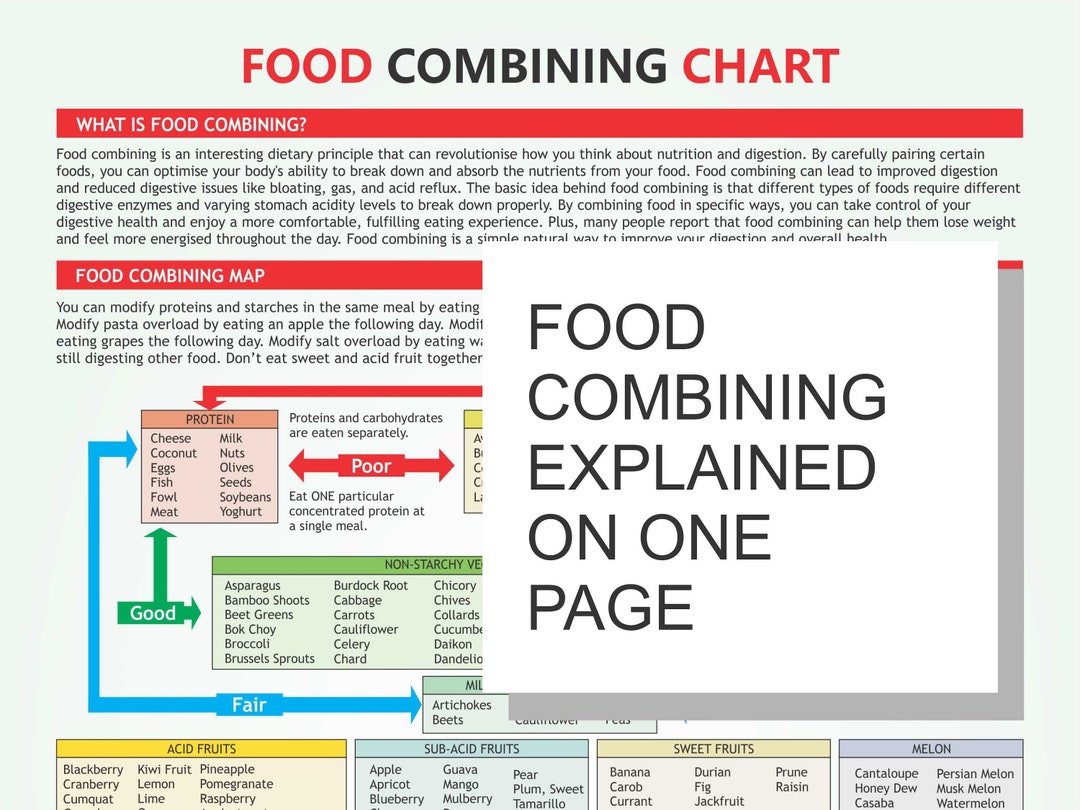
Food Combining Chart

Food combining is the practice of eating certain foods together that are believed to enhance digestion and absorption, while avoiding combinations that are thought to interfere with these processes.
The food combining chart is a tool that can help you make informed choices about which foods to combine for optimal health. The chart is divided into different food groups, including fruits, vegetables, proteins, and grains. Each food group is assigned a color or symbol to indicate its compatibility with other food groups.
Fruits
- Fruits are best eaten alone or with other fruits.
- Avoid combining fruits with proteins or grains.
Vegetables
- Vegetables can be combined with other vegetables, proteins, or grains.
- Avoid combining vegetables with fruits.
Proteins
- Proteins can be combined with vegetables or grains.
- Avoid combining proteins with fruits or other proteins.
Grains
- Grains can be combined with vegetables or proteins.
- Avoid combining grains with fruits or other grains.
Food Combining Principles
Food combining principles propose that combining certain foods during meals can enhance digestion and nutrient absorption while avoiding potential digestive distress. These principles are rooted in the concept that different foods require varying digestive environments and enzymes to be efficiently broken down and utilized by the body.
Digestion and Nutrient Absorption, Food combining chart
The process of digestion involves the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food into smaller molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Food combining principles suggest that consuming compatible foods together optimizes this process by ensuring that foods are digested at a similar rate and that the necessary enzymes are present for their breakdown.
For instance, combining acidic fruits with alkaline vegetables can create a balanced pH level in the stomach, promoting efficient digestion of both food groups.
Gut Health
Proper food combining is believed to support gut health by minimizing digestive issues such as bloating, gas, and constipation. By consuming compatible foods together, the body can more easily break down and absorb nutrients, reducing the likelihood of undigested food particles fermenting in the gut and causing discomfort.
Additionally, food combining may promote a healthy gut microbiome by providing a balanced supply of prebiotics and probiotics, which are essential for maintaining a diverse and beneficial microbial community.
Meal Planning with Food Combining
Meal planning with food combining principles involves creating balanced meals that optimize digestion and nutrient absorption. By understanding the compatible food combinations, you can design meals that promote a healthy gut environment and overall well-being.
Sample Meal Plans
Here are sample meal plans that demonstrate compatible food combinations:
- Breakfast:Oatmeal with berries and nuts
- Lunch:Salad with grilled chicken, vegetables, and quinoa
- Dinner:Salmon with roasted vegetables and brown rice
- Snack:Apple with peanut butter
These meal plans provide a balance of protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats while avoiding incompatible food combinations that can slow down digestion.
Importance of Hydration and Mindful Eating
Proper hydration is crucial for supporting the food combining process. Drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially before and after meals, to aid in digestion and prevent dehydration.
Mindful eating is also essential. Pay attention to your body’s signals and eat slowly, savoring each bite. This allows for better digestion and promotes a sense of satisfaction after meals.
Food Combining for Specific Diets

Food combining can provide unique benefits for individuals with specific dietary needs. By understanding the principles of food combining and tailoring charts to specific dietary restrictions, individuals can optimize their digestion and nutrient absorption.
Here are some key considerations for food combining in specific diets:
Vegan Diets
- Combine complementary proteins:Combine legumes (e.g., beans, lentils) with grains (e.g., brown rice, quinoa) to ensure adequate protein intake.
- Avoid combining acidic fruits with starchy vegetables:Fruits like citrus and berries should be consumed separately from vegetables like potatoes and carrots.
- Include fermented foods:Fermented foods like sauerkraut and kimchi aid digestion and provide beneficial probiotics.
Gluten-Free Diets
- Choose gluten-free grains:Focus on consuming gluten-free grains like brown rice, quinoa, and millet.
- Combine grains with vegetables:Pair gluten-free grains with non-starchy vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, and spinach.
- Avoid combining gluten-free grains with sugary foods:Sugary foods can hinder the absorption of nutrients from gluten-free grains.
Low-Carb Diets
- Focus on non-starchy vegetables:Include plenty of non-starchy vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, and leafy greens.
- Limit fruit intake:Fruits contain carbohydrates, so limit their consumption to small portions.
- Combine protein with non-starchy vegetables:Pair lean protein sources like chicken, fish, or tofu with non-starchy vegetables.
Potential Limitations and Challenges:
While food combining can be beneficial for many, it’s important to note potential limitations and challenges:
- Rigidity:Food combining can be restrictive and may not be suitable for all individuals.
- Limited scientific evidence:While some studies support the principles of food combining, more research is needed to fully validate its benefits.
- Individual variations:Each person’s digestive system is unique, and what works for one may not work for another.
Key Questions Answered
What are the main principles of food combining?
Food combining involves grouping foods based on their compatibility, considering factors such as digestion time, pH level, and nutrient composition.
Does food combining have any scientific backing?
While there is limited scientific evidence directly supporting food combining, some studies suggest that certain food combinations can enhance digestion and nutrient absorption.
Is food combining suitable for all diets?
Food combining can be adapted to various dietary needs, including vegan, gluten-free, and low-carb diets. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes.
