Dr gundry butyrate foods – Dr. Gundry’s revolutionary approach to nutrition emphasizes the importance of butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid that plays a pivotal role in maintaining a healthy gut microbiome, reducing inflammation, and boosting overall well-being.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the world of butyrate-rich foods, exploring their diverse sources, understanding their profound health benefits, and providing practical tips for incorporating them into your diet.
Dr. Gundry and Butyrate

Dr. Steven Gundry, a renowned cardiologist and author, has played a pivotal role in promoting the importance of butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid, for overall health. Through his extensive research and clinical practice, Dr. Gundry has shed light on the crucial role butyrate plays in maintaining a healthy gut microbiome, reducing inflammation, and supporting overall well-being.
Significance of Butyrate in the Human Body
Butyrate is a primary energy source for colonocytes, the cells lining the large intestine. It plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity of the intestinal barrier, protecting against harmful bacteria and toxins. Butyrate also possesses anti-inflammatory properties, helping to reduce inflammation throughout the body.
Additionally, it has been linked to improved cognitive function, insulin sensitivity, and immune system regulation.
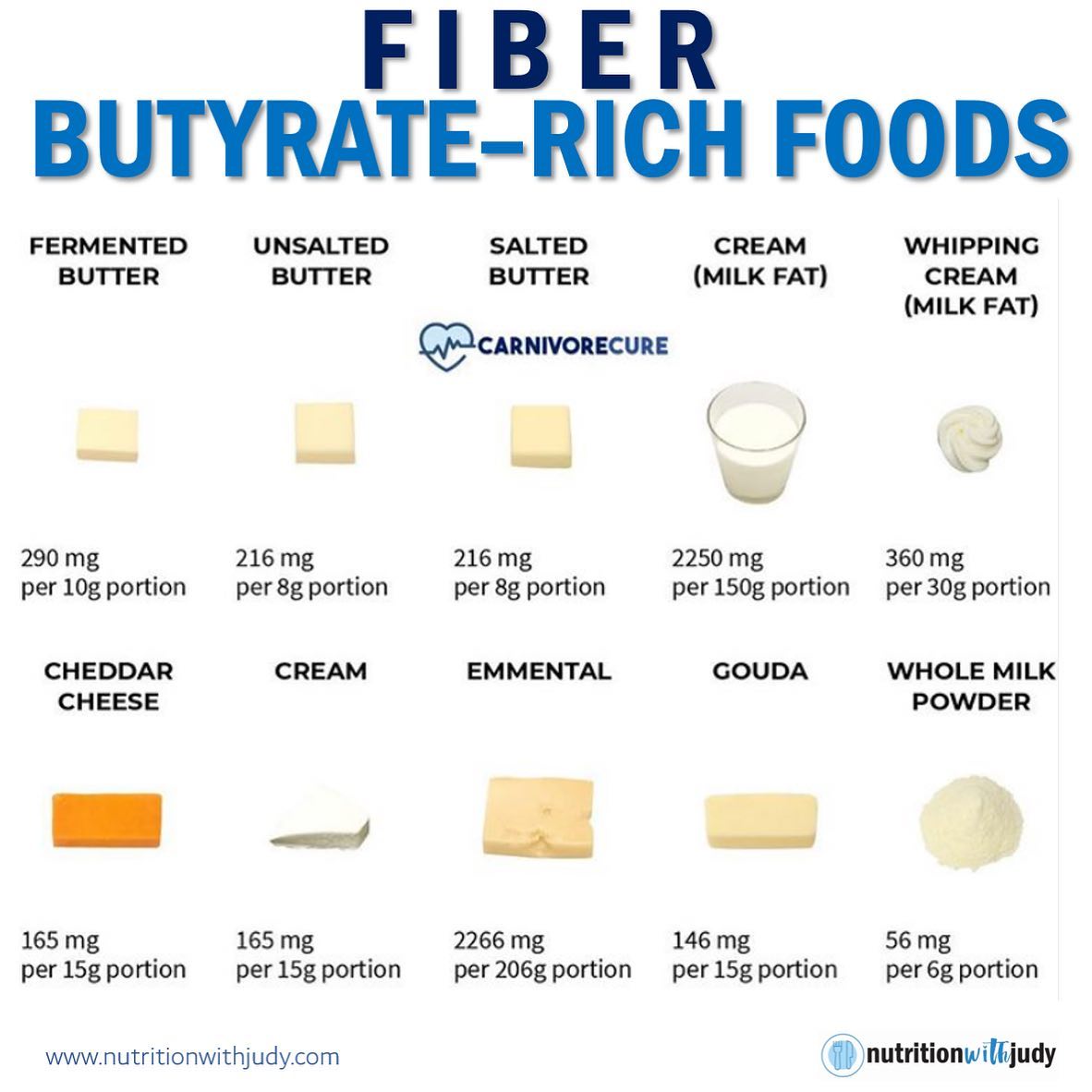
Butyrate-Rich Foods

Butyrate is a short-chain fatty acid that has numerous health benefits, including reducing inflammation, improving gut health, and boosting energy levels. It can be produced by the body or obtained from certain foods.
Here is a comprehensive list of foods rich in butyrate:
Vegetables, Dr gundry butyrate foods
- Jerusalem artichokes
- Asparagus
- Leeks
- Onions
- Garlic
Fruits
- Avocados
- Bananas
- Apples
- Pears
- Berries
Fermented Foods
- Yogurt
- Kefir
- Kombucha
- Sauerkraut
- Kimchi
Butyrate’s Health Benefits
Butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid, plays a pivotal role in maintaining overall health and well-being. Its consumption is associated with numerous health benefits, particularly in the realm of gut health, inflammation reduction, and immune function.
Gut Health
Butyrate serves as the primary energy source for colonocytes, the cells lining the colon. It nourishes these cells, promoting their health and integrity. Additionally, butyrate helps maintain a healthy gut barrier, preventing the entry of harmful substances into the bloodstream.
Inflammation Reduction
Butyrate possesses potent anti-inflammatory properties. It inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, thereby reducing inflammation throughout the body. This anti-inflammatory effect is particularly beneficial in conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease and arthritis.
Immune Function
Butyrate supports immune function by regulating the production of immune cells and antibodies. It promotes the development and differentiation of regulatory T cells, which help suppress excessive immune responses and prevent autoimmune diseases.
Butyrate and Gut Microbiome: Dr Gundry Butyrate Foods
Butyrate plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy gut microbiome. It acts as a primary energy source for colonocytes, the cells lining the colon. By providing nourishment to these cells, butyrate supports the integrity of the intestinal barrier, preventing the leakage of harmful substances into the bloodstream.
Gut Microbial Balance
Butyrate’s presence in the gut influences the composition and diversity of the gut microbiome. It selectively promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria, such as Bifidobacteriumand Lactobacillus, while inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria, including Clostridium difficileand Escherichia coli. This shift in microbial balance creates a favorable environment for gut health, reducing the risk of infections and inflammatory conditions.
Dietary Recommendations
To increase your butyrate intake, consider incorporating the following dietary recommendations into your daily meals.
Focus on consuming a diet rich in fiber, particularly soluble fiber, which is broken down by gut bacteria to produce butyrate. Excellent sources of soluble fiber include fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains.
Fermented Foods
- Incorporate fermented foods into your diet, such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha. These foods contain probiotics, live bacteria that can help increase butyrate production in the gut.
- Consider taking a probiotic supplement to introduce beneficial bacteria directly into your digestive system, supporting butyrate production.
Resistant Starch
- Include foods containing resistant starch in your meals. Resistant starch is a type of fiber that resists digestion in the small intestine, reaching the colon intact, where it can be fermented by gut bacteria to produce butyrate. Good sources of resistant starch include cooked and cooled potatoes, green bananas, and legumes.
- Consider using a prebiotic supplement to promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, enhancing butyrate production.
Query Resolution
What are some common butyrate-rich foods?
Butyrate can be found in various foods, including butter, ghee, coconut oil, avocados, walnuts, and fermented foods like sauerkraut and kimchi.
How does butyrate benefit gut health?
Butyrate nourishes the cells lining the colon, promoting a healthy gut barrier and supporting a balanced gut microbiome.
Can I take butyrate supplements?
Yes, butyrate supplements are available in capsule or powder form. However, it’s always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements.
