Natural food colors, derived from plants, animals, and microorganisms, are revolutionizing the food industry with their vibrant hues and wholesome goodness. These colors not only enhance the visual appeal of food but also offer potential health benefits, making them a popular choice among consumers seeking healthier and more sustainable options.
From the vibrant reds of beets to the deep blues of spirulina, natural food colors bring a kaleidoscope of colors to our plates. Their use dates back centuries, with ancient civilizations employing natural pigments to decorate food and beverages. Today, natural food colors are widely used in various food products, including beverages, confectionery, dairy products, and more.
Natural Food Colors: An Overview
Natural food colors are pigments derived from plants, animals, or minerals. They are used to enhance the visual appeal of food products and provide various functional properties.
Natural food colors play a significant role in food processing by imparting color, improving stability, and extending shelf life. They offer several advantages, including their natural origin, consumer acceptability, and potential health benefits.
Advantages of Natural Food Colors
- Natural Origin:Derived from natural sources, they are generally perceived as safer and healthier than synthetic colors.
- Consumer Acceptability:Consumers prefer natural ingredients, and natural food colors align with this preference.
- Potential Health Benefits:Some natural food colors, such as anthocyanins, have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Disadvantages of Natural Food Colors
- Stability Issues:Natural food colors can be sensitive to light, heat, and pH, affecting their color and stability.
- Limited Color Range:The color palette of natural food colors is narrower compared to synthetic colors.
- Higher Cost:Natural food colors can be more expensive than synthetic counterparts due to extraction and processing costs.
Sources of Natural Food Colors
Natural food colors are derived from various sources, primarily plants, animals, and microorganisms. These sources provide a diverse range of pigments that impart vibrant hues to food products.
Plant-based Sources
- Fruits:Fruits like berries, cherries, and oranges contain anthocyanins, carotenoids, and other pigments that provide red, orange, and yellow colors.
- Vegetables:Vegetables such as spinach, broccoli, and carrots contain chlorophyll, carotenoids, and anthocyanins, providing green, orange, and red-purple colors.
- Herbs:Herbs like turmeric, paprika, and saffron contain curcuminoids, capsanthin, and crocin, which impart yellow, orange, and red colors.
Animal-based Sources, Natural food colors
- Insects:Insects like cochineal beetles produce carminic acid, a red pigment used in food coloring.
- Seafood:Seafood such as squid ink and spirulina contain melanins and phycocyanins, providing black and blue-green colors.
Microorganisms
Microorganisms, including bacteria and fungi, can produce various pigments through fermentation or extraction processes. For example, Monascus purpureusproduces red pigments, while Beta vulgarisproduces yellow and orange pigments.
Extraction and Production of Natural Food Colors
Natural food colors are derived from various sources, including plants, animals, and minerals. The extraction and production of these colors involve several methods to obtain concentrated and purified pigments.
Extraction Methods
- Solvent Extraction:Involves using organic solvents, such as ethanol or acetone, to dissolve and extract pigments from source materials.
- Water Extraction:Utilizes water as the solvent to extract water-soluble pigments, such as anthocyanins from berries.
- Supercritical Fluid Extraction:Employs carbon dioxide in a supercritical state to extract pigments, offering high efficiency and selectivity.
- Enzyme-Assisted Extraction:Uses enzymes to break down cell walls and enhance pigment release, improving extraction yields.
Purification and Concentration
Once extracted, natural food colors undergo purification and concentration processes to remove impurities and enhance their stability and color intensity. These methods include:
- Filtration:Removes suspended solids and other impurities.
- Centrifugation:Separates pigments based on density.
- Chromatography:Isolates specific pigments through selective adsorption and elution.
- Spray Drying:Converts liquid extracts into dry powders for enhanced stability and storage.
Quality Control
Ensuring the safety and efficacy of natural food colors is crucial. Quality control measures include:
- Microbial Testing:Verifies the absence of harmful microorganisms.
- Heavy Metal Analysis:Detects and quantifies heavy metals, such as lead and cadmium.
- Color Stability Testing:Assesses the color retention of pigments under various conditions, such as light, heat, and pH.
- Regulatory Compliance:Adherence to regulatory standards and guidelines, such as those established by the FDA and EFSA.
Applications of Natural Food Colors
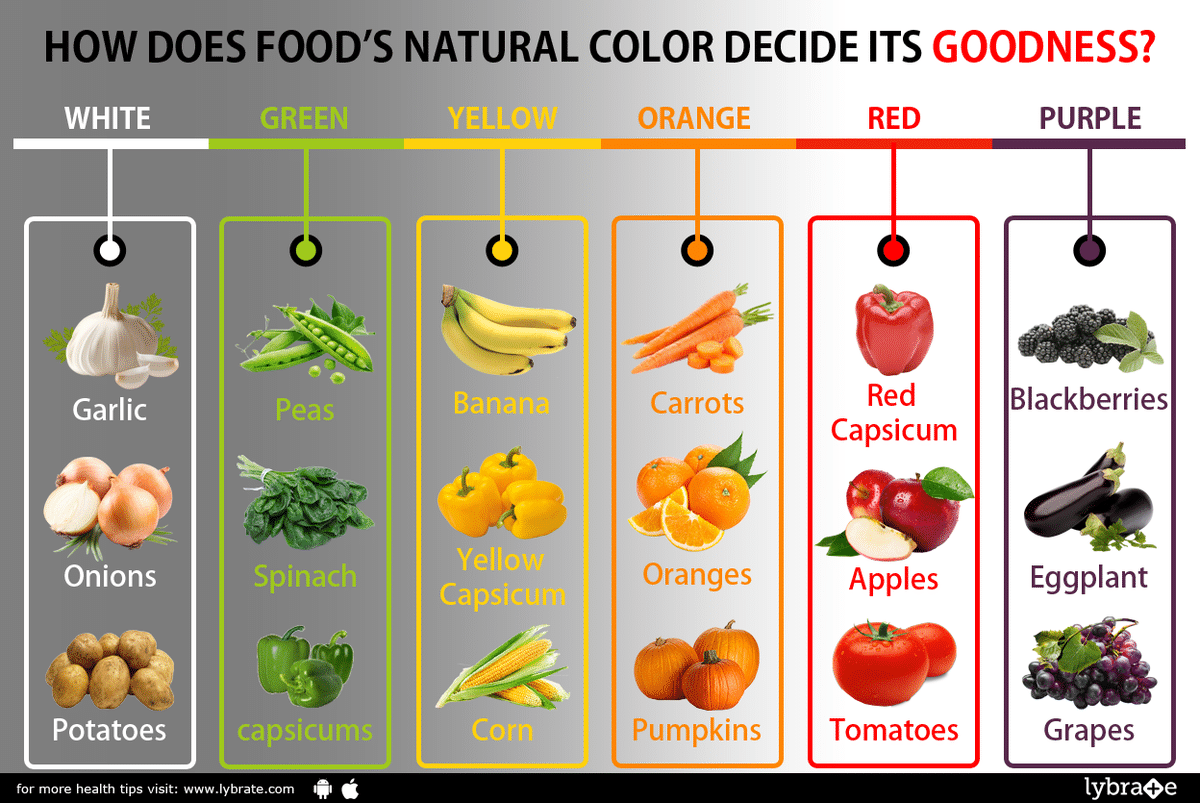
Natural food colors have gained significant popularity in the food industry due to their health benefits, vibrant hues, and consumer demand for clean-label products. These colors are extracted from natural sources such as fruits, vegetables, minerals, and plants, offering a wide range of shades and hues to enhance the visual appeal and perceived quality of food products.
Examples of Natural Food Colors in Food Products
Natural food colors find applications in a diverse range of food products, including:
- Beverages:Fruit juices, sports drinks, and soft drinks often incorporate natural food colors to achieve vibrant shades and enhance their visual appeal.
- Confectionery:Candies, chocolates, and baked goods utilize natural food colors to create eye-catching hues and enhance their overall appearance.
- Dairy products:Yogurt, cheese, and ice cream can benefit from natural food colors to improve their visual appeal and create unique flavor combinations.
Regulatory Aspects of Natural Food Colors
The use of natural food colors is subject to regulatory oversight in different countries to ensure consumer safety and product quality. Regulatory bodies establish guidelines for the extraction, production, and application of natural food colors, including:
- Permitted Sources:Defining the specific natural sources from which food colors can be extracted.
- Purity and Safety Standards:Establishing purity and safety criteria to ensure the absence of harmful contaminants or residues.
- Labeling Requirements:Regulating the labeling of food products containing natural food colors to inform consumers about their presence.
Trends and Innovations in Natural Food Colors
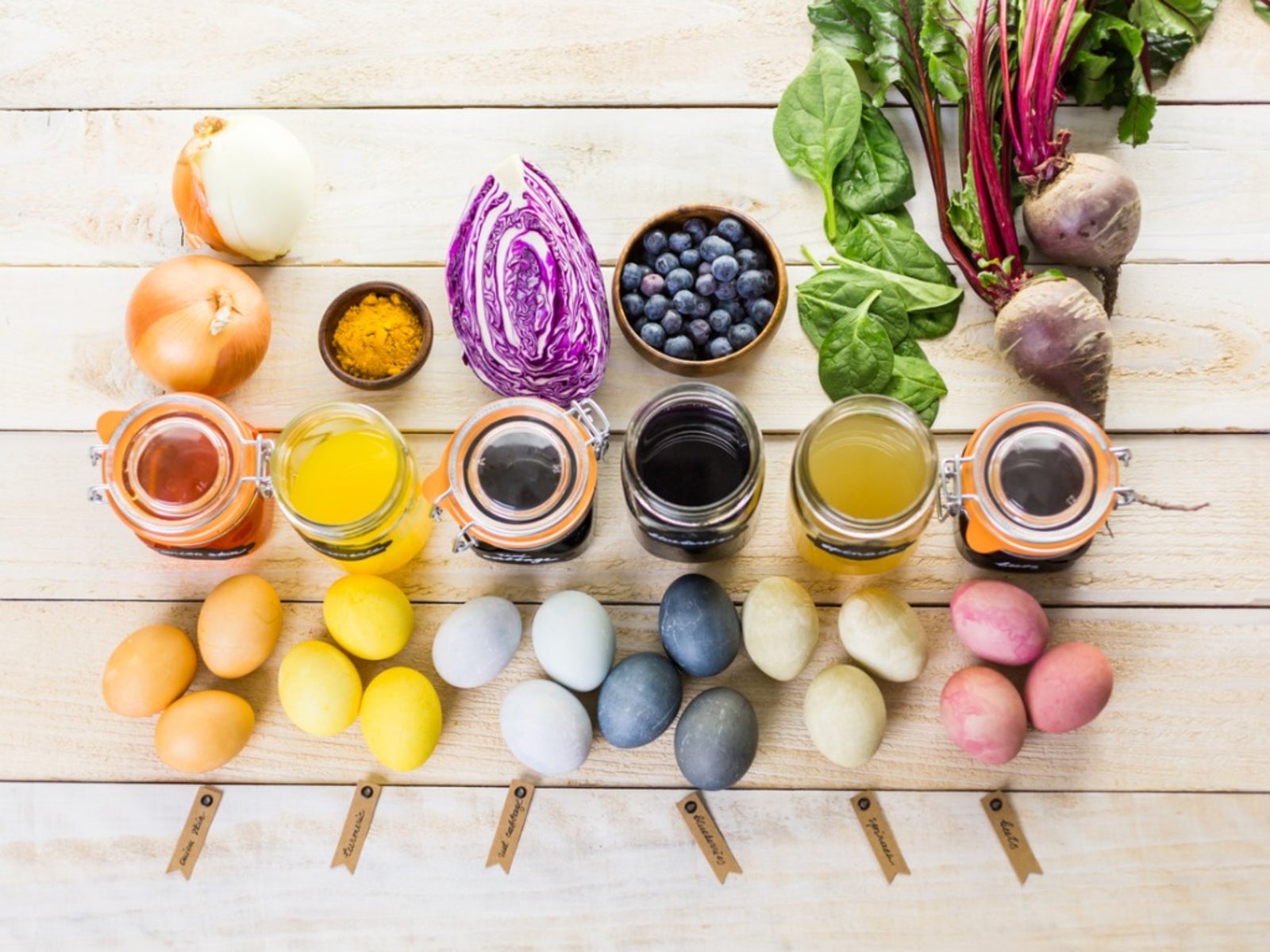

The global natural food colors market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing consumer demand for clean-label and natural ingredients. This has led to the emergence of several trends and innovations in the industry.
One key trend is the development of new technologies for extracting and producing natural food colors. These technologies include supercritical fluid extraction, which uses carbon dioxide to extract colors from plant materials, and fermentation, which uses microorganisms to produce colors.
These technologies offer several advantages, such as improved efficiency, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced color stability.
Potential of Novel Sources
Another trend is the exploration of novel sources for natural food colors. Researchers are investigating the potential of various plant materials, such as fruits, vegetables, and algae, as sources of natural colors. These novel sources offer the potential to expand the range of available colors and meet the growing demand for natural ingredients.
Health and Safety Considerations
Natural food colors are generally considered safe for consumption, but like any food additive, there are certain safety considerations to keep in mind.
One potential concern is the presence of heavy metals in some natural food colors. Heavy metals, such as lead and cadmium, can accumulate in the body over time and cause various health problems. Therefore, it is essential to ensure that natural food colors are produced using processes that minimize heavy metal contamination.
Regulations and Standards
To ensure the safety of natural food colors, various regulations and standards have been established by regulatory bodies worldwide. These regulations typically specify limits on the allowable levels of heavy metals and other potential contaminants in natural food colors. Additionally, they may require manufacturers to conduct safety assessments and provide documentation to demonstrate the safety of their products.
Comparison with Synthetic Food Colors

Natural food colors and synthetic food colors both have their own advantages and disadvantages. Natural food colors are derived from natural sources such as plants, animals, or minerals, while synthetic food colors are chemically synthesized. Natural food colors are generally considered to be safer and healthier than synthetic food colors, as they do not contain any harmful chemicals.
However, natural food colors can be more expensive and less stable than synthetic food colors. Here is a table comparing the advantages and disadvantages of natural food colors with synthetic food colors:
| Advantage | Natural Food Colors | Synthetic Food Colors |
|---|---|---|
| Safety | Generally considered to be safer and healthier | May contain harmful chemicals |
| Health | Can provide nutritional benefits | No nutritional benefits |
| Cost | More expensive | Less expensive |
| Stability | Less stable | More stable |
| Availability | May be less available | More readily available |
Natural food colors can be used as an alternative to synthetic food colors in a variety of applications. They can be used to color food, beverages, cosmetics, and other products. Natural food colors are often preferred by consumers who are looking for healthier and more natural products.
In recent years, there has been a growing trend towards using natural food colors in place of synthetic food colors.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Consumers are increasingly demanding natural and healthy products. This trend has led to a growing demand for natural food colors. Natural food colors are perceived as being safer and healthier than synthetic food colors, and they can also provide nutritional benefits.
As a result, many food manufacturers are switching to natural food colors in order to meet consumer demand.
The market for natural food colors is expected to grow significantly in the coming years. This growth is being driven by the increasing demand for natural and healthy products, as well as the growing awareness of the health risks associated with synthetic food colors.
Question Bank
Are natural food colors safe to consume?
Yes, natural food colors are generally considered safe for consumption. They are derived from natural sources and have been used for centuries in food and beverages.
What are the advantages of using natural food colors?
Natural food colors offer several advantages over synthetic food colors. They are derived from natural sources, are perceived as healthier, and may have potential health benefits.
Are natural food colors more expensive than synthetic food colors?
In general, natural food colors can be more expensive than synthetic food colors due to their lower yield and more complex extraction processes.
