i Foods, a revolutionary concept in nutrition, are transforming the way we think about food and health. These nutrient-rich, plant-based foods offer a myriad of health benefits and play a vital role in various dietary approaches.
From preventing chronic diseases to promoting overall well-being, i Foods are poised to revolutionize the food industry and empower individuals to lead healthier, more fulfilling lives.
Definition and Overview of I Foods
The term “i foods” refers to a category of food products that are designed to provide enhanced nutritional value and functionality beyond basic sustenance. These foods are often fortified with additional nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, and may also contain probiotics or other beneficial ingredients.
The concept of i foods emerged in response to the growing demand for healthier and more convenient food options. Consumers are increasingly seeking foods that can support their overall well-being and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. I foods aim to meet this demand by providing a convenient and effective way to obtain essential nutrients and promote health.
Significance of I Foods
I foods play a significant role in promoting public health and well-being. By providing enhanced nutritional value, these foods can help to address nutrient deficiencies and reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, stroke, and cancer. Additionally, i foods can support healthy aging, improve cognitive function, and enhance overall vitality.
I foods are particularly beneficial for individuals who may have difficulty obtaining adequate nutrition from their regular diet. This includes people with food allergies or intolerances, those with certain medical conditions, and individuals who are on restrictive diets.
Misconceptions about I Foods
There are several common misconceptions about i foods that should be addressed. Firstly, it is important to clarify that i foods are not intended to replace a balanced diet. They are designed to supplement a healthy diet and provide additional nutritional benefits.
Secondly, i foods are not necessarily more expensive than regular foods. Many i foods are available at affordable prices and can be incorporated into a budget-friendly diet.
Finally, it is important to note that i foods are not a magic bullet for health. While they can provide significant nutritional benefits, they should be consumed as part of a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise and adequate sleep.
Categories of I Foods

I foods encompass a diverse range of substances that exhibit unique properties and characteristics. To facilitate their study and application, i foods can be categorized into distinct groups based on their shared attributes. This classification aids in understanding the nature and potential of these substances.
The following table presents a comprehensive overview of the various categories of i foods, along with their descriptions and representative examples:
Category 1: Natural I Foods
Natural i foods occur naturally in various biological systems, such as plants, animals, and microorganisms. They are typically produced through metabolic processes or as components of cellular structures.
- Description:Found in nature, not synthetically produced.
- Examples:Vitamins, minerals, enzymes, antioxidants.
Category 2: Synthetic I Foods
Synthetic i foods are artificially created in laboratories or industrial settings. They do not exist naturally in biological systems and are designed to mimic or enhance the properties of natural i foods.
- Description:Man-made, not found naturally.
- Examples:Artificial sweeteners, food additives, preservatives.
Category 3: Fortified I Foods
Fortified i foods are natural or processed foods that have been enriched with additional i foods to enhance their nutritional value. This process involves adding essential nutrients that may not be present or are present in insufficient quantities in the original food.
- Description:Natural or processed foods with added nutrients.
- Examples:Vitamin D-fortified milk, iron-fortified cereals.
Category 4: Functional I Foods
Functional i foods are foods that provide specific health benefits beyond their basic nutritional value. They contain bioactive compounds that have been shown to have positive effects on various aspects of health, such as reducing the risk of chronic diseases or improving cognitive function.
- Description:Foods with additional health benefits.
- Examples:Omega-3 fatty acid-rich fish, probiotic yogurt.
Health Benefits of I Foods
I foods are nutritional powerhouses that offer a wide range of health benefits. Their rich composition of vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber makes them an essential part of a balanced diet. Consuming I foods has been associated with preventing and managing various health conditions, including heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and some types of cancer.
Role in Preventing and Managing Health Conditions
- Heart Health:I foods are rich in soluble fiber, which helps lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease. They also contain antioxidants that protect against oxidative damage to blood vessels and improve blood flow.
- Stroke Prevention:The fiber in I foods helps lower blood pressure, which is a major risk factor for stroke. Additionally, I foods contain compounds that prevent blood clots and improve circulation.
- Type 2 Diabetes Management:I foods have a low glycemic index, which means they release sugar slowly into the bloodstream. This helps regulate blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Cancer Prevention:I foods contain antioxidants that protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. Some studies have suggested that consuming I foods may reduce the risk of certain types of cancer, such as colon and prostate cancer.
Role of I Foods in Different Diets
Incorporating i foods into various dietary approaches offers unique nutritional benefits. Let’s explore their role in vegan, vegetarian, and flexitarian diets.
Vegan Diets, I foods
- Provide essential nutrients like protein, iron, calcium, and vitamin B12, often lacking in vegan diets.
- Support plant-based protein intake, promoting satiety and muscle maintenance.
- Contribute to fiber intake, aiding digestion and overall gut health.
Vegetarian Diets
- Supplement protein and other nutrients, enhancing overall dietary balance.
- Provide essential amino acids that may be limited in vegetarian diets.
- Offer a wider variety of nutrient-rich foods, promoting dietary diversity.
Flexitarian Diets
- Introduce plant-based protein sources, reducing reliance on animal products.
- Provide a balance of nutrients, supporting overall health and well-being.
- Promote environmental sustainability by reducing meat consumption.
Challenges and Considerations in Consuming I Foods
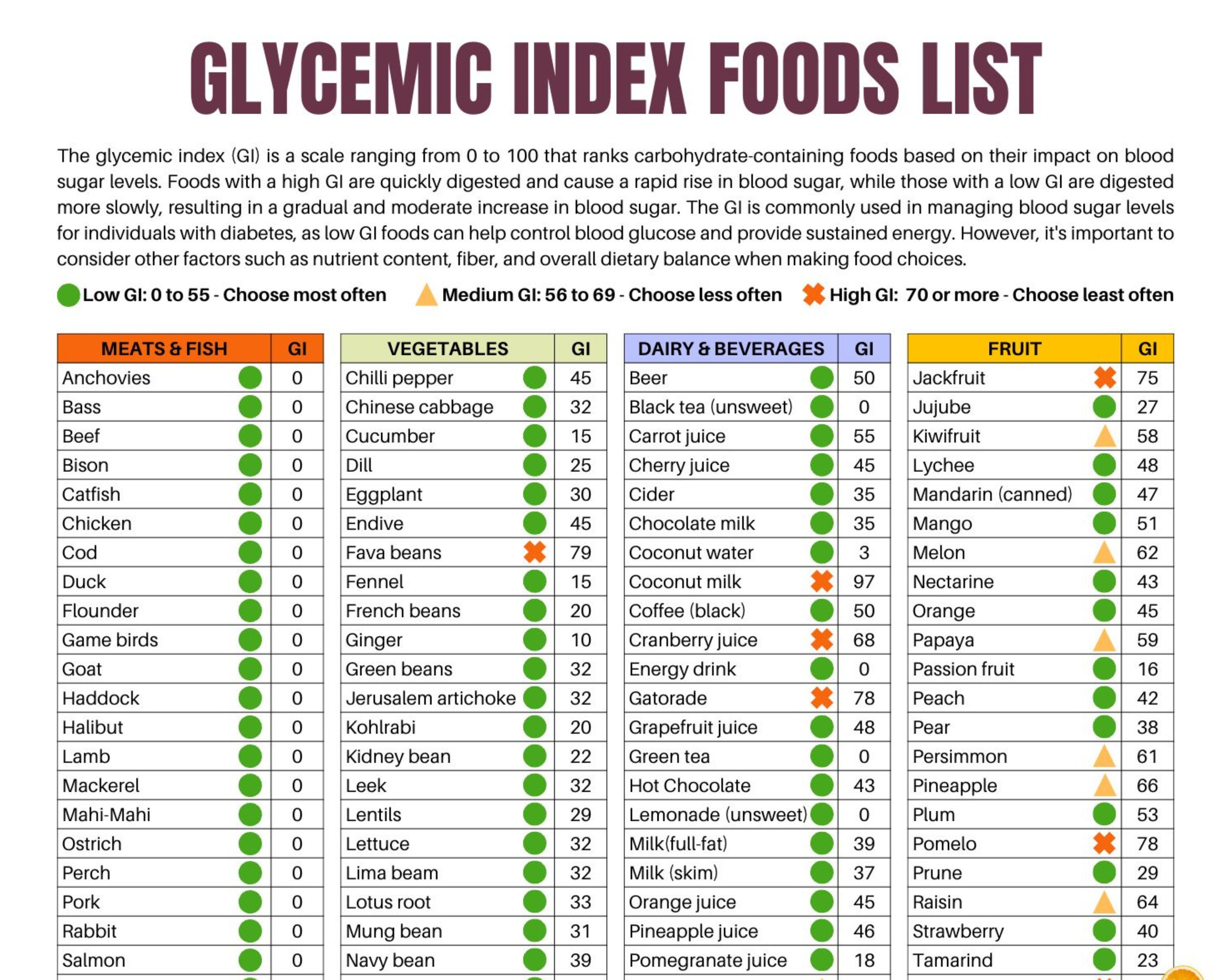
Consuming i foods offers numerous health benefits, but it is essential to be aware of potential challenges and considerations. These include concerns related to allergies, nutrient deficiencies, and food safety.
Allergies
Certain i foods, such as peanuts and tree nuts, are common allergens. Consuming these foods can trigger severe allergic reactions in individuals who are allergic to them. It is crucial for individuals with known allergies to avoid consuming the specific foods that trigger their reactions.
Nutrient Deficiencies
While i foods are nutrient-rich, they may not provide all the essential nutrients required by the body. Consuming a balanced diet that includes a variety of foods from all food groups is necessary to ensure adequate nutrient intake.
Food Safety
I foods, like other food products, can be susceptible to contamination and spoilage. Proper food handling and storage practices are essential to prevent foodborne illnesses. Additionally, consuming i foods that are not properly processed or cooked can pose health risks.
Future Trends and Innovations in I Foods

The field of i foods is constantly evolving, with new trends and innovations emerging all the time. These advancements are driven by a growing demand for healthier, more sustainable, and more convenient food options. In this section, we will explore some of the most promising future trends and innovations in the development and production of i foods.
One of the most exciting trends in the i food industry is the development of new products that are designed to meet the specific needs of different consumers. For example, there is a growing demand for i foods that are tailored to the needs of athletes, seniors, and people with specific dietary restrictions.
These products are often fortified with essential nutrients and antioxidants, and they can help to improve overall health and well-being.
Another major trend in the i food industry is the development of new technologies that can improve the production and quality of i foods. For example, some companies are developing new ways to use artificial intelligence (AI) to optimize the production process and reduce waste.
Others are developing new ways to package and store i foods, which can help to extend their shelf life and maintain their quality.
Research and Development
In addition to the trends mentioned above, there are a number of other promising areas of research and development in the field of i foods. These include:
- The development of new plant-based i foods that are high in protein and other essential nutrients.
- The development of new ways to use fermentation to create i foods that are both healthy and delicious.
- The development of new technologies that can improve the bioavailability of nutrients in i foods.
These are just a few of the many exciting trends and innovations that are shaping the future of the i food industry. As these technologies continue to develop, we can expect to see even more innovative and groundbreaking i food products in the years to come.
FAQ Summary
What are i Foods?
i Foods are plant-based foods that are fortified with essential nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
What are the health benefits of i Foods?
i Foods offer a range of health benefits, including reducing the risk of chronic diseases, improving cognitive function, and boosting energy levels.
How can i Foods be incorporated into different diets?
i Foods can be easily incorporated into vegan, vegetarian, and flexitarian diets as a source of essential nutrients.
Are there any concerns about consuming i Foods?
While i Foods are generally safe for consumption, individuals with allergies or specific dietary restrictions should consult a healthcare professional before incorporating them into their diet.
