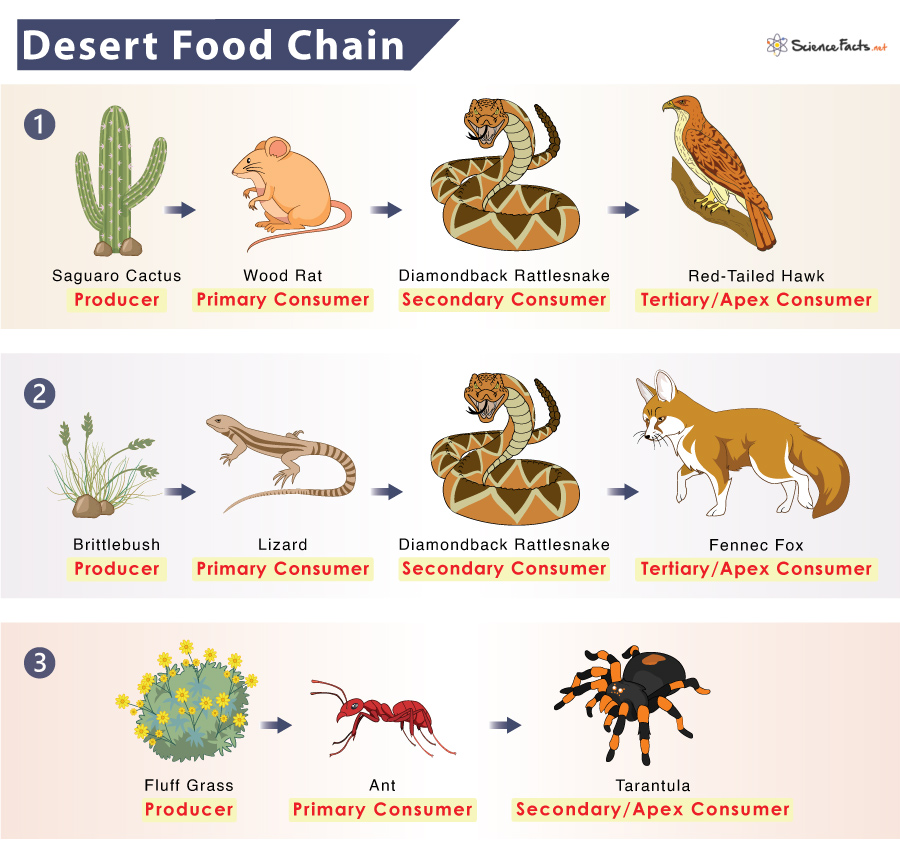
Delve into the intricate tapestry of the desert ecosystem food chain, where survival thrives amidst scarcity. Discover the remarkable adaptations and interdependencies that sustain life in this arid realm.
Within this harsh environment, primary producers, such as desert plants, harness the sun’s energy through photosynthesis, fueling the foundation of the food chain. Herbivores, like desert rodents, feed on these plants, while carnivores, such as desert foxes, hunt them for sustenance.
Omnivores, like coyotes, adapt to consume both plant and animal matter.
Consumers in the Desert Food Chain

Within the desert ecosystem, consumers play a vital role in maintaining ecological balance. These organisms obtain energy and nutrients by consuming other living beings, forming interconnected trophic levels within the food chain.
Categorization of Consumers
- Herbivores:These animals feed primarily on plant matter, including leaves, stems, fruits, and seeds. Examples include desert tortoises, jackrabbits, and kangaroo rats.
- Carnivores:These animals consume other animals, including insects, rodents, and even larger herbivores. Examples include coyotes, foxes, and snakes.
- Omnivores:These animals have a mixed diet, consuming both plant and animal matter. Examples include kit foxes, roadrunners, and badgers.
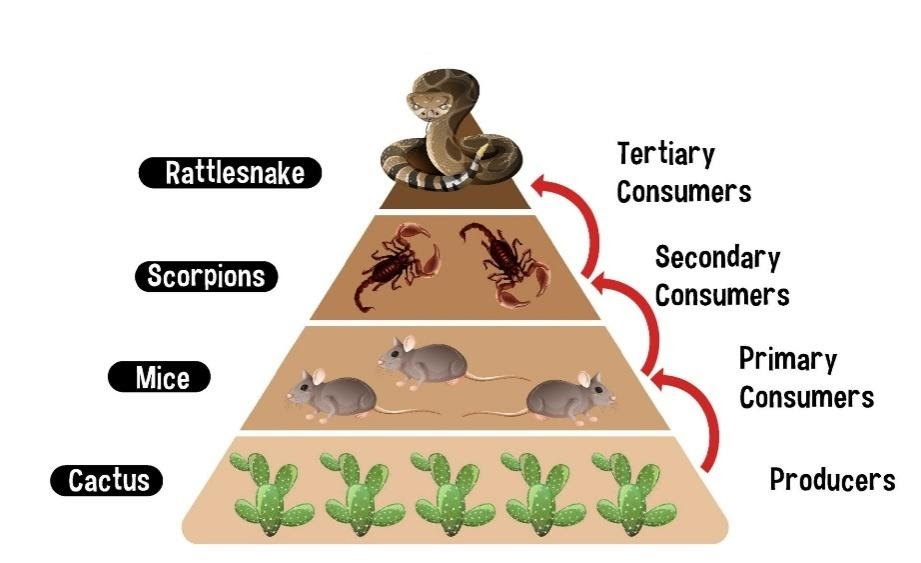
Energy Transfer Between Trophic Levels, Desert ecosystem food chain
Energy flows through the desert food chain as consumers consume organisms from lower trophic levels. Each level represents a 10% energy transfer efficiency, meaning that only 10% of the energy consumed at one level is passed on to the next.
This energy loss is due to metabolic processes, heat dissipation, and waste production.
Energy transfer efficiency: 10% from one trophic level to the next
As a result, the biomass and number of organisms decrease at higher trophic levels. This phenomenon highlights the importance of conserving primary producers, such as plants, as they form the foundation of the desert food chain.
Human Impact on the Desert Food Chain
Human activities can disrupt the delicate balance of the desert food chain. Habitat loss, pollution, and climate change pose significant threats to desert organisms and their ecosystems.
Habitat Loss
- Urbanization, mining, and agriculture are encroaching on desert habitats, fragmenting ecosystems and reducing the availability of food and shelter for wildlife.
- Loss of vegetation reduces food sources for herbivores, leading to population declines and cascading effects throughout the food chain.
Pollution
- Industrial activities and vehicle emissions release pollutants into the desert environment, contaminating water sources and harming wildlife.
- Toxic substances can accumulate in organisms, affecting their health and reproductive success.
- Plastic waste can entangle animals, disrupt habitats, and leach harmful chemicals into the ecosystem.
Climate Change
- Rising temperatures and altered precipitation patterns are altering the distribution and abundance of desert species.
- Changes in vegetation can affect food availability for herbivores, while extreme weather events can disrupt the entire food chain.
- Climate change also exacerbates other human-induced threats, such as habitat loss and pollution.
Conservation Strategies
Protecting the desert food chain requires a multifaceted approach involving conservation efforts, sustainable land management practices, and mitigating climate change.
- Establish protected areas to preserve critical habitats and wildlife populations.
- Implement sustainable land use practices to minimize habitat fragmentation and pollution.
- Reduce greenhouse gas emissions to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
- Educate the public about the importance of desert ecosystems and the threats they face.
Question Bank: Desert Ecosystem Food Chain
What are the unique adaptations of desert organisms?
Desert organisms exhibit remarkable adaptations, such as water storage mechanisms, heat tolerance, and efficient energy metabolism.
How does decomposition contribute to the desert ecosystem?
Decomposition plays a crucial role in nutrient cycling, releasing essential nutrients back into the soil, which supports plant growth and overall ecosystem productivity.
What are the key threats to the desert ecosystem food chain?
Habitat loss, pollution, and climate change pose significant threats to the desert ecosystem food chain, disrupting the delicate balance of species interactions.