Chart food combining sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. The principles and practices of food combining have been passed down through generations, and this article delves into the historical origins, scientific theories, and practical applications of this dietary approach.
Food combining is a holistic approach to nutrition that emphasizes the compatibility of different food groups during digestion. By understanding the principles behind food combining, individuals can optimize their digestive health, reduce inflammation, and enhance their overall well-being.
Introduction to Food Combining
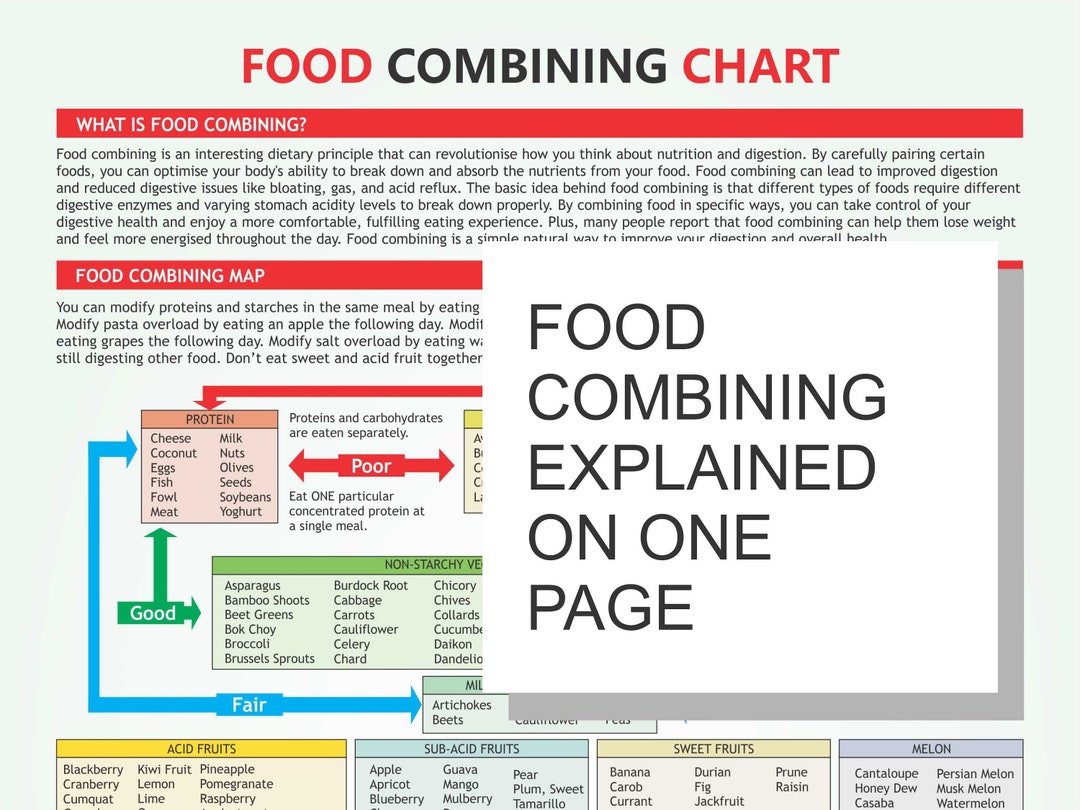
Food combining is a dietary practice that involves eating certain foods together to enhance digestion and nutrient absorption. It’s based on the belief that different foods have different digestive requirements, and combining them properly can improve digestion, reduce gas and bloating, and promote overall well-being.
The concept of food combining has been around for centuries, with origins in traditional Eastern medicine and Ayurvedic practices. Over time, various theories and approaches to food combining have emerged, each with its own set of rules and guidelines.
Common Food Combining Charts
There are numerous food combining charts available, each offering specific guidelines on which foods to combine and avoid. Some common charts include:
- Dr. Herbert Shelton’s Food Combining Chart
- The Hay Diet Food Combining Chart
- Dr. William Howard Hay’s Food Combining Chart
- The Wahls Protocol Food Combining Chart
- The Paleo Food Combining Chart
Principles of Food Combining: Chart Food Combining
Food combining is a dietary practice that advocates consuming compatible food groups together to enhance digestion and absorption of nutrients. It’s based on the principle that different food groups have varying digestion rates and incompatibilities that can hinder optimal nutrient assimilation.
Digestion Rates
The table below compares the digestion times of different food groups:
| Food Group | Digestion Time |
|---|---|
| Fruits | 30-60 minutes |
| Vegetables | 30-120 minutes |
| Starches | 120-180 minutes |
| Proteins | 180-240 minutes |
| Fats | 240-360 minutes |
Food Combining Guidelines
Based on the digestion rates, the following guidelines are recommended for optimal digestion:
- Consume fruits alone:Fruits digest quickly and can interfere with the digestion of other foods.
- Combine vegetables with starches or proteins:Vegetables provide fiber and enzymes that aid in the digestion of starches and proteins.
- Avoid combining starches and proteins:These foods have different digestion times and can compete for digestive enzymes.
- Limit fat intake:Fats can slow down digestion and interfere with the absorption of other nutrients.
Benefits and Limitations of Food Combining

Food combining, a dietary approach that advocates consuming specific food groups together to enhance digestion and reduce inflammation, offers potential benefits. However, it also comes with certain limitations and challenges.
Benefits of Food Combining, Chart food combining
- Improved Digestion:By combining compatible food groups, food combining aims to reduce the digestive burden and promote optimal nutrient absorption.
- Reduced Inflammation:Certain food combinations, such as pairing fruits with vegetables, can help reduce inflammation by balancing the pH levels in the body.
- Increased Energy Levels:Food combining proponents suggest that proper food combinations can improve energy levels by reducing digestive stress and promoting efficient nutrient utilization.
Limitations and Challenges of Food Combining
- Restrictive:Food combining diets can be restrictive, as they require careful planning and attention to food combinations.
- Inconsistent Scientific Evidence:While anecdotal evidence and some studies support the benefits of food combining, there is a lack of comprehensive scientific evidence to conclusively establish its effectiveness.
- Social Challenges:Following a food combining diet can be challenging in social settings, as it may require specific meal choices or preparation.
Incorporating Food Combining into a Balanced Diet
To incorporate food combining into a balanced diet, consider the following tips:
- Focus on Whole, Unprocessed Foods:Prioritize nutrient-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Experiment with Compatible Combinations:Gradually experiment with different food combinations, observing how your body responds.
- Listen to Your Body:Pay attention to how your body feels after eating different food combinations. Adjust your approach based on your experiences.
Practical Applications of Food Combining

Food combining in practice involves implementing the principles discussed earlier into daily meals. This can be achieved through meal planning and understanding which food combinations to avoid and encourage.
Sample Meal Plan
A sample meal plan based on food combining principles might look like this:
-
-*Breakfast
Oatmeal with berries and nuts (alkaline + acid)
-*Lunch
Salad with grilled chicken, quinoa, and vegetables (neutral + protein + alkaline)
-*Dinner
Salmon with roasted vegetables (protein + alkaline)
-*Snacks
Apple with almond butter (alkaline + fat)
Food Combinations to Avoid and Encourage
The following table Artikels food combinations to avoid and encourage:|
- *Combinations to Avoid |
- *Combinations to Encourage |
|—|—|| Protein and starch | Protein and vegetables || Starch and sugar | Vegetables and fats || Fruit and protein | Fruit and vegetables |
Personalized Food Combining Chart
Creating a personalized food combining chart for specific dietary needs involves identifying individual food sensitivities and preferences. This can be done by working with a registered dietitian or nutritionist to develop a tailored plan.
Conclusion
In summary, food combining is a dietary approach that advocates for consuming compatible food groups at specific times to enhance digestion and nutrient absorption. While it may offer potential benefits like improved digestion, reduced bloating, and increased energy levels, it’s crucial to remember its limitations, including the lack of scientific evidence and the potential for nutrient deficiencies if not followed correctly.
Before making any significant dietary changes, it’s always advisable to consult with healthcare professionals to ensure the approach aligns with your individual health needs and goals.
FAQs
What are the main principles of food combining?
The main principles of food combining include:
- Combining foods with similar digestion times
- Avoiding combining acidic and alkaline foods
- Consuming fruits and vegetables separately from other food groups
What are the benefits of food combining?
Food combining can offer several benefits, such as:
- Improved digestion
- Reduced inflammation
- Enhanced nutrient absorption
- Increased energy levels
Are there any limitations to food combining?
Food combining can be a restrictive dietary approach, and it may not be suitable for everyone. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes.
