Discover the AB blood type food chart, a comprehensive guide to unlocking the secrets of personalized nutrition for individuals with this unique blood type. Dive into a fascinating exploration of dietary recommendations, foods to avoid, and potential health implications, empowering you to make informed choices for a healthier and more vibrant life.
The AB blood type, known for its adaptability and open-mindedness, presents a distinct set of nutritional needs. By understanding the specific foods that nourish and support this blood type, we can harness the power of nature to optimize our well-being.
Introduction to AB Blood Type: Ab Blood Type Food Chart
AB blood type, often known as the “universal recipient,” is a rare and unique blood group characterized by the presence of both A and B antigens on red blood cells, but lacking anti-A and anti-B antibodies in the plasma.
Adhering to the AB blood type food chart can lead to improved well-being, but it’s equally important to consider the materials used in food preparation. 3D printing food safe filament offers a solution, ensuring the safety and integrity of printed food.
By incorporating this advanced technology into your kitchen, you can enjoy both the benefits of the AB blood type food chart and the convenience of 3D printed culinary creations.
The discovery of the AB blood type is attributed to Austrian scientist Karl Landsteiner in 1901. Landsteiner’s groundbreaking work on blood typing laid the foundation for modern blood transfusions and paved the way for advancements in blood banking and compatibility testing.
Prevalence
The prevalence of the AB blood type varies significantly across different populations. It is most common in people of Korean, Japanese, and Chinese descent, where it can account for up to 20-30% of the population. In contrast, it is less common in people of European and African descent, where it typically ranges from 2-5%.
Diet Recommendations for AB Blood Type
AB blood type individuals possess a unique digestive system that requires specific dietary considerations. To optimize health and well-being, following a tailored diet that aligns with their blood type is crucial.
This table Artikels a comprehensive list of recommended foods for AB blood types, categorized into fruits, vegetables, proteins, and grains. Incorporating these nutrient-rich foods into your diet can support optimal digestion, enhance energy levels, and promote overall vitality.
Recommended Foods for AB Blood Type
| Fruits | Vegetables | Proteins | Grains |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Foods to Avoid for AB Blood Type
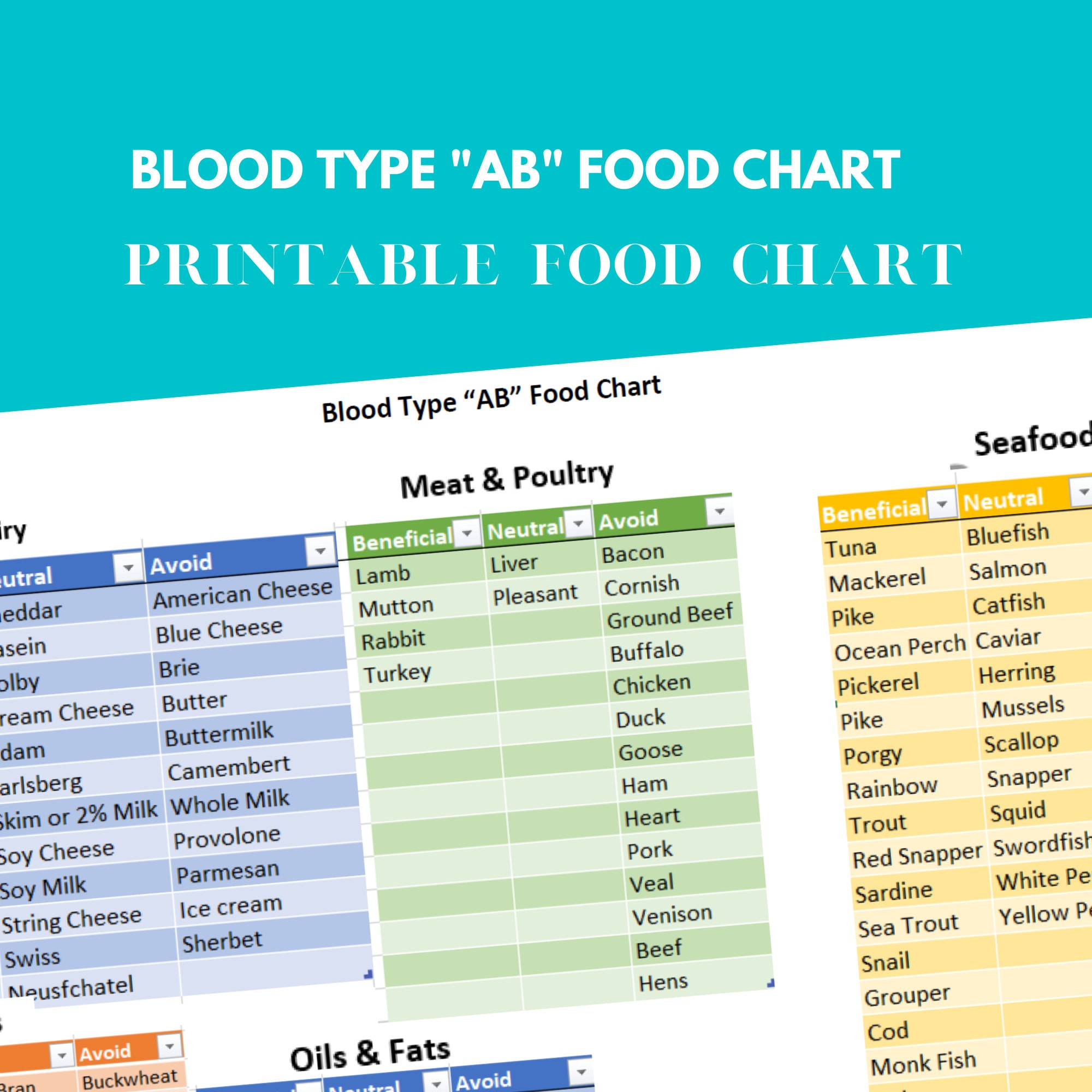
Individuals with AB blood type may experience certain adverse reactions when consuming specific foods. Understanding these sensitivities and adhering to dietary recommendations can promote overall well-being and minimize potential health issues.
The following foods are generally discouraged for AB blood types due to their potential impact on the digestive system, immune responses, and overall health:
Dairy Products
- Cow’s milk: Contains beta-casein, a protein that can trigger inflammation and digestive discomfort.
- Goat’s milk: While generally easier to digest than cow’s milk, it still contains beta-casein and may cause sensitivities in some AB individuals.
- Cheese: Rich in saturated fat and can contribute to weight gain and inflammation.
Gluten-Containing Grains, Ab blood type food chart
- Wheat: Contains lectins that can bind to the gut lining and cause inflammation and digestive issues.
- Rye: Similar to wheat, rye contains lectins that can trigger adverse reactions.
- Barley: May contain gluten and can cause digestive discomfort.
Legumes
- Soy: Contains lectins and phytates that can interfere with nutrient absorption and cause digestive problems.
- Kidney beans: High in lectins, which can lead to inflammation and digestive discomfort.
- Peanuts: Technically a legume, peanuts are known to cause allergic reactions in some individuals.
Nightshade Vegetables
- Tomatoes: Contain solanine, a compound that can cause inflammation and joint pain.
- Potatoes: High in starch and can contribute to weight gain and inflammation.
- Eggplant: May contain lectins that can trigger adverse reactions.
Other Foods
- Red meat: High in saturated fat and cholesterol, which can increase the risk of heart disease and other health issues.
- Processed foods: Contain artificial ingredients, preservatives, and other additives that can be harmful to health.
- Sugary drinks: High in calories and can contribute to weight gain and other health problems.
It’s important to note that individual sensitivities may vary, and not all AB blood type individuals will experience adverse reactions to these foods. However, paying attention to dietary recommendations and avoiding foods that may trigger discomfort can help promote optimal health and well-being.
Summary
In conclusion, the AB blood type food chart provides a valuable roadmap for individuals seeking to align their dietary choices with their unique genetic makeup. By embracing the recommendations Artikeld in this guide, you can unlock a world of culinary delights that not only satisfy your taste buds but also promote optimal health and longevity.
Remember, personalized nutrition is key to unlocking your body’s full potential, and the AB blood type food chart is your trusted companion on this transformative journey.
