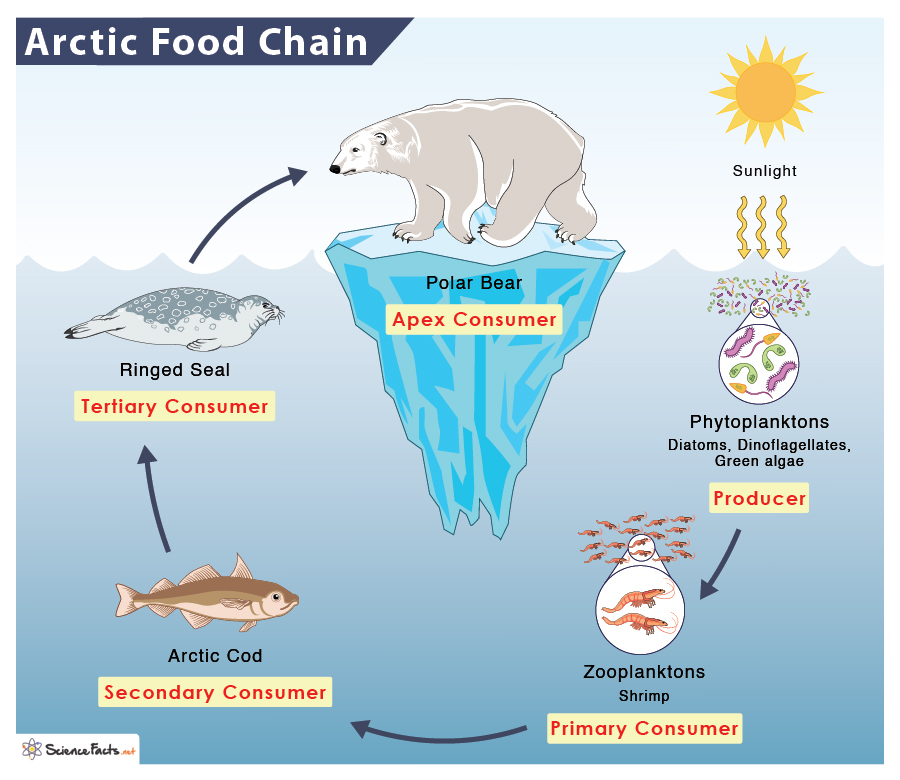
The polar bear food web is a complex and fascinating ecosystem that supports a diverse array of species in the Arctic. At the heart of this web lies the polar bear, an apex predator that relies on a steady supply of prey to survive.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the polar bear food web, exploring the hunting techniques employed by these formidable predators, the nutritional value of their prey, and the potential impacts of climate change on this delicate balance.
Polar Bear Hunting Techniques: Polar Bear Food Web
Polar bears exhibit remarkable hunting prowess, employing a diverse array of techniques to secure their prey. Their hunting strategies are meticulously adapted to the specific characteristics of their target species.
Seal Hunting
Polar bears primarily prey on ringed and bearded seals, which inhabit the sea ice and open water, respectively. When hunting seals, polar bears employ several methods:
Still-hunting
Bears patiently wait near seal breathing holes or on the ice’s edge, blending into their surroundings and ambushing unsuspecting seals as they surface.
Stalking
Bears stealthily approach seals, using the ice ridges and hummocks as cover to conceal their movements.
Diving
In rare instances, bears may dive into the water to pursue seals, utilizing their powerful forelimbs for propulsion.
Walrus Hunting
Walruses, with their massive size and formidable tusks, pose a significant challenge to polar bears. Bears typically target younger or weaker individuals and employ the following techniques:
Ambush
Bears conceal themselves behind ice floes or within ice caves, waiting for walruses to approach.
Opportunistic feeding
Bears may scavenge on walrus carcasses left behind by other predators or humans.
Role of Sea Ice
Sea ice plays a crucial role in polar bear hunting success. It provides a stable platform for bears to stalk and ambush their prey. During the summer months, when sea ice retreats, bears face greater challenges in finding food and may rely on scavenging or hunting terrestrial prey.
Food Web Interactions

The Arctic ecosystem is a complex web of interconnected food chains, with polar bears occupying a critical position as apex predators. Their survival and well-being depend on the availability and abundance of their prey species.
Keystone Species, Polar bear food web
Polar bears are keystone species within the Arctic food web, meaning their presence has a disproportionate impact on the entire ecosystem. By preying on seals and other marine mammals, they help regulate their populations, preventing overgrazing and maintaining a balance within the ecosystem.
Prey Abundance
Changes in prey abundance can significantly impact polar bear populations. When prey is plentiful, polar bears have access to ample food sources, leading to higher reproductive rates and increased survival. Conversely, when prey abundance declines, polar bears face food shortages, which can result in decreased reproduction, lower survival rates, and increased vulnerability to disease.
Climate Change and Polar Bear Food Web

Climate change is a major threat to the Arctic ecosystem and the polar bears that depend on it. The loss of sea ice due to climate change is having a significant impact on polar bear prey species, such as seals and walruses.
These animals rely on sea ice for breeding, resting, and hunting. As the sea ice melts, these animals are forced to travel further to find suitable habitat, which makes them more vulnerable to predation and other threats.
Sea Ice Loss and Polar Bear Hunting Patterns
The loss of sea ice is also affecting polar bear hunting patterns and success rates. Polar bears typically hunt seals and walruses from the edge of the sea ice. As the sea ice melts, polar bears are forced to travel further to find suitable hunting grounds.
This can lead to increased energy expenditure and decreased hunting success, which can have a negative impact on polar bear populations.
Mitigation Strategies for Polar Bear Food Security
There are a number of mitigation strategies that can be implemented to support polar bear food security in a changing climate. These strategies include:* Reducing greenhouse gas emissions to slow the rate of sea ice loss
- Protecting and restoring polar bear habitat
- Providing supplemental food sources for polar bears
- Managing human activities in the Arctic to minimize disturbance to polar bears and their prey
Clarifying Questions
What is the primary food source for polar bears?
Polar bears primarily feed on seals, particularly ringed seals and bearded seals.
How do polar bears adapt their hunting strategies to different prey species?
Polar bears use different hunting techniques depending on the prey species. For example, they may stalk seals on sea ice or swim underwater to ambush them.
What is the role of sea ice in polar bear hunting success?
Sea ice is crucial for polar bears as it provides a platform for hunting seals. Loss of sea ice due to climate change can significantly impact polar bear hunting success.
