Pink mould on food can be a common and concerning sight, raising questions about its potential health hazards and the best course of action. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of pink mould, providing insights into its identification, causes, and effective prevention measures to safeguard your food and health.
Health Hazards of Pink Mould on Food
Consuming food contaminated with pink mold poses potential health risks. The mold produces mycotoxins, toxic substances that can cause adverse reactions in humans.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Pink mold can cause gastrointestinal distress, such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. These symptoms typically appear within a few hours of consuming contaminated food.
Allergic Reactions
Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to pink mold. Symptoms can range from mild skin irritation to more severe reactions, such as difficulty breathing or anaphylaxis.
Immune System Suppression
Mycotoxins can suppress the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and diseases. Prolonged exposure to pink mold can weaken the immune response, increasing the risk of health complications.
Importance of Discarding Moldy Food
To prevent health issues, it is crucial to discard any food that shows signs of mold growth. Even if only a small portion of the food appears moldy, it is best to discard the entire item to avoid potential contamination.
Identification of Pink Mould on Food
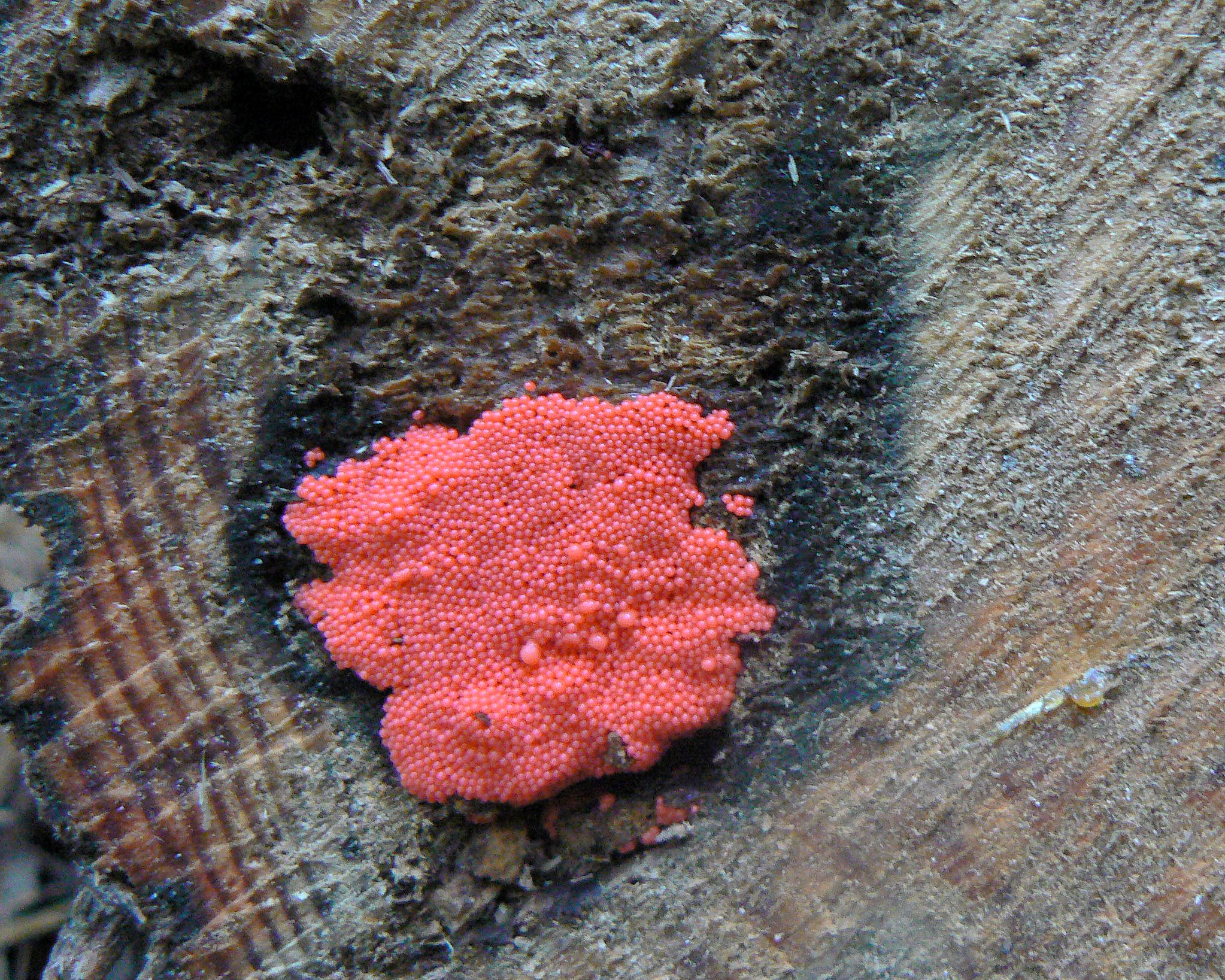

Pink mold, scientifically known as Neurospora crassa, is a common type of mold that can grow on a variety of food items. It is characterized by its distinctive pink or reddish color, which can range from pale to deep hues. Pink mold typically has a fuzzy or cottony texture and can appear on the surface of food as small, circular patches or larger, spreading colonies.
Pink mold is often found on bread, pastries, fruits, vegetables, and other food items that contain high levels of sugar or starch. It can also grow on dairy products, such as cheese and yogurt, as well as on meat and poultry.
Visual Aids for Identification
Visual aids, such as images or illustrations, can be helpful in accurately identifying pink mold on food. Here are some examples:
- Pink mold on bread:Pink mold on bread typically appears as small, circular patches of fuzzy pink growth. The mold can spread quickly, covering large areas of the bread.
- Pink mold on fruit:Pink mold on fruit can appear as small, pink spots or larger, spreading colonies. The mold can cause the fruit to become soft and mushy.
- Pink mold on cheese:Pink mold on cheese can appear as small, pink spots or larger, spreading colonies. The mold can cause the cheese to become slimy and discolored.
Distinguishing Pink Mold from Other Types of Mold
It is important to be able to distinguish pink mold from other types of mold that may appear on food. Some common types of mold that can be mistaken for pink mold include:
- White mold:White mold is a common type of mold that can grow on a variety of food items. It is characterized by its white or grayish color and fuzzy texture. White mold is typically harmless and can be safely removed from food.
- Green mold:Green mold is another common type of mold that can grow on food. It is characterized by its green color and fuzzy texture. Green mold can be harmful if ingested and should be discarded.
- Black mold:Black mold is a type of mold that is often found in damp or humid environments. It is characterized by its black or dark green color and fuzzy texture. Black mold can be harmful if ingested and should be discarded.
If you are unsure whether or not a particular type of mold is pink mold, it is best to err on the side of caution and discard the food item.
Causes of Pink Mould Growth on Food
Pink mold thrives in environments that meet its specific growth requirements. Understanding these factors is crucial for preventing and controlling its development on food.
Moisture is a primary driver of pink mold growth. High humidity levels create a moist environment that favors the mold’s spores to germinate and establish colonies. Pink mold can also tolerate a wide range of temperatures, but it grows optimally between 40-77°F (4-25°C).
pH Levels
Pink mold prefers slightly acidic to neutral pH levels, ranging from 5.5 to 7.0. Foods with higher acidity, such as citrus fruits or vinegar, tend to inhibit mold growth. However, some pink mold species can tolerate slightly alkaline environments.
Food Composition
The composition of food also influences pink mold development. Foods high in carbohydrates and low in protein, such as bread, baked goods, and fruits, provide an ideal substrate for mold growth. Additionally, the presence of fats and oils can further enhance mold growth.
Storage Methods
Improper storage methods can significantly contribute to pink mold growth. Storing food at room temperature or in humid environments creates favorable conditions for mold to thrive. Refrigeration can slow down mold growth, but it is not always sufficient to prevent it entirely.
Examples of Susceptible Foods
Some foods are particularly susceptible to pink mold growth, including:
- Bread and baked goods
- Fruits, especially berries and citrus fruits
- Dairy products, such as cheese and yogurt
- Meat and poultry products
- Nuts and seeds
Prevention of Pink Mould on Food
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/67056409/GettyImages_758591313.0.jpg)
Preventing pink mold growth on food is crucial for maintaining food quality and safety. By implementing proper storage techniques, handling practices, and environmental control, you can effectively reduce the risk of contamination.
Proper Food Storage
- Refrigerate perishable foods promptly:Keep foods that require refrigeration at or below 40°F (4°C) to inhibit mold growth.
- Store dry goods in airtight containers:Grains, cereals, and other dry goods should be stored in airtight containers to prevent moisture accumulation, which promotes mold growth.
- Avoid overpacking:Overcrowded refrigerators and pantries restrict airflow and increase the likelihood of mold formation.
- Regularly clean and disinfect storage areas:Regularly wipe down shelves, drawers, and containers with a mild disinfectant to eliminate potential mold spores.
Food Handling Practices
- Wash hands before handling food:Hands can carry mold spores, so it’s essential to wash your hands thoroughly before preparing or storing food.
- Use clean utensils:Avoid using contaminated utensils that could transfer mold spores to food.
- Discard spoiled food:If you notice any signs of mold on food, discard the entire item immediately to prevent cross-contamination.
Environmental Control
Maintaining a clean and dry environment for food storage is vital for preventing mold growth. Consider the following:
- Control humidity:High humidity levels in storage areas promote mold growth. Use dehumidifiers or air conditioners to reduce humidity below 60%.
- Ensure proper ventilation:Adequate ventilation allows air to circulate and reduces moisture accumulation. Open windows or use fans to promote airflow.
- Clean and disinfect surfaces:Regularly clean and disinfect surfaces where food is stored or prepared to eliminate mold spores.
Preservatives and Other Methods, Pink mould on food
In certain cases, using preservatives or other methods can further inhibit mold growth on food:
- Preservatives:Some food additives, such as sodium benzoate and potassium sorbate, have antimicrobial properties that can prevent mold growth.
- Modified atmosphere packaging (MAP):This technique involves altering the gas composition within food packaging to reduce oxygen levels and slow down mold growth.
- Irradiation:Exposing food to ionizing radiation can kill mold spores and inhibit their growth.
Remediation of Pink Mould on Food
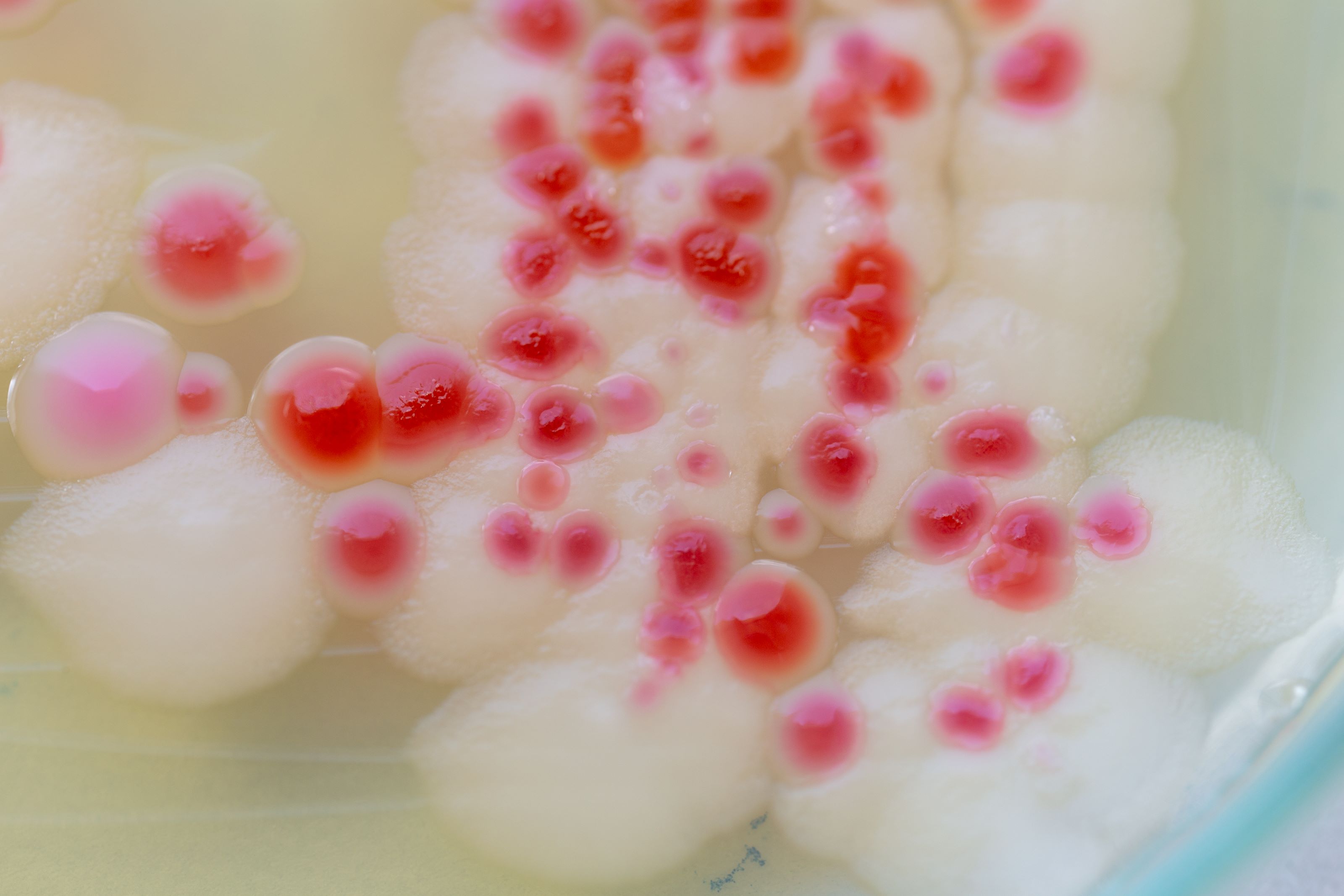
Discovering pink mould on food can be alarming, and it’s essential to handle the situation appropriately. While it may be tempting to salvage affected food items, it’s crucial to understand the potential risks involved.
Pink mould, a type of yeast, can produce mycotoxins, which are toxic substances that can cause adverse health effects. Attempting to remove mould from food by cutting away the visible portion may not eliminate the presence of mycotoxins, as they can penetrate deeply into the food.
Discarding Contaminated Food
In most cases, it’s advisable to discard any food that shows signs of pink mould growth. Heavily contaminated food items pose a significant health hazard and should be disposed of promptly to prevent further spoilage and potential health risks.
Question & Answer Hub: Pink Mould On Food
What are the health risks of consuming pink mould?
Consuming food contaminated with pink mould can lead to various health issues, including gastrointestinal distress, allergic reactions, and respiratory problems. It is crucial to discard mouldy food to prevent these potential health hazards.
How can I identify pink mould on food?
Pink mould typically appears as fuzzy or slimy pink or orange growth on food surfaces. It can be found on various food items, such as bread, fruits, and dairy products. Accurate identification is essential to distinguish it from other types of mould.
What causes pink mould to grow on food?
Pink mould growth is influenced by environmental factors like moisture, temperature, and pH levels. Improper food storage, high humidity, and warm temperatures can create favourable conditions for mould development.
How can I prevent pink mould from growing on food?
Preventing pink mould growth involves proper food storage techniques, such as refrigeration, airtight containers, and maintaining a clean and dry environment. Additionally, using preservatives or anti-mould agents can further inhibit mould development.
Can I remove pink mould from food and still consume it?
Attempting to salvage mouldy food is not recommended. Even if you remove visible mould, the food may still contain harmful toxins or spores that can cause health issues. It is best to discard heavily contaminated food items to prevent further spoilage and potential health hazards.
