Nutrient dense foods chart, a valuable tool for health-conscious individuals, provides a comprehensive overview of nutrient-rich foods that offer a plethora of health benefits. This guide will delve into the concept of nutrient density, its significance, and practical ways to incorporate nutrient-dense foods into daily meals.
Nutrient-dense foods are a cornerstone of a healthy diet, providing an abundance of essential vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber while being relatively low in calories and unhealthy fats. Consuming these nutrient-packed foods promotes overall well-being, reduces the risk of chronic diseases, and supports a healthy weight.
Definition of Nutrient-Dense Foods: Nutrient Dense Foods Chart

Nutrient-dense foods are those that provide a high amount of nutrients relative to their calorie content. These nutrients include vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants. Nutrient-dense foods are important for overall health and well-being, as they provide the body with the essential nutrients it needs to function properly.
Importance of Consuming Nutrient-Dense Foods
Consuming nutrient-dense foods has many benefits, including:
- Reduced risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and some types of cancer
- Improved immune function
- Increased energy levels
- Better mood and cognitive function
- Healthy weight management
Creating a Nutrient-Dense Foods Chart

To make informed choices about your diet, it’s essential to have a comprehensive understanding of nutrient-dense foods. A nutrient-dense foods chart can be a valuable tool in this regard, providing you with a quick and easy reference guide to the most nutritious foods available.
Design a Responsive HTML Table
A well-designed nutrient-dense foods chart should be responsive, meaning it can be viewed and used easily on any device, including smartphones, tablets, and desktops. To create a responsive HTML table, use the following code:
| Food Group | Examples |
|---|---|
| Fruits | Berries, apples, bananas, oranges |
| Vegetables | Leafy greens, broccoli, carrots, tomatoes |
| Whole Grains | Brown rice, quinoa, oatmeal, whole-wheat bread |
| Lean Protein | Chicken, fish, beans, lentils |
This table is responsive because it uses relative units (percentages) for its widths, ensuring that it will scale appropriately to fit any screen size.
Provide Examples of Nutrient-Dense Foods
Once you have created a responsive HTML table, you can start filling it in with examples of nutrient-dense foods. Here are some examples for each food group:
- Fruits:Berries, apples, bananas, oranges, kiwi, mango
- Vegetables:Leafy greens, broccoli, carrots, tomatoes, sweet potatoes, bell peppers
- Whole Grains:Brown rice, quinoa, oatmeal, whole-wheat bread, whole-wheat pasta
- Lean Protein:Chicken, fish, beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh
Food Groups and Nutrient Profiles
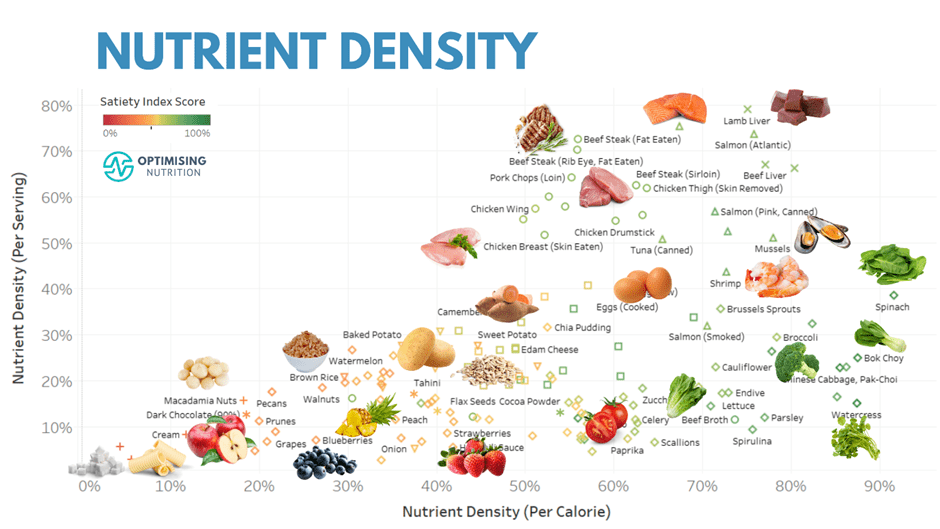
Organizing nutrient-dense foods into food groups helps you easily identify the variety of nutrients available from different sources. Each food group offers a unique blend of vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients.
Here are the main food groups and their nutrient profiles:
Fruits
- Rich in vitamins A, C, and K, as well as potassium and fiber.
- Provide antioxidants that protect against cellular damage.
Vegetables, Nutrient dense foods chart
- Excellent sources of vitamins A, C, and K, as well as folate, fiber, and antioxidants.
- Cruciferous vegetables (e.g., broccoli, cauliflower) contain compounds linked to cancer prevention.
Whole Grains
- Provide complex carbohydrates, fiber, B vitamins, and iron.
- Help regulate blood sugar levels and promote digestive health.
Legumes
- Rich in protein, fiber, iron, and B vitamins.
- Excellent meat alternatives for vegetarians and vegans.
Nuts and Seeds
- Provide healthy fats, protein, fiber, and minerals like magnesium and zinc.
- Can help reduce cholesterol levels and promote heart health.
Lean Protein
- Essential for building and repairing tissues.
- Sources include fish, poultry, beans, and tofu.
Dairy (Optional)
- Provides calcium, vitamin D, and protein.
- Fortified plant-based milk alternatives can provide similar nutrients.
Key Questions Answered
What are nutrient-dense foods?
Nutrient-dense foods are foods that provide a high amount of nutrients relative to their calorie content. They are rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber, and low in unhealthy fats and added sugars.
Why is it important to consume nutrient-dense foods?
Consuming nutrient-dense foods is important because it provides the body with the essential nutrients it needs to function properly. These nutrients support overall health and well-being, reduce the risk of chronic diseases, and promote a healthy weight.
How can I incorporate nutrient-dense foods into my diet?
There are many ways to incorporate nutrient-dense foods into your diet. Some simple tips include:
- Choose whole grains over refined grains.
- Eat a variety of fruits and vegetables.
- Choose lean protein sources.
- Limit processed foods and sugary drinks.
