Embark on a fascinating journey into the intricate tapestry of life with food web draw, a tool that unveils the complex interactions and dependencies within ecosystems. From primary producers to apex predators, this visual representation unravels the delicate balance that sustains our planet.
Food web draw empowers you to explore the interconnectedness of organisms, trace the flow of energy, and witness the dynamic nature of ecological communities. Immerse yourself in a world where every species plays a crucial role, and the health of one impacts the well-being of all.
Food Web Structure
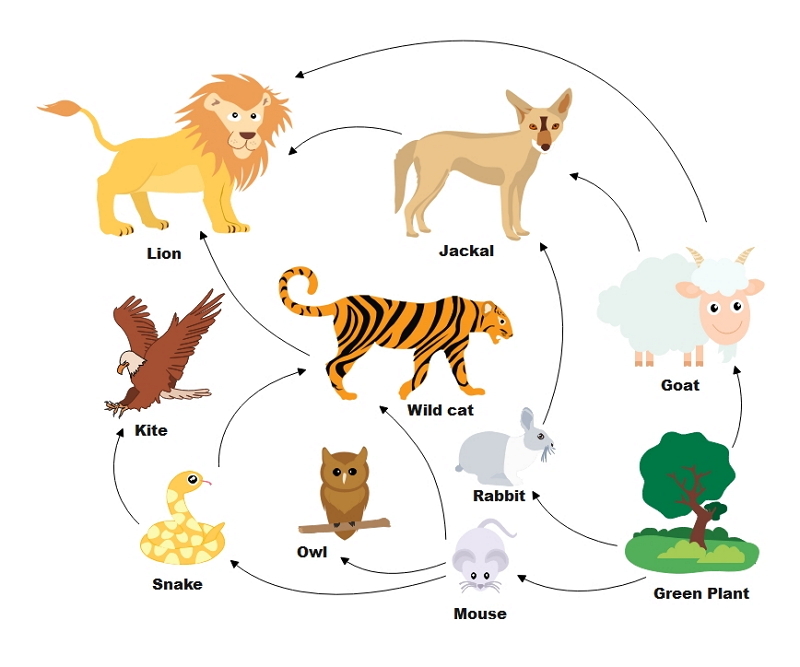
A food web is a graphical representation of the feeding relationships between organisms in an ecosystem. It illustrates the flow of energy and nutrients through the community and provides insights into the complex interactions that sustain life on Earth.
Food webs can be analyzed using various approaches, including:
Visual Representation
A common way to visualize a food web is through a table with responsive columns, as shown below:
| Trophic Level | Organisms |
|---|---|
| Producers | Plants, algae |
| Primary Consumers | Herbivores (e.g., deer, rabbits) |
| Secondary Consumers | Carnivores (e.g., foxes, owls) |
| Tertiary Consumers | Top predators (e.g., lions, eagles) |
This table provides a basic overview of the trophic levels within the food web, but it does not capture the full complexity of the interactions.
Food Web Dynamics
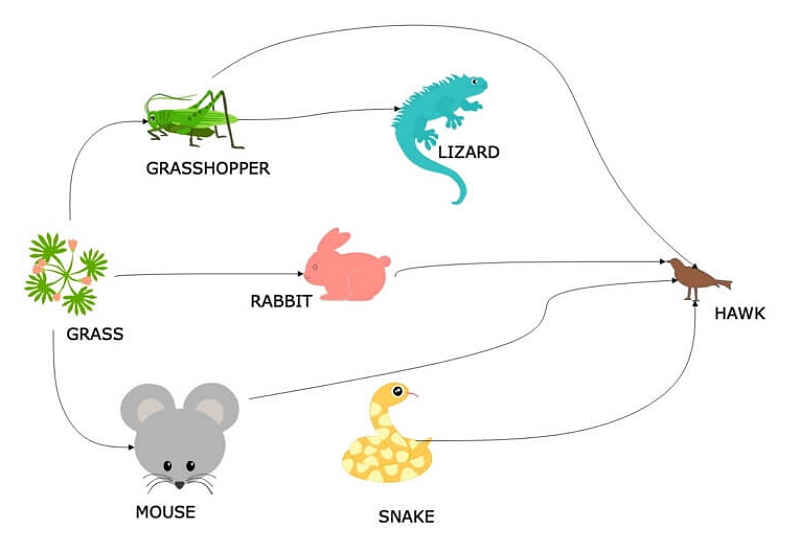
Food webs are not static entities; they are constantly changing in response to various factors. These changes can be small, such as the addition or removal of a single species, or they can be large, such as the collapse of an entire ecosystem.
Impact of Keystone Species on Food Webs
Keystone species are species that have a disproportionately large impact on their ecosystem relative to their abundance. The removal of a keystone species can have cascading effects on the food web, leading to changes in the abundance and distribution of other species.
For example, sea otters are keystone species in kelp forests. They prey on sea urchins, which in turn eat kelp. When sea otters are removed from a kelp forest, the sea urchin population explodes, leading to a decline in kelp forests.
Food Web Changes Over Time
Food webs can also change over time in response to environmental changes, such as climate change or pollution. These changes can lead to the extinction of some species and the introduction of new species.
For example, climate change is causing the ranges of many species to shift. This can lead to changes in the food webs in these areas, as new species compete for resources with existing species.
Trophic Cascades
Trophic cascades are indirect effects that occur when a change in the abundance of one species affects the abundance of other species in the food web.
For example, the removal of wolves from Yellowstone National Park led to an increase in the population of elk. This increase in elk led to a decrease in the abundance of aspen trees, which were being browsed by the elk.
Role of Competition and Predation in Shaping Food Webs
Competition and predation are two important forces that shape food webs. Competition occurs when two or more species compete for the same resources, such as food or habitat. Predation occurs when one species eats another species.
Competition and predation can lead to changes in the abundance and distribution of species in a food web. For example, competition can lead to the extinction of one species, while predation can lead to the decline of a prey species.
Human Activities and Food Webs, Food web draw
Human activities can have a significant impact on food webs. These activities can include habitat destruction, pollution, and the introduction of invasive species.
Habitat destruction can lead to the loss of species and the disruption of food webs. Pollution can harm or kill organisms, and it can also alter the availability of resources.
Food Web Applications

Food webs find numerous applications in various fields, including conservation biology, environmental science, agriculture, education, and raising awareness about environmental issues.
In conservation biology, food webs are used to assess the impact of human activities on ecosystems. By understanding the interconnections between species, scientists can identify keystone species—those that have a disproportionately large impact on the ecosystem relative to their abundance—and prioritize conservation efforts accordingly.
Food webs also help identify species that are particularly vulnerable to environmental changes, such as habitat loss or climate change.
Predicting the Impact of Environmental Changes
Food webs can help predict the impact of environmental changes on ecosystems. For example, scientists can use food webs to model the effects of climate change on species distributions and interactions. This information can help land managers develop strategies to mitigate the negative impacts of climate change on biodiversity.
Sustainable Agriculture
In sustainable agriculture, food webs are used to design farming systems that minimize environmental impacts and promote biodiversity. By understanding the food web interactions in agricultural ecosystems, farmers can develop practices that enhance natural pest control, reduce the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides, and improve soil health.
Educational Value
Food webs have great educational value. They provide a simplified representation of complex ecological systems, making them an excellent tool for teaching students about ecology and the interconnectedness of nature. Food webs can also be used to raise awareness about environmental issues and the importance of conservation.
Raising Awareness
Food webs can be used to raise awareness about environmental issues. For example, food webs can be used to illustrate the impact of pollution on ecosystems or the importance of protecting keystone species.
FAQs: Food Web Draw
What is a food web?
A food web is a visual representation of the feeding relationships between different species in an ecosystem, showing how energy and nutrients flow through the community.
What is the difference between a food chain and a food web?
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which energy and nutrients pass, while a food web is a more complex network of interconnected food chains.
What is the importance of food webs?
Food webs help us understand the structure and dynamics of ecosystems, identify keystone species, and predict the impact of environmental changes on ecological communities.
