Cereal food labels, often overlooked but brimming with valuable information, serve as a gateway to understanding the nutritional content and potential health implications of our breakfast bowls. Delve into this comprehensive guide to decipher the intricate details of cereal food labels, empowering you to make informed choices that nourish your body and tantalize your taste buds.
Health Claims and Nutrient Content Claims

Health claims and nutrient content claims are statements on food labels that describe the relationship between a food or its components and health or a disease risk. These claims are regulated by government agencies to ensure they are accurate, truthful, and not misleading.
There are two main types of health claims:
- Authorized health claims: These claims are based on significant scientific agreement and have been approved by the regulatory agency. Examples include claims about the relationship between fiber and heart disease, and between calcium and osteoporosis.
- Qualified health claims: These claims are based on emerging scientific evidence and are allowed on food labels with qualifying language that acknowledges the limited scientific evidence. An example is a claim about the relationship between green tea and reduced risk of certain types of cancer.
Nutrient content claims describe the level of a nutrient in a food. These claims are based on the amount of the nutrient in the food and are regulated to ensure they are accurate and not misleading. Examples of nutrient content claims include “high in fiber” and “low in sodium.”
Regulations and Requirements
The regulations and requirements for making health claims and nutrient content claims vary by country. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates these claims. The FDA has established specific criteria that food manufacturers must meet in order to make these claims on their food labels.
Examples
Some common health claims and nutrient content claims found on cereal labels include:
- “Whole grain” – This claim means that the cereal contains at least 51% whole grains.
- “High in fiber” – This claim means that the cereal contains at least 5 grams of fiber per serving.
- “Low in sodium” – This claim means that the cereal contains less than 140 milligrams of sodium per serving.
- “Good source of vitamin D” – This claim means that the cereal contains at least 10% of the Daily Value for vitamin D.
Allergen Information: Cereal Food Label

Knowing what’s in your cereal is crucial, especially if you have allergies or sensitivities. Food labels provide vital information about potential allergens, empowering you to make informed choices.
Cereal products often contain various ingredients, including grains, nuts, seeds, and milk derivatives. Some of the most common allergens found in cereals include:
Wheat and Gluten
- Wheat, a common cereal grain, contains gluten, a protein that can trigger an immune response in people with celiac disease or gluten intolerance.
Nuts and Seeds
- Nuts, such as almonds, peanuts, and walnuts, are prevalent allergens in cereal products.
- Seeds, including sunflower seeds, sesame seeds, and flax seeds, can also cause allergic reactions.
Dairy
- Milk and milk derivatives, like whey and casein, are common ingredients in cereals, particularly those marketed towards children.
- Individuals with lactose intolerance or milk allergies should be aware of these ingredients.
Cereal labels clearly display allergen information in the ingredient list. Look for statements like “Contains wheat” or “May contain nuts.” Additionally, manufacturers often highlight allergens in bold or use separate allergen statements to make them more noticeable.
Other Label Information
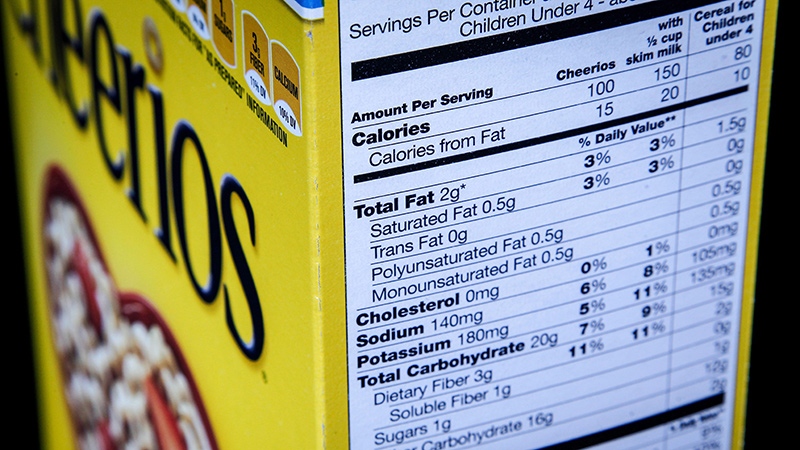
In addition to the mandatory information, cereal food labels may also include other important details that provide consumers with valuable insights.
These may encompass storage recommendations, manufacturer contact information, and environmental or sustainability claims, each serving a specific purpose in informing consumers.
Storage Recommendations
Storage instructions are crucial for maintaining the quality and freshness of cereal products. These recommendations typically specify the optimal conditions for storage, such as keeping the cereal in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture.
Following these instructions helps preserve the cereal’s texture, flavor, and nutritional value, ensuring that consumers enjoy a wholesome and satisfying experience.
Manufacturer Contact Information, Cereal food label
Manufacturer contact information is essential for consumers who have questions or concerns about the product. This information typically includes the company’s name, address, phone number, and website.
By providing this contact information, manufacturers demonstrate transparency and accountability, enabling consumers to reach out with inquiries or feedback, fostering trust and building a stronger brand reputation.
Environmental or Sustainability Claims
In today’s environmentally conscious market, cereal manufacturers may make claims about the environmental or sustainability aspects of their products.
- These claims can relate to the use of sustainable packaging materials, reduced carbon footprint during production, or support for ethical farming practices.
- Such claims provide consumers with information about the manufacturer’s commitment to environmental stewardship and responsible business practices.
However, it’s important to note that these claims should be substantiated with credible evidence and certifications to ensure their authenticity and prevent misleading consumers.
Key Questions Answered
What is the significance of serving size information on cereal food labels?
Serving size information provides a standardized reference point for comparing the nutritional content of different cereals. It ensures that consumers can accurately assess the amount of nutrients they are consuming per serving, aiding in portion control and informed dietary choices.
How can I interpret the ingredient list on a cereal food label?
The ingredient list is arranged in descending order of weight, with the most prevalent ingredient listed first. By scrutinizing the ingredient list, consumers can gain insights into the composition of the cereal, identify potential allergens, and make informed decisions based on their dietary preferences and health considerations.
What are some common health claims found on cereal food labels?
Cereal food labels may feature health claims such as “low in sodium” or “good source of fiber.” These claims are regulated by government agencies and must meet specific criteria to ensure accuracy and prevent misleading consumers. Understanding these claims empowers consumers to make informed choices that align with their health goals.
