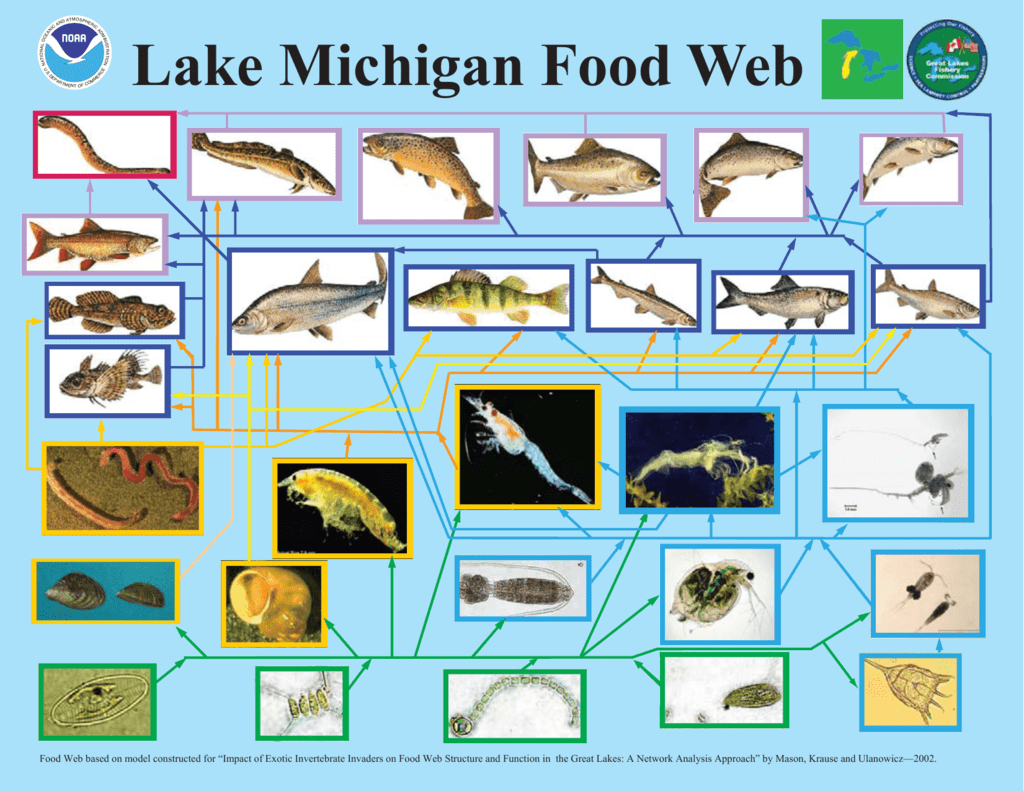
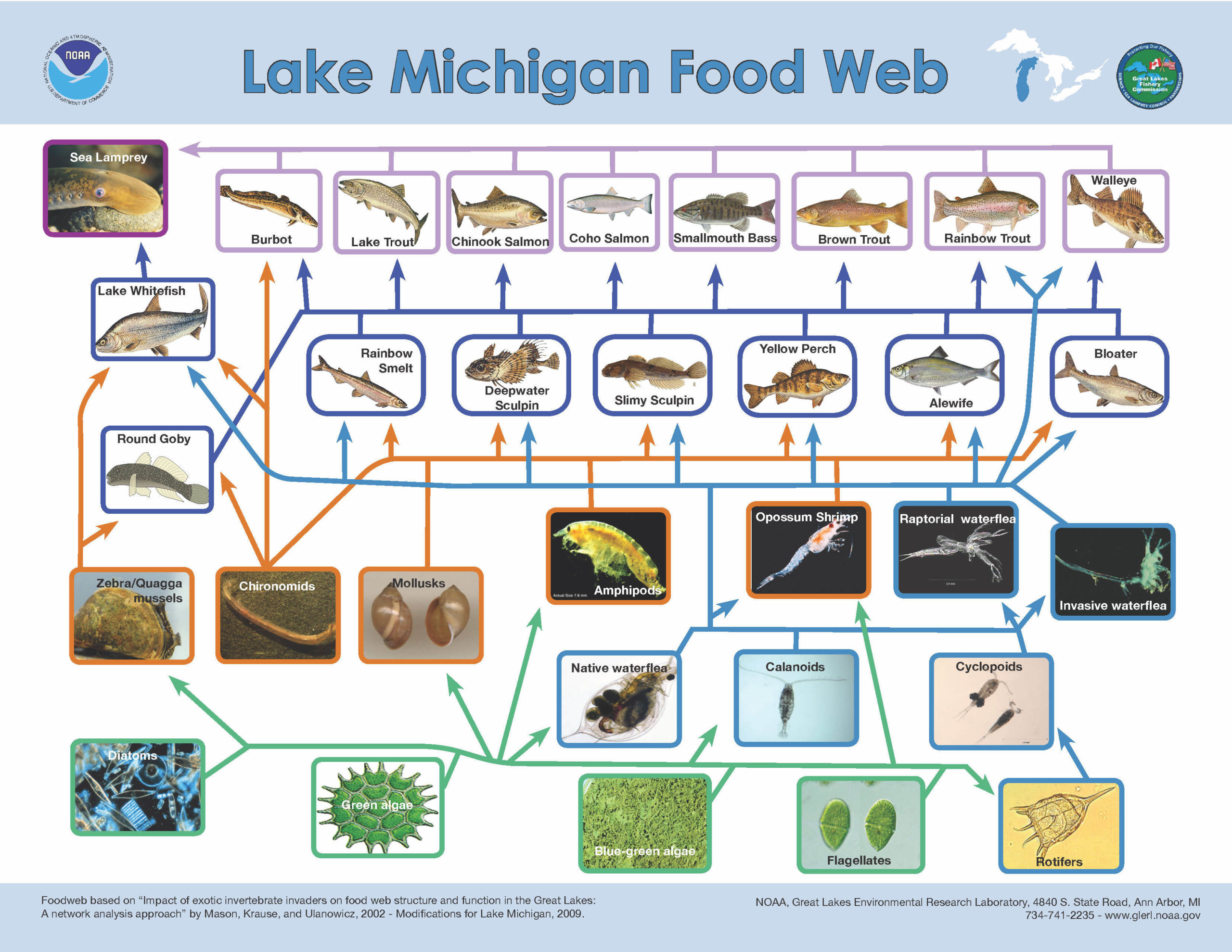
Unraveling the intricate tapestry of life within lakes, we embark on a journey to explore the lake food web, a vibrant and interconnected network that sustains the aquatic realm. From microscopic phytoplankton to apex predators, each organism plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of this fascinating ecosystem.
As we dive deeper, we’ll discover the primary producers that fuel the web, the diverse consumers that transfer energy through trophic levels, and the decomposers that recycle essential nutrients. Along the way, we’ll uncover the intricate relationships between abiotic and biotic factors, the impact of disturbances, and the resilience of these aquatic communities.
Disturbances and Resilience
Lakes, like all ecosystems, are subject to disturbances that can impact their food web structure and dynamics. These disturbances can be either natural or human-induced.
Natural Disturbances, Lake food web
Natural disturbances in lake ecosystems include events such as storms, droughts, and wildfires. Storms can cause physical damage to lake habitats, such as uprooting trees and altering shoreline structures. Droughts can reduce water levels, leading to changes in the availability of food and habitat for aquatic organisms.
Wildfires can release nutrients into lakes, which can stimulate algal growth and alter the food web balance.
Human Impacts
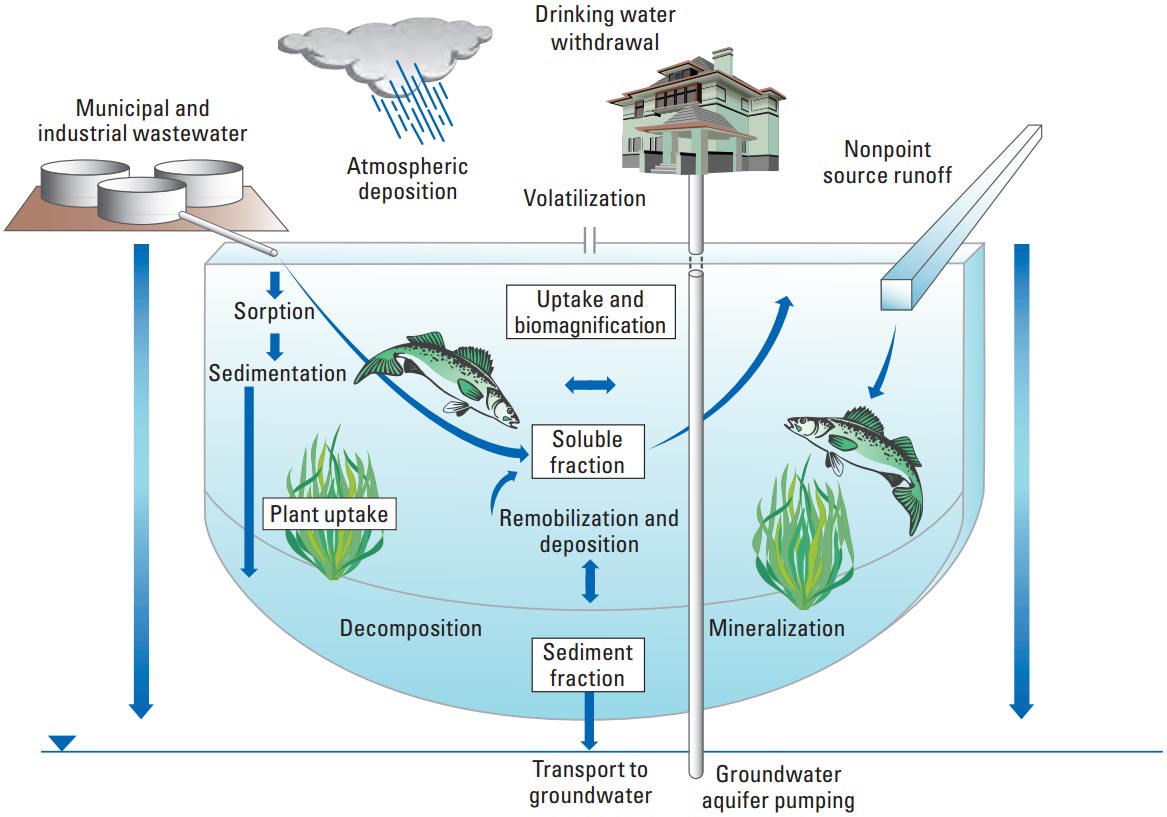
Human activities can also significantly impact lake food webs. Pollution from industrial, agricultural, and domestic sources can introduce harmful substances into lakes, affecting the health and survival of aquatic organisms. Eutrophication, caused by excess nutrient inputs, can lead to algal blooms, which can deplete oxygen levels and disrupt the food web.
Overfishing and the introduction of invasive species can also alter the balance of lake food webs.
User Queries: Lake Food Web
What is the foundation of a lake food web?
Primary producers, such as phytoplankton and macrophytes, form the base of the lake food web, converting sunlight and nutrients into organic matter.
What is the role of zooplankton in the lake food web?
Zooplankton are tiny aquatic animals that feed on phytoplankton and transfer energy to higher trophic levels, including fish and benthic invertebrates.
How do decomposers contribute to the lake ecosystem?
Decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, break down organic matter, releasing nutrients back into the ecosystem and maintaining the balance of the food web.