Embark on a culinary adventure as we delve into the realm of good food groups, where nutrition meets taste. From essential dietary guidelines to the symphony of flavors and health benefits, this narrative unravels the secrets of a balanced diet, leaving you inspired and empowered to make informed food choices.
Navigating the diverse landscape of food groups, we’ll uncover their macronutrient composition, exploring the vital roles of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in our bodies. Vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants take center stage, showcasing the nutritional richness hidden within each food group.
Dietary Guidelines
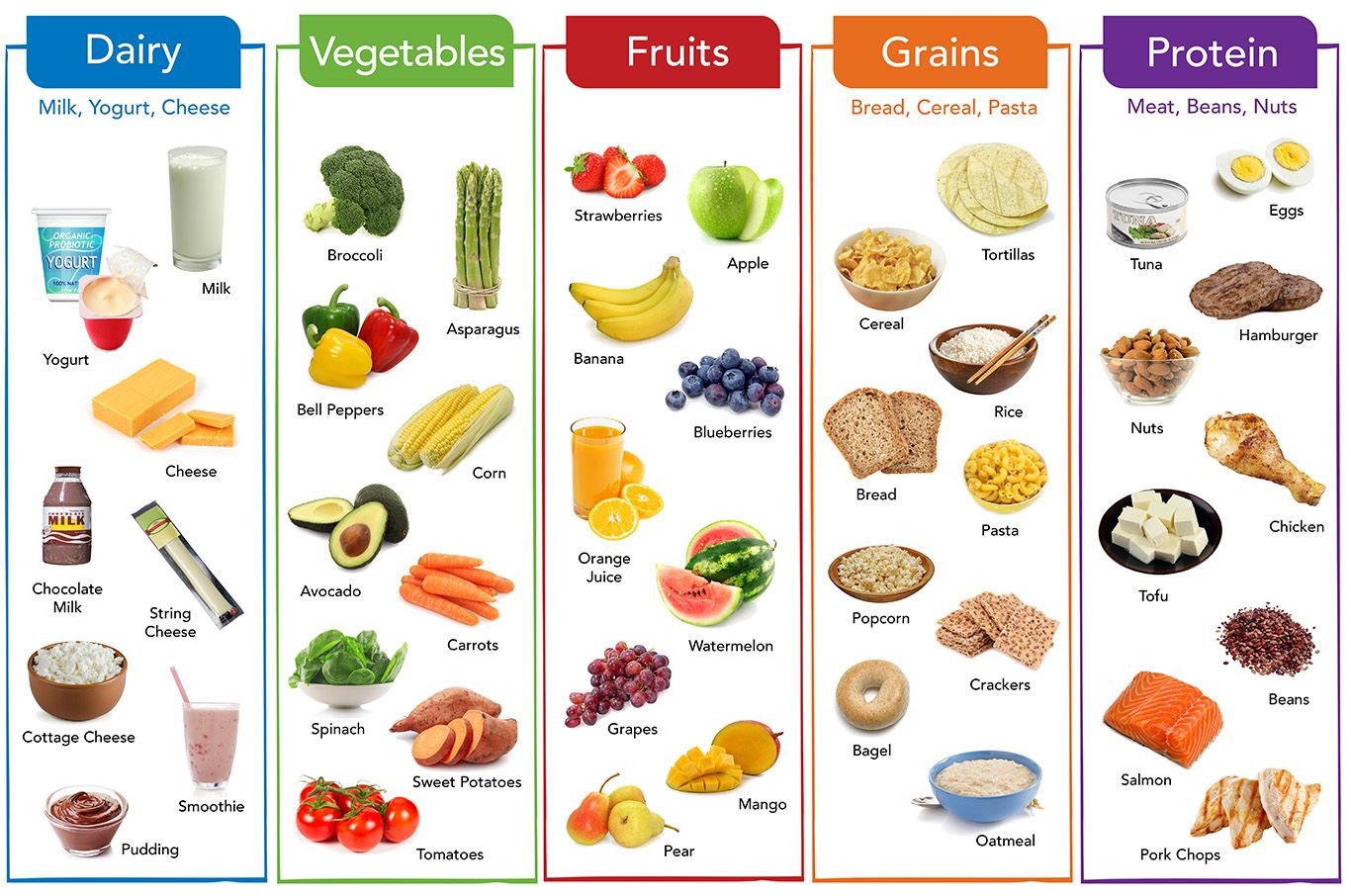
Dietary guidelines provide evidence-based recommendations to promote healthy eating patterns and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. These guidelines categorize foods into food groups based on their nutrient composition and function in the body.
Understanding food groups and their recommended daily servings is essential for maintaining a balanced diet that meets individual nutritional needs.
Essential Food Groups
Most dietary guidelines recommend consuming foods from the following essential food groups:
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Whole grains
- Lean protein
- Dairy or calcium-rich alternatives
Recommended Daily Servings
The recommended daily servings for each food group vary depending on factors such as age, sex, and activity level. Here is a general overview:
| Food Group | Recommended Daily Servings |
|---|---|
| Fruits | 2-4 cups |
| Vegetables | 2-4 cups |
| Whole grains | 6-8 ounces |
| Lean protein | 5-6 ounces |
| Dairy or calcium-rich alternatives | 3 cups |
Macronutrient Content
Food groups vary significantly in their macronutrient composition, primarily consisting of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. These macronutrients play crucial roles in the body’s energy production, growth, and repair processes.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary energy source. They are broken down into glucose, which is used for energy by cells. Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are rich sources of carbohydrates.
Proteins
Proteins are essential for building and repairing tissues. They are composed of amino acids, which are required for various bodily functions. Meat, poultry, fish, and legumes are good sources of protein.
Fats
Fats provide energy and help absorb vitamins. They also play a role in hormone production and cell function. Healthy fats are found in olive oil, avocados, and nuts.
Nutritional Value
Food groups provide an array of essential nutrients that are vital for maintaining optimal health and well-being. Each group contributes unique nutrients, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that work synergistically to support various bodily functions.
The nutritional value of food groups varies widely, depending on the specific foods they contain. However, certain nutrients are predominantly found in specific groups, as highlighted below:
Fruits and Vegetables
- Rich in vitamins (A, C, E, K), minerals (potassium, magnesium, calcium), and antioxidants
- Antioxidants, such as carotenoids and flavonoids, protect against cellular damage
- High fiber content promotes digestive health and satiety
Whole Grains, Good food group
- Excellent source of fiber, B vitamins (thiamin, riboflavin, niacin), and iron
- Fiber helps regulate blood sugar levels and reduces the risk of heart disease
- B vitamins support energy production and nervous system function
Lean Protein
- Provides essential amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins
- Supports muscle growth and repair, and promotes satiety
- Sources include poultry, fish, beans, and tofu
Dairy Products
- Rich in calcium, protein, and vitamin D
- Calcium is essential for bone health and muscle function
- Vitamin D supports bone health and immune function
Healthy Fats
- Sources include olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds
- Provide essential fatty acids, which support brain function and heart health
- Help absorb fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K)
The following table provides a summary of key nutrients present in each food group:
| Food Group | Key Nutrients |
|---|---|
| Fruits and Vegetables | Vitamins A, C, E, K; Minerals (potassium, magnesium, calcium); Antioxidants |
| Whole Grains | Fiber; B vitamins (thiamin, riboflavin, niacin); Iron |
| Lean Protein | Essential amino acids |
| Dairy Products | Calcium; Protein; Vitamin D |
| Healthy Fats | Essential fatty acids; Vitamins A, D, E, K |
Health Benefits
Consuming a balanced diet rich in different food groups provides numerous health benefits. It helps reduce the risk of chronic diseases, promotes overall well-being, and supports optimal bodily functions.
A balanced diet ensures adequate intake of essential nutrients, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. These nutrients play crucial roles in maintaining a healthy immune system, regulating metabolism, and protecting against various health conditions.
Role in Reducing Chronic Disease Risk
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein has been linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases such as:
- Heart disease:Soluble fiber in oats, beans, and apples helps lower cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Type 2 diabetes:Whole grains and fruits regulate blood sugar levels, improving insulin sensitivity and reducing the risk of diabetes.
- Certain types of cancer:Antioxidants in fruits and vegetables, such as vitamin C and beta-carotene, protect cells from damage and reduce the risk of certain cancers.
- Osteoporosis:Calcium-rich foods like dairy products and leafy green vegetables strengthen bones, reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
Food Group Interactions
Food group interactions play a crucial role in maximizing nutrient absorption and enhancing overall health. Consuming certain food groups together can synergistically improve the bioavailability and utilization of specific nutrients.
For instance, pairing iron-rich foods (e.g., red meat, spinach) with vitamin C-rich foods (e.g., citrus fruits, bell peppers) enhances iron absorption by up to 200%. Vitamin C acts as a reducing agent, converting non-heme iron (found in plant-based foods) into a more absorbable form.
Complementary Food Group Pairings
- Iron + Vitamin C:Enhances iron absorption.
- Calcium + Vitamin D:Facilitates calcium absorption for strong bones.
- Protein + Carbohydrates:Balances blood sugar levels and promotes satiety.
- Fiber + Water:Supports digestion and prevents constipation.
- Antioxidants + Healthy Fats:Enhances antioxidant absorption and protects cells from damage.
Food Group Substitutions

Maintaining a balanced diet is crucial for overall well-being. Food group substitutions play a significant role in ensuring that individuals meet their nutritional needs even when they cannot consume foods from specific food groups due to allergies, intolerances, or personal preferences.
Substituting foods from different food groups requires careful consideration to maintain nutritional adequacy. It involves identifying foods that provide similar nutrients to the foods being replaced. For instance, if someone cannot consume dairy products, they can substitute them with fortified plant-based milk or leafy green vegetables to ensure adequate calcium intake.
Common Food Group Substitutions
- Dairy:Fortified plant-based milk, yogurt, or cheese; leafy green vegetables
- Protein:Beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, nuts, seeds
- Fruits:Whole grains, vegetables, 100% fruit juice
- Vegetables:Whole grains, fruits, beans, lentils
- Whole Grains:Fruits, vegetables, beans, lentils, nuts, seeds
User Queries: Good Food Group
What are the key food groups?
Fruits, vegetables, grains, protein foods, and dairy products are the cornerstone food groups.
How do I ensure I’m getting enough of each food group?
Refer to dietary guidelines or consult with a registered dietitian to determine the recommended daily servings for each food group based on your age, sex, and activity level.
Can I substitute foods from different food groups?
Yes, food group substitutions can maintain nutritional adequacy. For example, legumes can replace meat as a protein source, and fortified plant-based milk can substitute dairy milk.
