Food apex, the pinnacle of the food chain, reigns supreme in ecosystems worldwide. These apex predators play a pivotal role in maintaining ecological equilibrium, shaping human cultures, and inspiring scientific innovations.
From the majestic lions of the African savanna to the formidable sharks of the deep sea, food apex species exhibit remarkable adaptations and hunting strategies, dominating their respective ecological niches.
Definition of Food Apex

A food apex, or apex predator, is a species that occupies the highest trophic level in a food chain or food web. These predators are characterized by their ability to consume other organisms without being preyed upon by any other species.
The concept of a food chain refers to the linear sequence of organisms through which energy and nutrients pass, starting with producers (organisms that can make their own food) and ending with top predators. Apex predators play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance by regulating populations of their prey species.
By consuming prey, apex predators prevent overpopulation and ensure the availability of resources for other species in the ecosystem.
Significance of Food Apex Predators
The presence of apex predators in an ecosystem has several important implications:
- Population Control:Apex predators regulate the populations of their prey species, preventing overpopulation and maintaining a balance in the ecosystem.
- Biodiversity:By preventing overpopulation of certain prey species, apex predators indirectly support the diversity of other species in the ecosystem.
- Trophic Cascade:The presence of apex predators can have a cascading effect on the entire food chain, influencing the populations and behaviors of species at lower trophic levels.
- Ecosystem Stability:Apex predators play a vital role in maintaining the stability and resilience of ecosystems by regulating prey populations and preventing ecosystem collapse.
Understanding the role and significance of food apex predators is essential for effective conservation and management of ecosystems.
Characteristics of Food Apex Species
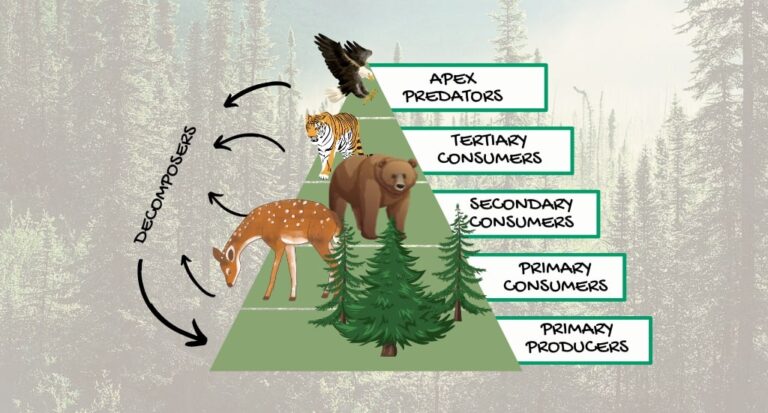
Food apex species, often referred to as top predators, occupy the highest trophic level within their ecosystems, exerting a profound influence on the structure and dynamics of their respective habitats. These species exhibit a remarkable array of physical adaptations, hunting strategies, and ecological niches that enable them to maintain their dominant position in the food chain.
Physical Adaptations
Food apex species typically possess exceptional physical attributes that facilitate their predatory success. These adaptations may include:
- Sharp claws, teeth, and beaks:Used for capturing and subduing prey.
- Keen senses:Enhanced vision, hearing, and smell allow them to detect and track prey efficiently.
- Speed and agility:Enables them to chase and capture elusive prey.
li> Strength and endurance:Necessary for overpowering and subduing larger prey.
Hunting Strategies
Food apex species employ diverse hunting strategies to secure their food supply. These strategies may include:
- Ambush predators:Lie in wait for unsuspecting prey, using camouflage or stealth to conceal their presence.
- Pursuit predators:Actively chase and pursue prey, relying on their speed and endurance to overtake them.
- Opportunistic predators:Feed on prey that is weakened, injured, or vulnerable, often scavenging or stealing from other predators.
Ecological Niches
Food apex species occupy a range of ecological niches, reflecting their diverse adaptations and hunting strategies. Some common niches include:
- Apex predators:Occupy the highest trophic level, preying on other predators and herbivores.
- Mesopredators:Feed on both predators and herbivores, playing a crucial role in regulating prey populations.
- Keystone predators:Have a disproportionately large impact on their ecosystems, controlling the abundance of dominant prey species.
Importance of Food Apex Species in Ecosystems
Food apex species play a critical role in maintaining the health and biodiversity of ecosystems. Their presence and abundance influence the dynamics of entire food chains, shaping community structure and ecosystem processes.
The removal or decline of apex predators can trigger a cascade of effects throughout the ecosystem. This phenomenon is known as trophic cascades.
Apex Predators and Prey Populations, Food apex
Apex predators regulate prey populations by consuming individuals from various age and size classes. This selective predation can prevent prey populations from becoming too large, reducing competition for resources and mitigating the impact of overgrazing on vegetation.
For example, in the Yellowstone ecosystem, the reintroduction of wolves led to a decline in elk populations. As a result, aspen and willow trees, which had been overbrowsed by elk, began to recover.
Apex Predators and Ecosystem Dynamics
Apex predators also influence ecosystem dynamics by affecting the behavior and distribution of their prey. For instance, in marine ecosystems, the presence of sharks can cause prey species to alter their swimming patterns and habitat use, reducing their vulnerability to predation.
Furthermore, apex predators can indirectly influence the abundance and diversity of other species within the ecosystem. For example, in coral reef ecosystems, the presence of sharks can promote the growth of coral by reducing the number of herbivorous fish that graze on coral.
Human Impacts on Food Apex Species
Human activities significantly impact food apex species, altering ecosystem dynamics and human well-being. Habitat loss, overhunting, and pollution pose severe threats to these species and their ecological roles.
Habitat Loss:Human development, agriculture, and deforestation destroy and fragment habitats, reducing the availability of food, shelter, and breeding grounds for food apex species. This loss disrupts their populations and affects their ability to regulate prey species.
Overhunting
- Subsistence and Commercial Hunting:Humans hunt food apex species for food, traditional practices, and commercial purposes. Overhunting can deplete populations, disrupting ecosystem balance and reducing biodiversity.
- Trophy Hunting:Killing apex predators for sport can significantly impact their numbers, affecting prey populations and ecosystem stability.
Pollution
- Toxins and Contaminants:Industrial pollution, agricultural chemicals, and plastics can accumulate in food apex species through bioaccumulation. These toxins can harm their health, reduce reproduction, and alter their behavior.
- Noise and Light Pollution:Noise from human activities can interfere with communication and hunting for food apex species. Artificial light at night can disrupt their circadian rhythms and alter prey availability.
Consequences:The decline of food apex species has far-reaching consequences. It disrupts predator-prey relationships, leading to population explosions of prey species that can damage ecosystems. It also affects human well-being by reducing ecosystem services, such as pest control and nutrient cycling, provided by food apex species.
Conservation Strategies:Protecting food apex species and their habitats is crucial for maintaining ecosystem health and human well-being. Conservation measures include:
- Habitat Protection:Establishing protected areas, managing land use, and restoring degraded habitats.
- Sustainable Hunting Practices:Regulating hunting quotas, enforcing hunting laws, and promoting responsible hunting practices.
- Pollution Control:Reducing emissions, implementing waste management strategies, and promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
- Education and Awareness:Raising public awareness about the importance of food apex species and encouraging responsible actions.
Food Apex Species in Cultural and Historical Contexts
Food apex species have played a significant role in human cultures and histories worldwide. They have been revered, feared, and respected, and their presence has shaped human understanding of the natural world.
In many cultures, apex predators are seen as symbols of strength, power, and authority. For example, in ancient Egypt, the pharaohs were often depicted with the head of a lion, symbolizing their divine power. In Native American cultures, the eagle is considered a sacred animal, representing wisdom and courage.
Mythology and Folklore
Apex predators have also featured prominently in mythology and folklore. In Greek mythology, the god Zeus is often depicted with an eagle at his side, representing his power and authority. In Norse mythology, the wolf Fenrir is a symbol of chaos and destruction.
These stories reflect the awe and fear that humans have felt towards apex predators throughout history.
Traditional Practices
In some cultures, apex predators have been hunted for their fur, meat, or other resources. However, in other cultures, they have been protected and revered. For example, in some Native American cultures, it is considered taboo to kill a bear, as they are seen as sacred animals.
Human Understanding of the Natural World
Apex predators have played a significant role in shaping human understanding of the natural world. By observing their behavior and interactions, humans have learned about the importance of predator-prey relationships and the delicate balance of ecosystems. Apex predators are also indicators of environmental health, and their presence or absence can provide valuable insights into the state of an ecosystem.
Emerging Research and Innovations in Food Apex Species Conservation

Recent advancements in research and technology are significantly contributing to the conservation of food apex species. These innovations include the use of tracking devices, genetic analysis, and habitat modeling to monitor and protect apex predators. Additionally, innovative approaches are being developed to mitigate human-wildlife conflicts and promote coexistence between humans and apex species.
Tracking Devices
Tracking devices, such as GPS collars and satellite tags, provide valuable data on the movements, behavior, and habitat use of apex predators. This information helps researchers identify critical habitats, assess population trends, and understand the impacts of human activities on these species.
Genetic Analysis
Genetic analysis techniques, such as DNA sequencing and microsatellite analysis, are used to study the genetic diversity and population structure of apex predators. This information helps researchers identify genetically distinct populations, assess the risk of inbreeding, and inform conservation management strategies.
Habitat Modeling
Habitat modeling uses GIS and remote sensing data to predict the distribution and abundance of apex predators based on environmental variables. These models help identify areas of suitable habitat, prioritize conservation efforts, and mitigate the impacts of land-use changes on apex predator populations.
Mitigating Human-Wildlife Conflicts
Innovative approaches are being developed to mitigate human-wildlife conflicts and promote coexistence between humans and apex species. These approaches include:
Non-lethal deterrents
Using noisemakers, flashing lights, or chemical repellents to deter apex predators from approaching human settlements or livestock.
Predator-proof fencing
Installing physical barriers, such as electric fences or livestock guardian dogs, to prevent apex predators from accessing areas where they may pose a threat to humans or livestock.
Public education and outreach
Educating the public about the importance of apex predators and promoting responsible behavior in areas where these species are present.
FAQ Overview: Food Apex
What is the primary function of food apex species in ecosystems?
Food apex species regulate prey populations, maintaining ecosystem balance and preventing overpopulation.
How do human activities impact food apex species?
Habitat loss, overhunting, and pollution threaten food apex species, disrupting ecosystem dynamics.
What are the consequences of the decline of food apex species?
The decline of apex predators can trigger cascading effects throughout the food chain, leading to ecosystem instability and biodiversity loss.
