Akkermansia foods, a crucial component of a healthy diet, play a significant role in promoting the growth and activity of Akkermansia muciniphila, a beneficial gut bacteria associated with various health benefits.
Understanding the relationship between Akkermansia muciniphila and specific dietary components can empower individuals to make informed choices that support their gut health and overall well-being.
Akkermansia muciniphila Overview: Akkermansia Foods
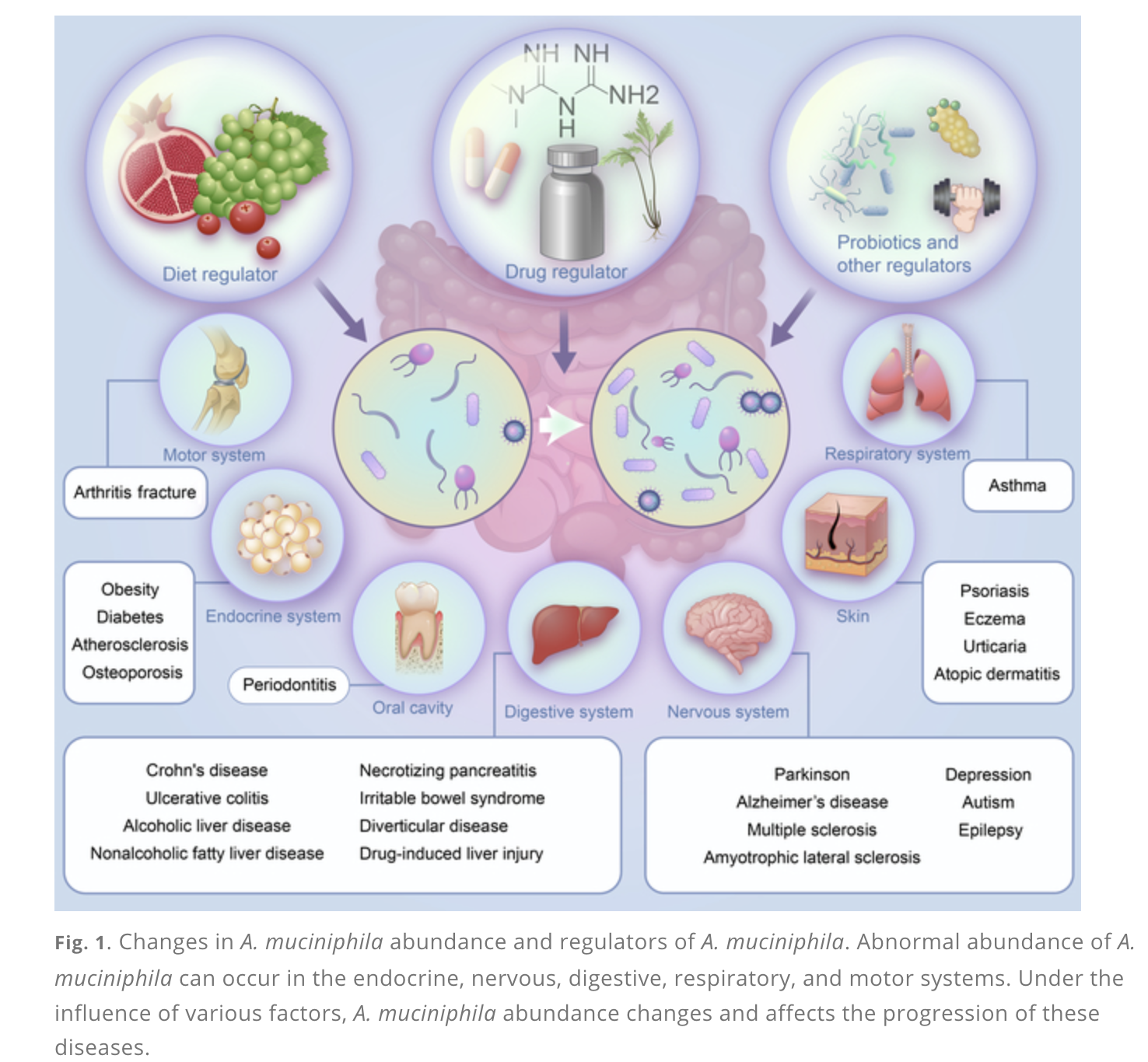
Akkermansia muciniphila is a Gram-negative, anaerobic, and mucin-degrading bacterium belonging to the phylum Verrucomicrobia. It is a dominant member of the human gut microbiome, particularly in individuals with a healthy metabolic profile.
Akkermansia muciniphila plays a crucial role in maintaining gut health and overall well-being. It contributes to the breakdown of complex carbohydrates, including mucin, a major component of the intestinal mucus layer. This mucus layer protects the intestinal lining from pathogens and harmful substances.
Significance
The presence and abundance of Akkermansia muciniphila have been associated with several health benefits. Studies have shown a correlation between higher levels of Akkermansia muciniphila and improved metabolic health, reduced inflammation, and protection against obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
Akkermansia muciniphila and the Gut Microbiome
Akkermansia muciniphila is an essential player in the gut microbiome ecosystem. Its presence and abundance are closely intertwined with the composition and diversity of other gut microbiota, significantly influencing the overall balance and functionality of the gut microbiome.
Interactions with Other Gut Microbiota, Akkermansia foods
Akkermansia muciniphila engages in complex interactions with various gut bacteria. It promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria like Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus, which produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) that nourish the gut lining and regulate immune responses.
Conversely, Akkermansia muciniphila inhibits the growth of pathogenic bacteria such as Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae. By maintaining a healthy balance between beneficial and harmful bacteria, Akkermansia muciniphila contributes to gut microbial homeostasis.
Influence on Gut Microbial Diversity and Ecosystem Balance
The presence of Akkermansia muciniphila is associated with increased gut microbial diversity. It promotes the colonization of different bacterial species, enhancing the overall complexity and stability of the gut microbiome ecosystem.
This increased diversity is crucial for maintaining a resilient gut environment, as it provides functional redundancy and resilience against environmental changes or challenges. A diverse microbiome is better equipped to adapt and respond to various dietary and environmental factors.
Impact on Gut Barrier Function and Immune Regulation
Akkermansia muciniphila plays a vital role in maintaining gut barrier integrity. It stimulates the production of mucin, a protective layer that lines the intestinal wall and prevents the entry of harmful substances into the bloodstream.
Additionally, Akkermansia muciniphila modulates immune responses in the gut. It promotes the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines and regulates the activity of immune cells, contributing to immune tolerance and reducing the risk of chronic inflammatory conditions.
Akkermansia muciniphila and Diet
Dietary choices play a significant role in promoting the growth and activity of Akkermansia muciniphila. Studies have identified specific foods and food groups that support the abundance and metabolic activity of this beneficial bacterium.
Foods that Support Akkermansia muciniphila
Incorporating the following foods into a healthy diet can help maintain optimal levels of Akkermansia muciniphila:
| Food Group | Specific Foods |
|---|---|
| Fruits | Apples, blueberries, bananas |
| Vegetables | Spinach, kale, carrots |
| Whole Grains | Brown rice, quinoa, oats |
| Legumes | Lentils, beans, chickpeas |
| Nuts and Seeds | Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds |
| Fermented Foods | Yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut |
These foods provide essential nutrients and compounds, such as fiber, polyphenols, and prebiotics, that nourish and stimulate the growth of Akkermansia muciniphila.
Akkermansia muciniphila and Prebiotics/Probiotics

Prebiotics are non-digestible food ingredients that promote the growth and activity of beneficial bacteria in the gut, including Akkermansia muciniphila. Probiotics, on the other hand, are live microorganisms that provide direct health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts.
Several prebiotic and probiotic supplements contain Akkermansia muciniphila or its metabolites. These supplements aim to enhance Akkermansia muciniphila levels in the gut, thereby improving gut health and overall well-being.
Supplements Containing Akkermansia muciniphila or Its Metabolites
The following table compares different prebiotic and probiotic supplements that contain Akkermansia muciniphila or its metabolites:
| Supplement | Type | Akkermansia Component |
|---|---|---|
| Akkermansia muciniphila Probiotic | Probiotic | Live Akkermansia muciniphila bacteria |
| Prebiotic Inulin | Prebiotic | Inulin, a prebiotic that promotes Akkermansia muciniphila growth |
| Akkermansia Metabolites Supplement | Prebiotic | Isolated metabolites produced by Akkermansia muciniphila |
Potential Benefits:
- Improved gut barrier function
- Reduced inflammation
- Enhanced weight management
- Improved blood sugar control
Limitations:
- Not all supplements are created equal, and some may not contain sufficient amounts of Akkermansia muciniphila or its metabolites to be effective.
- Some people may experience side effects, such as gas or bloating, when taking these supplements.
Akkermansia muciniphila and Metabolic Health
Akkermansia muciniphila has been linked to various metabolic disorders, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Studies have shown that individuals with lower levels of Akkermansia muciniphila have a higher risk of developing these conditions.
Obesity
Akkermansia muciniphila is involved in regulating energy metabolism and appetite. It produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which have anti-inflammatory and appetite-suppressing effects. Lower levels of Akkermansia muciniphila have been associated with increased body weight, fat mass, and insulin resistance.
Studies in animal models have shown that supplementation with Akkermansia muciniphila can reduce obesity and improve insulin sensitivity. In a study published in the journal Nature Medicine, obese mice that were given Akkermansia muciniphila supplements for 12 weeks showed a significant reduction in body weight, fat mass, and blood sugar levels.
Type 2 Diabetes
Akkermansia muciniphila may also play a role in the development of type 2 diabetes. Studies have found that individuals with type 2 diabetes have lower levels of Akkermansia muciniphila compared to healthy individuals.
Animal studies have shown that Akkermansia muciniphila supplementation can improve glucose tolerance and reduce insulin resistance. In a study published in the journal Diabetes, diabetic mice that were given Akkermansia muciniphila supplements for 8 weeks showed improved glucose tolerance and reduced insulin resistance.
Cardiovascular Disease
Akkermansia muciniphila has been linked to cardiovascular disease, including atherosclerosis and heart failure. Studies have found that individuals with cardiovascular disease have lower levels of Akkermansia muciniphila compared to healthy individuals.
Animal studies have shown that Akkermansia muciniphila supplementation can reduce atherosclerosis and improve heart function. In a study published in the journal Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, mice that were given Akkermansia muciniphila supplements for 12 weeks showed reduced atherosclerosis and improved heart function.
Akkermansia muciniphila and Immune Function

Akkermansia muciniphila plays a crucial role in regulating the immune system, particularly in the context of immune-related disorders. It modulates immune responses through various mechanisms, including the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, the enhancement of regulatory T cells, and the maintenance of intestinal barrier integrity.
Immune Regulation
Akkermansia muciniphila promotes immune tolerance and reduces inflammation by producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), such as acetate and propionate. These SCFAs have immunomodulatory effects, inhibiting the activation of pro-inflammatory pathways and promoting the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines like IL-10.
Regulatory T Cells
Akkermansia muciniphila also enhances the differentiation and function of regulatory T cells (Tregs), which play a critical role in suppressing immune responses and maintaining immune balance. Tregs help prevent excessive inflammation and autoimmune disorders by controlling the activation of other immune cells.
Intestinal Barrier Integrity
Moreover, Akkermansia muciniphila contributes to the maintenance of intestinal barrier integrity by promoting the production of mucin, a protective layer that lines the intestinal tract. This helps prevent the leakage of harmful substances into the bloodstream, reducing the risk of inflammation and immune disorders.
Studies on Immune Function
- In a study on healthy individuals, supplementation with Akkermansia muciniphila was found to increase the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines and reduce the levels of pro-inflammatory markers.
- In a mouse model of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), treatment with Akkermansia muciniphila attenuated disease severity, reduced inflammation, and improved intestinal barrier function.
FAQ Explained
What are the key dietary factors that promote Akkermansia muciniphila growth?
Dietary fiber, polyphenols, and omega-3 fatty acids are known to support the growth and activity of Akkermansia muciniphila.
How can prebiotics and probiotics enhance Akkermansia muciniphila levels?
Prebiotics, such as inulin and oligofructose, provide nourishment for Akkermansia muciniphila, while probiotics containing specific strains of this bacteria can directly increase its population.
What are some specific Akkermansia foods that I can incorporate into my diet?
Foods rich in dietary fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, are excellent sources of Akkermansia foods.
