The vegetarian food pyramid is a valuable tool for vegetarians seeking a balanced and nutritious diet. It provides a comprehensive overview of the essential food groups and their recommended daily intake, ensuring optimal health and well-being.
Delving into the different levels of the pyramid, we explore the significance of whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and seeds in a vegetarian lifestyle. We also discuss the unique dietary considerations for various types of vegetarians, such as vegans and lacto-vegetarians.
Introduction to Vegetarian Food Pyramid
A food pyramid is a visual representation of the recommended daily intake of different food groups. It is a guide to help people make healthy eating choices and ensure they are getting the nutrients they need.
For vegetarians, a balanced diet is essential to ensure they are getting all the nutrients they need. The Vegetarian Food Pyramid provides guidance on the types and amounts of foods that vegetarians should eat each day to maintain good health.
Importance of a Balanced Diet for Vegetarians
Vegetarians have a higher risk of certain nutrient deficiencies, such as vitamin B12, iron, and calcium. This is because these nutrients are primarily found in animal products. Therefore, it is important for vegetarians to eat a variety of foods from all food groups to ensure they are getting all the nutrients they need.
A balanced diet for vegetarians includes:
- Fruits and vegetables
- Whole grains
- Legumes (beans, lentils, peas)
- Nuts and seeds
- Dairy products or fortified plant-based alternatives
- Vitamin B12 supplements
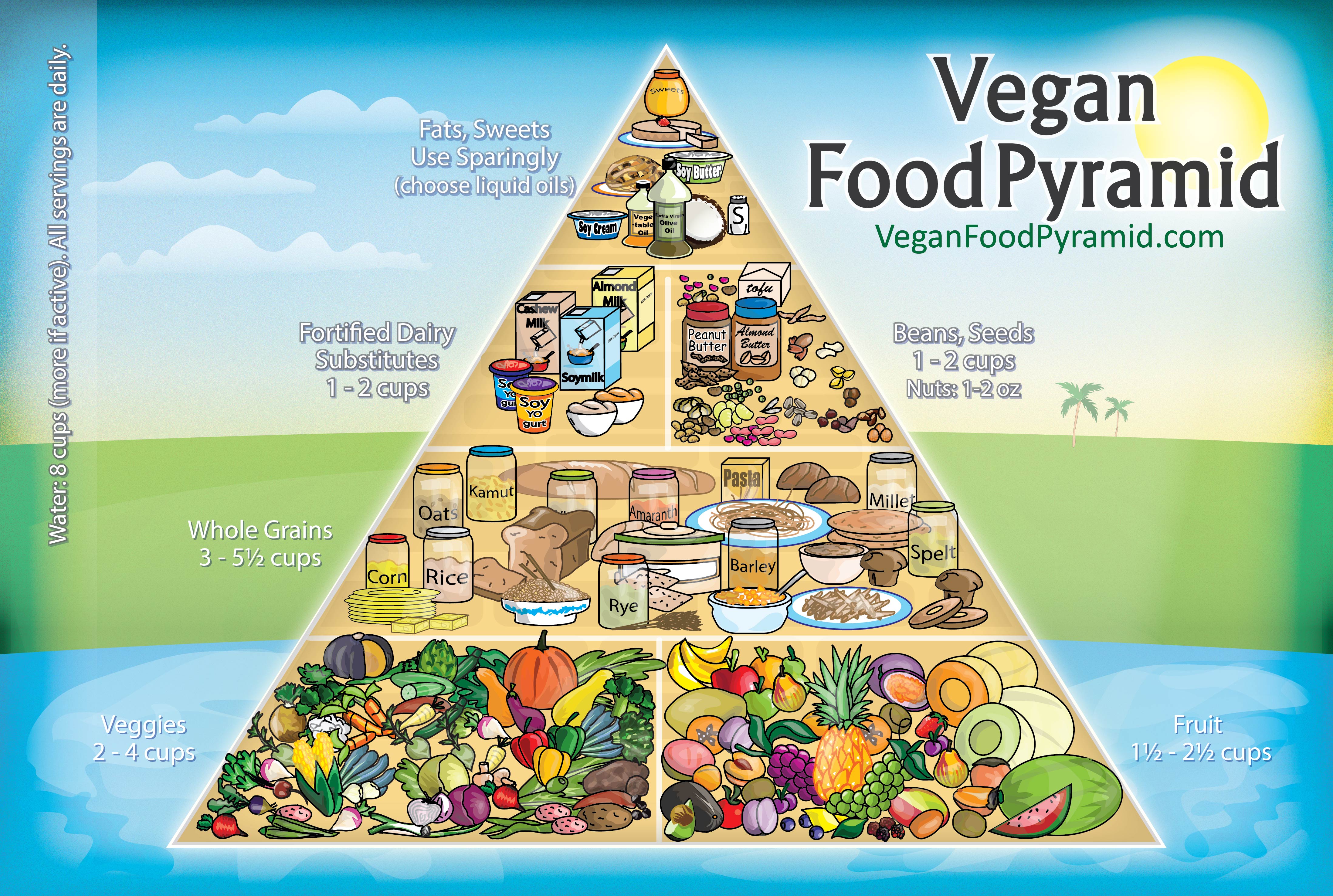
Levels of the Vegetarian Food Pyramid

The vegetarian food pyramid is a visual representation of the different food groups that vegetarians should eat to maintain a healthy diet. It is divided into several levels, each representing a different type of food group.The bottom level of the pyramid is the foundation of the vegetarian diet and consists of whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
These foods are packed with essential nutrients like fiber, vitamins, and minerals. The next level up is the protein level, which includes legumes, nuts, and seeds. These foods provide the body with essential amino acids that are necessary for building and repairing tissues.
The third level is the dairy level, which includes milk, yogurt, and cheese. These foods are a good source of calcium, vitamin D, and protein. The top level of the pyramid is the fats level, which includes healthy fats from sources like olive oil, avocados, and nuts.
These fats are essential for hormone production and cell function.
Benefits of Following the Vegetarian Food Pyramid
Adopting a vegetarian diet based on the Vegetarian Food Pyramid offers numerous potential health advantages. This structured approach to vegetarian nutrition ensures a balanced intake of essential nutrients, promoting overall well-being.
By adhering to the food pyramid’s recommendations, vegetarians can:
- Reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
- Maintain a healthy weight by consuming nutrient-rich foods that are typically lower in calories and saturated fat.
- Improve digestion and regularity by consuming ample fiber from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Support a healthy immune system by consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, and legumes, which are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Promote bone health by consuming calcium-rich foods such as leafy green vegetables, fortified plant-based milk, and tofu.
Role of the Food Pyramid in Promoting a Healthy Lifestyle
The Vegetarian Food Pyramid serves as a valuable tool for promoting a healthy vegetarian lifestyle. It provides clear and concise guidelines on the types and proportions of foods to consume, ensuring that vegetarians meet their nutritional needs while enjoying a balanced and satisfying diet.
By following the food pyramid’s recommendations, vegetarians can:
- Make informed food choices based on sound nutritional principles.
- Avoid nutrient deficiencies by ensuring a varied and balanced intake of foods from all food groups.
- Manage their weight effectively by consuming nutrient-dense foods that promote satiety.
- Reduce the risk of chronic diseases by limiting the intake of unhealthy fats, processed foods, and added sugars.
- Promote overall well-being by supporting a healthy digestive system, immune function, and hormonal balance.
In conclusion, following the Vegetarian Food Pyramid is an effective way to reap the numerous health benefits of a vegetarian diet. By providing clear guidelines on food choices and proportions, the food pyramid empowers vegetarians to make informed decisions that support their health and well-being.
Considerations for Different Types of Vegetarians
The vegetarian diet encompasses a wide range of eating patterns, each with its own unique nutritional considerations. To ensure adequate nutrient intake, it is essential to understand the specific dietary needs of different types of vegetarians.
Vegans, who consume no animal products whatsoever, must pay particular attention to obtaining essential nutrients such as vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids. Fortified plant-based foods, nutritional yeast, and supplements can help meet these needs.
Lacto-Vegetarians
Lacto-vegetarians include dairy products in their diet but exclude all other animal products. While dairy provides calcium and vitamin D, it is important to ensure adequate intake of vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids from plant-based sources or fortified foods.
Challenges and Solutions
Adopting a vegetarian diet based on the food pyramid can present certain challenges. However, with practical solutions and strategies, these obstacles can be overcome.
Meeting Protein Needs
Vegetarians may face challenges in meeting their protein requirements. However, plant-based sources such as beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, and quinoa provide ample protein.
Ensuring Adequate Iron Intake
Iron deficiency is a potential concern for vegetarians. Leafy green vegetables, fortified cereals, and beans are excellent sources of iron. Vitamin C aids in iron absorption, so including citrus fruits or bell peppers in meals is beneficial.
Getting Enough Calcium
Dairy products are a primary source of calcium, but vegetarians can obtain it from fortified plant-based milks, leafy green vegetables, and fortified cereals.
Maintaining Vitamin B12 Levels
Vitamin B12 is primarily found in animal products. Vegetarians can supplement their diet with fortified foods or consider taking a vitamin B12 supplement.
Social and Cultural Factors
Social and cultural factors can influence the adoption of a vegetarian diet. Dining out, attending social events, and traveling may pose challenges. It’s important to be prepared with vegetarian options and to communicate preferences clearly.
Example Meal Plans
Following a vegetarian food pyramid can be easy and enjoyable with the right meal plans. Here are some sample plans that provide a variety of nutrient-rich options while adhering to the pyramid’s recommendations.
Breakfast
- Oatmeal with berries, nuts, and seeds
- Yogurt parfait with fruit, granola, and honey
- Whole-wheat toast with avocado and eggs
- Smoothie made with fruits, vegetables, and plant-based milk
- Vegan breakfast burritos with beans, salsa, and vegetables
Lunch
- Salads with grilled tofu, quinoa, vegetables, and dressing
- Sandwiches on whole-wheat bread with hummus, vegetables, and sprouts
- Soups and stews made with beans, lentils, and vegetables
- Pasta dishes with whole-wheat pasta, vegetables, and a marinara sauce
li>Wraps with brown rice, beans, and vegetables
Dinner
- Stir-fries with tofu, vegetables, and brown rice
- Lentil tacos with corn tortillas, salsa, and vegetables
- Vegetable curries with chickpeas, vegetables, and coconut milk
- Baked tofu with roasted vegetables and quinoa
- Vegetable lasagna with whole-wheat noodles, ricotta cheese, and vegetables
Snacks
- Fruits and vegetables
- Nuts and seeds
- Yogurt
- Hummus with vegetable sticks
- Popcorn
Additional Resources

Exploring vegetarian nutrition can be enriched with additional resources. Here are some reputable organizations and websites to provide further information and support:
Organizations and Websites
- Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics: Provides credible information on vegetarian nutrition and registered dietitian referrals.
- American Vegetarian Association: Offers resources on vegetarianism, including recipes, nutrition tips, and support groups.
- The Vegetarian Resource Group: A non-profit organization dedicated to promoting vegetarianism and providing evidence-based nutrition information.
- North American Vegetarian Society: A membership organization that supports vegetarianism through education, advocacy, and community building.
- Plant-Based Nutrition Certificate Program: Provides comprehensive training on plant-based nutrition, including vegetarian and vegan diets.
Additionally, here are links to cookbooks and online resources for vegetarian recipes:
Cookbooks and Online Resources, Vegetarian food pyramid
- “The Vegetarian Cookbook” by Nava Atlas: A classic cookbook with over 400 recipes for a variety of vegetarian dishes.
- “Veganomicon” by Isa Chandra Moskowitz: A comprehensive guide to vegan cooking with over 500 recipes.
- “The Happy Herbivore Cookbook” by Lindsay S. Nixon: A collection of simple and delicious vegetarian recipes.
- Vegetarian Times: A magazine and website with recipes, nutrition tips, and articles on vegetarianism.
- Forks Over Knives: A website and cookbook promoting a whole-food, plant-based diet.
FAQ Summary
What is the vegetarian food pyramid?
The vegetarian food pyramid is a visual representation of the recommended daily intake of food groups for vegetarians. It provides guidance on the types and proportions of foods that should be consumed to maintain a healthy and balanced diet.
Why is it important for vegetarians to follow the food pyramid?
The food pyramid helps vegetarians ensure that they are consuming a wide variety of nutrient-rich foods from all food groups. By following the pyramid’s recommendations, vegetarians can reduce their risk of nutrient deficiencies and chronic diseases.
How can I make sure I’m getting enough protein on a vegetarian diet?
Plant-based sources of protein include legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas), tofu, tempeh, nuts, and seeds. By incorporating these foods into their meals, vegetarians can meet their daily protein requirements.
