Supply food is a crucial aspect of our global food system, ensuring that food reaches consumers safely and efficiently. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of supply food, exploring its key components, challenges, and the latest trends shaping the industry.
From the intricate network of food supply chains to the complexities of food production and distribution, this guide unravels the fascinating world of supply food, providing insights into its vital role in feeding the world.
Supply Chain Management for Food
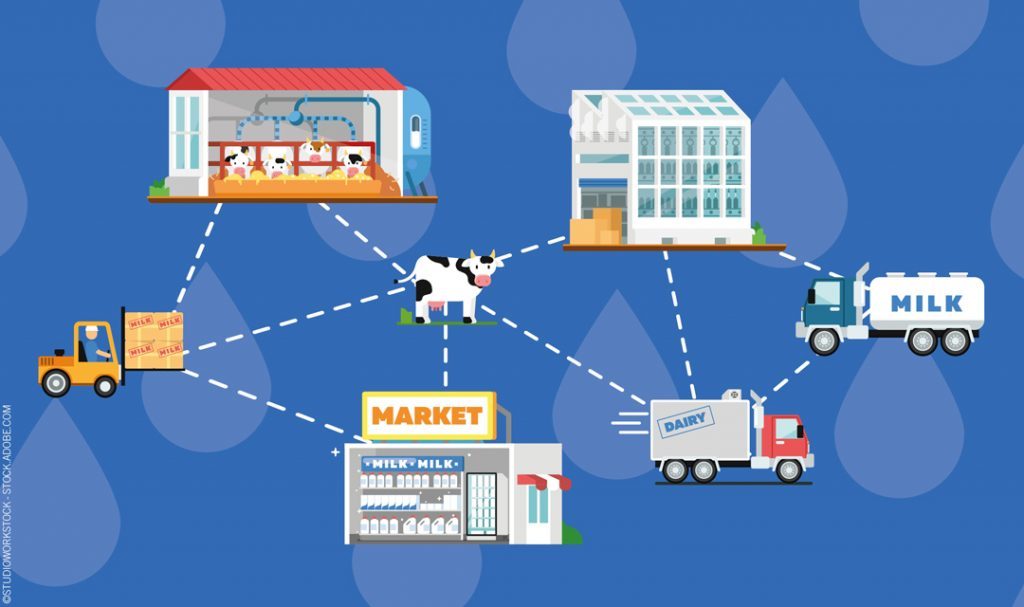
The food supply chain encompasses the interconnected network of organizations involved in producing, processing, distributing, and retailing food products. It ensures that food is safely and efficiently delivered from farm to fork.
Key components of a food supply chain include:
- Farmers and producers
- Processors and manufacturers
- Distributors and wholesalers
- Retailers and consumers
Food Supply Chain Models
Different food supply chain models exist, depending on the type of food product and the market it serves.
- Centralized model:A single entity controls all aspects of the supply chain, from production to distribution.
- Decentralized model:Multiple independent entities collaborate to manage different stages of the supply chain.
- Integrated model:Different stages of the supply chain are closely coordinated and managed as a single system.
Challenges and Opportunities in Food Supply Chain Management, Supply food
Managing a food supply chain involves numerous challenges and opportunities.
Challenges
- Ensuring food safety and quality
- Minimizing waste and spoilage
- Balancing supply and demand
- Adapting to changing consumer preferences
Opportunities
- Improving efficiency and reducing costs
- Enhancing transparency and traceability
- Leveraging technology to optimize operations
- Promoting sustainability and reducing environmental impact
Food Production and Supply

The global food production and supply system is a complex and interconnected network involving various stakeholders, including farmers, processors, distributors, retailers, and consumers. Understanding the trends and factors influencing this system is crucial for ensuring food security and addressing global food challenges.
Global food production has witnessed a steady increase over the past few decades, driven by technological advancements, improved farming practices, and increased land use. However, this growth has not been uniform across all regions and commodities. Some regions, such as Asia and South America, have experienced significant increases in production, while others, such as Africa, continue to face challenges in meeting their food demands.
Factors Influencing Food Production and Supply
Several factors influence global food production and supply, including:
- Climate Change:Extreme weather events, rising temperatures, and changes in precipitation patterns can significantly impact crop yields and livestock production.
- Technological Advancements:Innovations in agricultural machinery, biotechnology, and irrigation systems have contributed to increased productivity and efficiency in food production.
- Economic Conditions:Economic factors, such as market prices, subsidies, and trade policies, can influence the profitability of farming and the availability of food for consumers.
- Political Stability:Political instability, conflicts, and government policies can disrupt food production and distribution networks.
- Population Growth:Increasing population puts pressure on food resources, requiring sustainable production practices and efficient supply chains.
Major Food-Producing Regions and their Contributions
The major food-producing regions of the world are:
- Asia:Asia is the largest food-producing region, contributing over 50% of global agricultural output. China, India, and Southeast Asian countries are major producers of rice, wheat, vegetables, and fruits.
- North America:North America is a major exporter of agricultural products, including corn, soybeans, and meat. The United States is a leading producer of these commodities.
- South America:South America is a major producer of agricultural commodities such as soybeans, corn, wheat, and beef. Brazil and Argentina are significant contributors to the global food supply.
- Europe:Europe is a major producer of agricultural products, including wheat, dairy products, and meat. The European Union is a significant exporter of these commodities.
- Africa:Africa has the potential to become a major food producer, but challenges such as poverty, conflict, and climate change hinder its agricultural development.
Food Security and Distribution
Food security is a fundamental human right, ensuring access to adequate, safe, and nutritious food for all people at all times. It encompasses availability, accessibility, utilization, and stability of food supplies.
Ensuring food security faces numerous challenges, including population growth, climate change, and economic inequality. Strategies to address these challenges include sustainable agriculture practices, food storage and distribution systems, and social safety nets.
Successful Food Distribution Programs
Examples of successful food distribution programs include:
- The National School Lunch Program in the United States provides free or reduced-price meals to low-income children.
- The World Food Programme, which delivers food aid to millions of people in need worldwide.
- Community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs, which connect farmers directly with consumers, ensuring access to fresh, local produce.
Food Safety and Quality
Ensuring the safety and quality of food is crucial for protecting public health and preventing foodborne illnesses. Food safety involves preventing the contamination of food with harmful bacteria, viruses, parasites, or chemicals. Food quality refers to the sensory attributes, nutritional value, and overall acceptability of food.
Regulations and Standards
Food safety and quality are regulated by various national and international agencies, including the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) in the European Union, and the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC), a joint body of the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO).
- These agencies establish regulations and standards for food production, processing, and distribution to ensure food safety and quality.
- Food businesses are required to comply with these regulations to ensure the safety and quality of the food they produce and distribute.
Key Players and Responsibilities
Ensuring food safety and quality involves collaboration among various stakeholders:
- Food producersare responsible for implementing good agricultural practices, proper handling and storage, and adherence to food safety regulations.
- Food processorsare responsible for ensuring food safety during processing, packaging, and storage, as well as adhering to quality standards.
- Food distributorsare responsible for transporting and storing food safely, maintaining quality, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
- Retailersare responsible for proper storage, handling, and display of food, as well as providing accurate information to consumers.
- Consumersplay a crucial role in food safety by following proper food handling and storage practices.
- Government agenciesare responsible for enforcing food safety regulations, conducting inspections, and responding to foodborne illness outbreaks.
Food Waste and Sustainability: Supply Food

Food waste is a significant global problem, posing environmental, economic, and social challenges. It refers to the discarding or loss of food intended for human consumption at any stage of the food supply chain, from production to consumption.
According to the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), approximately one-third of all food produced for human consumption is wasted each year. This amounts to roughly 1.3 billion tons of food, with a value of approximately $1 trillion.
Causes of Food Waste
The causes of food waste are complex and vary across different stages of the food supply chain:
- Production:Overproduction, poor harvesting practices, and natural disasters can lead to food loss at the production stage.
- Processing and Packaging:Inefficient processing techniques, over-packaging, and quality standards can contribute to food waste.
- Distribution and Transportation:Improper storage, handling, and transportation can damage food and make it unsafe for consumption.
- Retail and Consumer:Overstocking, poor inventory management, and consumer behavior (e.g., buying more than needed) can lead to food waste at retail and consumer levels.
Consequences of Food Waste
Food waste has severe environmental, economic, and social consequences:
- Environmental:Food waste contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, water pollution, and deforestation. Decomposing food in landfills produces methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
- Economic:Food waste represents a significant loss of economic value. It also increases food prices for consumers and reduces profits for food producers.
- Social:Food waste exacerbates food insecurity and hunger, especially in developing countries. It also undermines efforts to achieve sustainable food systems.
Innovative Solutions for Reducing Food Waste
Reducing food waste requires a multi-pronged approach involving all stakeholders in the food supply chain:
- Improved Production Practices:Implementing sustainable farming techniques, optimizing harvesting, and reducing post-harvest losses can minimize food waste at the production stage.
- Efficient Processing and Packaging:Optimizing processing techniques, using sustainable packaging, and reducing over-packaging can help reduce food waste during processing.
- Enhanced Distribution and Transportation:Improving storage and handling practices, optimizing transportation routes, and reducing delays can minimize food loss during distribution.
- Responsible Retail and Consumer Behavior:Educating consumers about food waste, promoting responsible purchasing habits, and implementing food waste reduction programs in retail stores can reduce food waste at the consumer level.
- Food Recovery and Redistribution:Establishing food recovery programs to collect and redistribute surplus food to those in need can help reduce food waste and address food insecurity.
- Technological Innovations:Developing innovative technologies, such as smart packaging and food waste monitoring systems, can help track and reduce food waste throughout the supply chain.
Detailed FAQs
What are the key components of a food supply chain?
A food supply chain typically involves farmers, processors, distributors, retailers, and consumers.
What are the challenges in managing a food supply chain?
Challenges include ensuring food safety, maintaining quality, managing inventory, and responding to disruptions.
How can we ensure food security for all?
Strategies include increasing food production, reducing food waste, and improving access to food for vulnerable populations.
