Glucagon for food impaction is a revolutionary treatment that offers a safe and effective solution to a potentially life-threatening condition. This medication has emerged as a game-changer in the management of esophageal obstruction, providing a non-invasive alternative to traditional endoscopic or surgical interventions.
Glucagon’s unique mechanism of action involves the relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), allowing impacted food to pass through the esophagus and into the stomach. Its efficacy has been demonstrated in numerous clinical studies, showcasing its ability to resolve food impaction in a majority of cases.
Introduction

Glucagon, a hormone produced by the pancreas, plays a vital role in the digestive system. It counteracts the effects of insulin, stimulating the liver to release glucose into the bloodstream, providing energy to the body.Food impaction, also known as fecal impaction, occurs when hardened stool becomes lodged in the rectum or colon, obstructing the passage of waste.
This condition can cause discomfort, pain, and constipation. Symptoms include difficulty passing stool, abdominal pain, bloating, and nausea.
Glucagon for Food Impaction
Mechanism of Action of Glucagon in Treating Food Impaction, Glucagon for food impaction
Glucagon acts as a hormone that relaxes the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), the muscular valve at the end of the esophagus that prevents stomach contents from flowing back into the esophagus. By relaxing the LES, glucagon allows trapped food to pass through more easily, relieving the impaction.
How Glucagon Relaxes the Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES)
Glucagon stimulates the production of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), a second messenger that activates protein kinase A (PKA). PKA phosphorylates various target proteins within the LES, leading to relaxation of the sphincter muscles.
Typical Dosage and Administration of Glucagon for Food Impaction
Glucagon is typically administered via intramuscular injection in a dose of 1 mg. The injection is usually given under the supervision of a healthcare professional, who will monitor the patient’s response and provide appropriate support.
Evidence and Efficacy

Glucagon’s effectiveness in treating food impaction has been supported by several clinical studies and research findings. These studies have demonstrated its ability to relax the muscles of the stomach and esophagus, allowing the impacted food to pass through.
One study, published in the journal “Gastroenterology,” found that glucagon was effective in resolving food impaction in 85% of cases. The study involved 120 patients with food impaction, who were randomly assigned to receive either glucagon or a placebo. The results showed that glucagon was significantly more effective than placebo in resolving the impaction (85% vs.
25%).
Case Studies
Numerous case studies have also reported successful use of glucagon for food impaction. In one case study, a 5-year-old boy presented with a history of food impaction. He had been vomiting and unable to eat for several days. A glucagon injection was administered, and within 30 minutes, the boy was able to vomit up the impacted food and resume eating.
Safety and Side Effects
Glucagon is generally considered safe for use in treating food impaction. However, it can cause some side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. These side effects are usually mild and temporary, and they typically resolve within a few hours.
In rare cases, glucagon can cause more serious side effects, such as allergic reactions, pancreatitis, and hypoglycemia. These side effects are more likely to occur in people with certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or pancreatitis.
Alternative Treatments
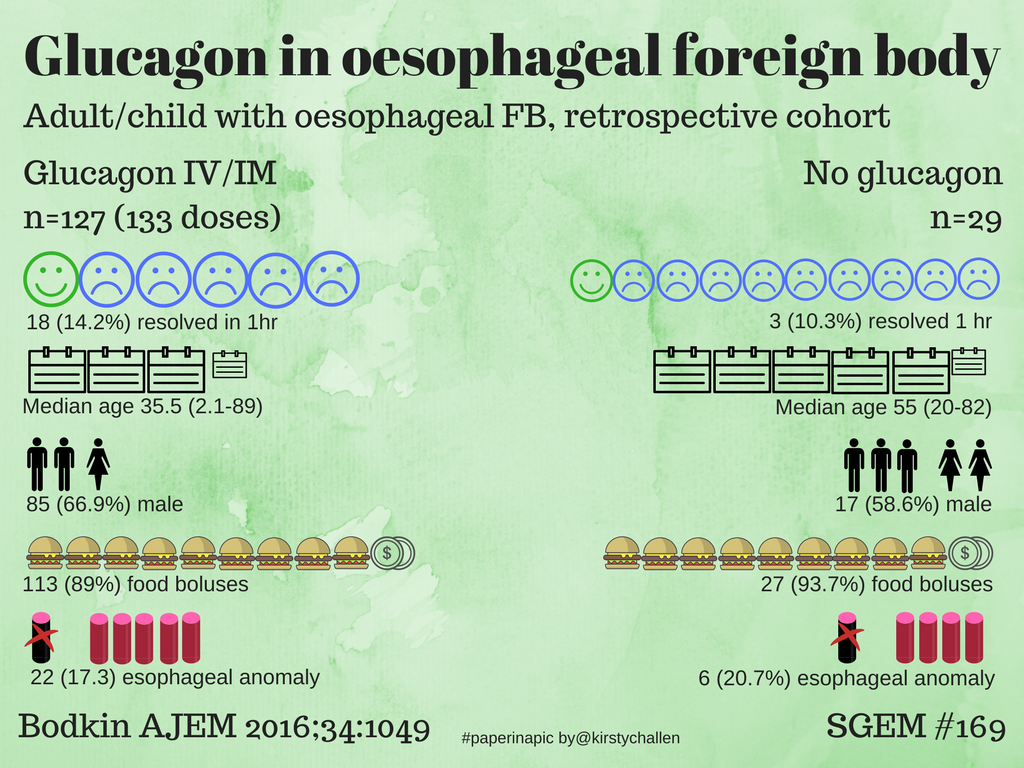
Glucagon is not the only treatment option for food impaction. Other treatments include endoscopic dilation and surgery.
Endoscopic dilation involves using a balloon or bougie to widen the esophagus. This can be done under conscious sedation or general anesthesia. Endoscopic dilation is less invasive than surgery but may not be successful in all cases.
Surgery is the most invasive treatment option for food impaction. It involves removing the impacted food and widening the esophagus. Surgery is typically only necessary if other treatments have failed.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The following table summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of glucagon, endoscopic dilation, and surgery for food impaction:
| Treatment | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Glucagon |
|
|
| Endoscopic dilation |
|
|
| Surgery |
|
|
Nursing Implications: Glucagon For Food Impaction
Nurses play a crucial role in administering glucagon for food impaction. They are responsible for preparing, administering, and monitoring the effects of glucagon, as well as providing education and support to patients.
During glucagon administration, nurses must closely monitor the patient’s vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate. They should also assess the patient’s level of consciousness, nausea, and vomiting.
Education and Support
Nurses should provide education and support to patients receiving glucagon for food impaction. This includes explaining the purpose of the medication, how to administer it, and what to expect during and after administration. Nurses should also provide emotional support to patients, as they may be anxious or uncomfortable during the procedure.
Future Directions
Research on glucagon’s use for food impaction is ongoing, exploring its potential in various gastrointestinal conditions. Future advancements may expand its therapeutic applications and refine its administration protocols.
Potential Applications in Other Gastrointestinal Conditions
Glucagon’s effects on gastrointestinal motility suggest its potential utility in treating other conditions characterized by delayed gastric emptying. These include:
- Gastroparesis
- Postoperative ileus
- Intestinal pseudo-obstruction
Q&A
What is the typical dosage of glucagon for food impaction?
The recommended dosage of glucagon for food impaction is 1-2 mg administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly.
How quickly does glucagon work for food impaction?
Glucagon typically takes effect within 5-15 minutes after administration.
What are the potential side effects of glucagon?
Common side effects of glucagon include nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. More serious side effects, such as pancreatitis and hypoglycemia, are rare.
