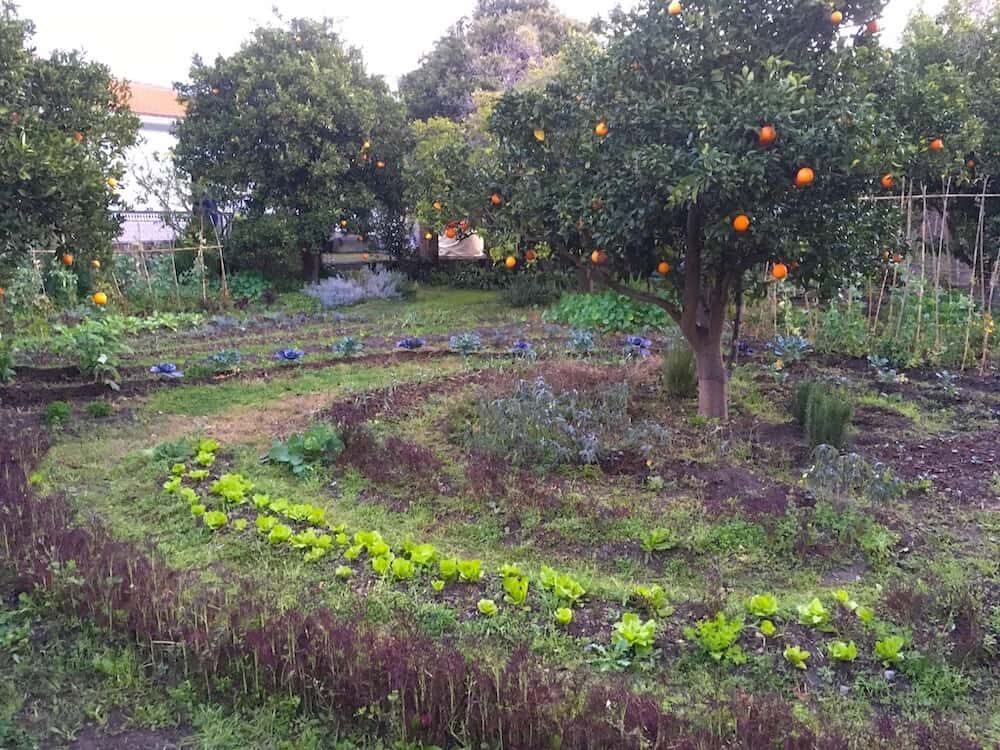
Food forest design, an innovative approach to land stewardship, offers a path to creating vibrant and sustainable edible ecosystems. By mimicking the intricate relationships found in natural forests, food forests provide a wealth of benefits, from enhanced biodiversity to increased food security.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the principles, practices, and rewards of food forest design, empowering you to transform your landscape into a thriving haven of nourishment and resilience.
Maintenance and Management of Food Forests

Food forests require ongoing care and management to ensure their long-term health and productivity. Implementing organic practices, controlling pests and diseases, and regularly pruning and harvesting are crucial aspects of food forest maintenance.
Benefits of Organic Practices in Food Forest Management
Organic practices promote the health and sustainability of food forests by:
- Improving soil health through the use of compost and cover crops.
- Reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides.
- Promoting biodiversity and attracting beneficial insects.
- Protecting the environment from harmful chemicals.
Tips for Controlling Pests and Diseases in a Food Forest
Preventing and controlling pests and diseases in food forests is essential for maintaining a healthy ecosystem. Some effective strategies include:
- Promoting plant diversity to create a balanced ecosystem.
- Using companion planting techniques to deter pests.
- Encouraging beneficial insects and predators.
- Practicing good sanitation by removing diseased plants and debris.
- Using organic pest and disease control methods, such as neem oil or insecticidal soap.
Importance of Regular Pruning and Harvesting
Regular pruning and harvesting are crucial for maintaining the health and productivity of food forests. Pruning removes dead or diseased branches, improves airflow, and encourages new growth. Harvesting prevents overcrowding, stimulates plant growth, and provides a regular supply of fresh produce.
Benefits of Food Forests
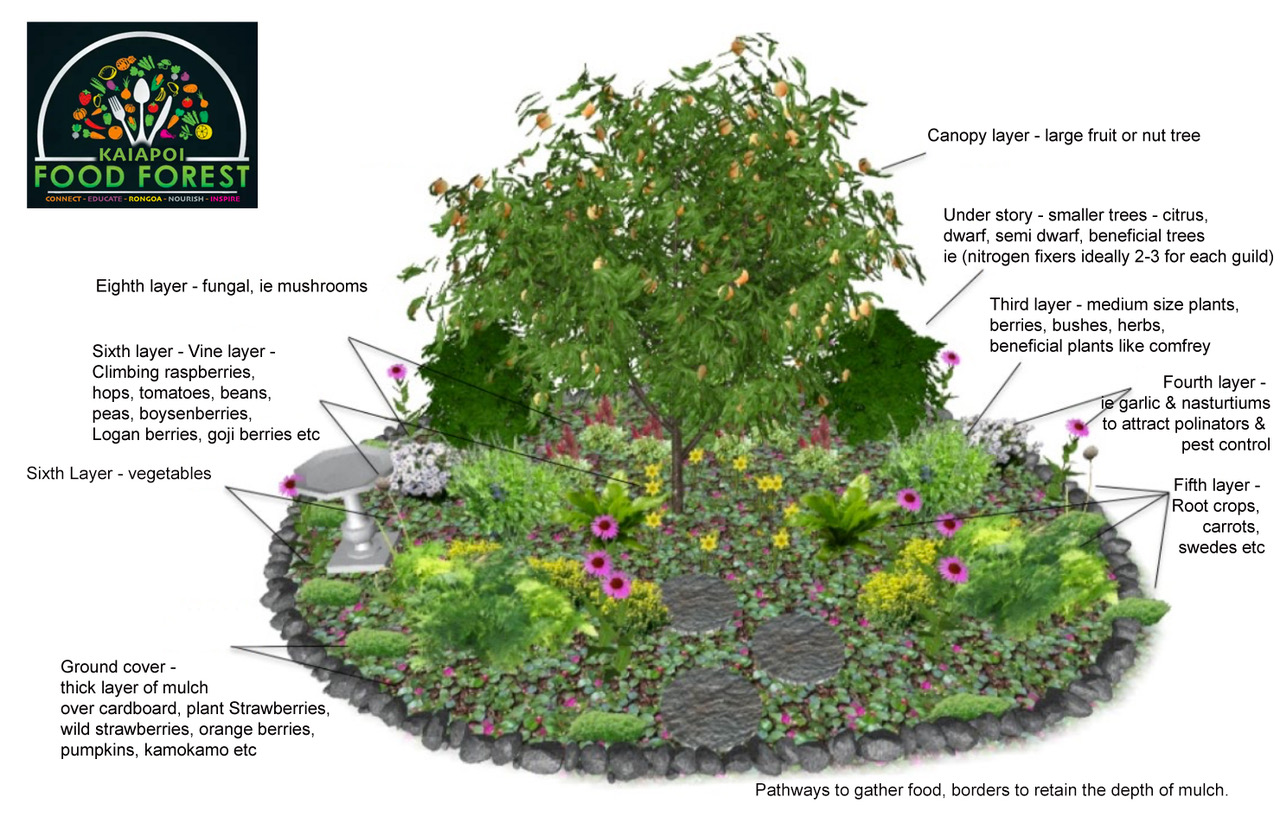
Food forests offer a multitude of benefits that extend beyond mere sustenance. Their environmental, economic, and social impacts make them a valuable tool for promoting sustainability and community well-being.
Environmental Benefits
Food forests play a significant role in carbon sequestration, helping to mitigate climate change. The dense vegetation of trees, shrubs, and groundcover plants absorbs carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and stores it in their biomass. Additionally, the deep root systems of trees help to stabilize soil, prevent erosion, and improve water infiltration.
Food forests also enhance biodiversity by providing habitat for a wide range of wildlife, including birds, insects, and mammals. The diversity of plant species in a food forest attracts a variety of pollinators, which are essential for the reproduction of many plants.
The presence of wildlife also contributes to the overall health and balance of the ecosystem.
Economic Benefits
Food forests can reduce food costs for households and communities by providing a reliable source of fresh, nutritious produce. By growing their own food, individuals and families can save money on grocery bills and reduce their dependence on imported produce.
Surplus produce from food forests can also be sold to generate additional income. This can provide financial benefits to individuals, families, and community organizations involved in food forest management. The sale of surplus produce can also contribute to the development of local food systems and support local businesses.
Community Development and Food Security, Food forest design
Food forests can contribute to community development by providing a shared space for people to gather, learn, and connect. Community members can participate in planting, harvesting, and food preservation activities, fostering a sense of community and collaboration.
Food forests also play a crucial role in improving food security, particularly in underserved communities. By providing access to fresh, nutritious food, food forests can help to address food insecurity and promote healthy eating habits. Community-managed food forests can empower residents to take control of their food system and improve their overall well-being.
Helpful Answers: Food Forest Design
What are the key principles of food forest design?
Food forest design emphasizes layering, companion planting, and selecting plants adapted to local conditions to create a self-sustaining ecosystem.
How does companion planting benefit food forests?
Companion planting improves plant growth, pest resistance, and nutrient uptake by creating mutually beneficial relationships between different species.
What is the role of nitrogen-fixing plants in food forests?
Nitrogen-fixing plants, such as legumes, enrich the soil with nitrogen, an essential nutrient for plant growth.

