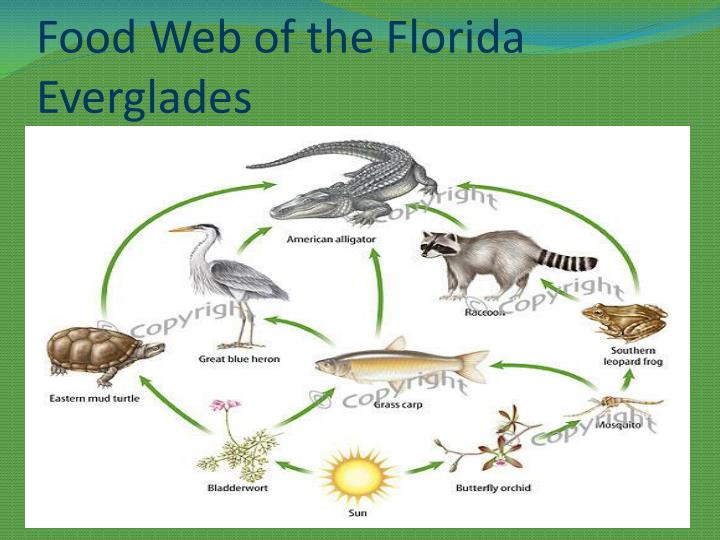
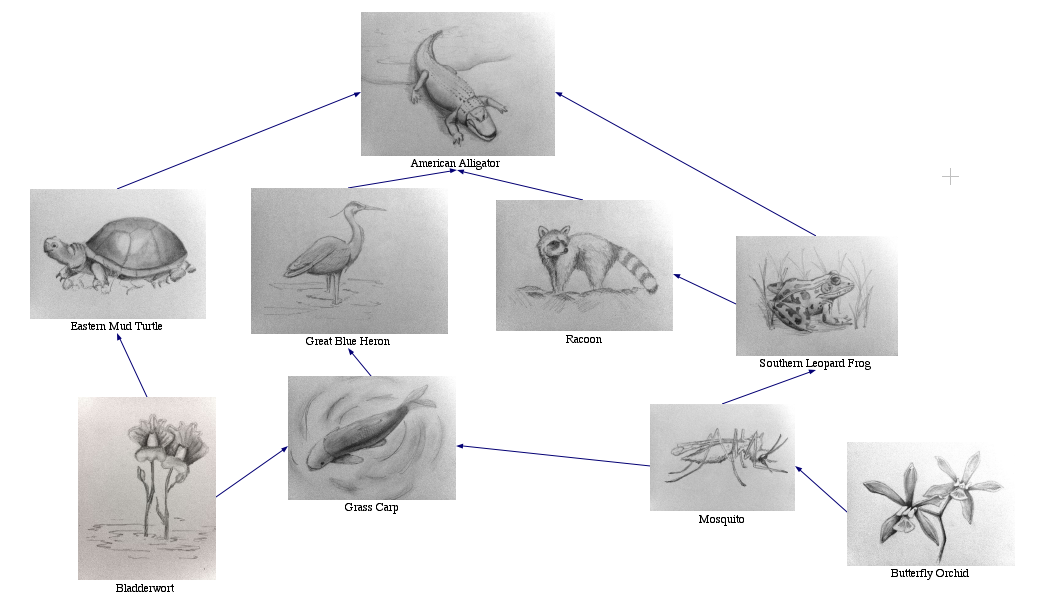
The Florida Everglades food web is a complex and interconnected ecosystem that supports a diverse array of plant and animal species. From the smallest algae to the apex predators, each organism plays a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of this unique and fragile environment.
This intricate tapestry of life has evolved over thousands of years, shaping the Everglades into a thriving and resilient ecosystem. However, human activities have had a significant impact on the food web, posing challenges to its stability and biodiversity.
Ecosystem Overview
The Florida Everglades, a vast subtropical wilderness, sprawls across the southern tip of Florida, covering an area of approximately 1.5 million acres. Its unique ecosystem has evolved over thousands of years, shaped by the intricate interplay of water flow, vegetation, and diverse wildlife.The
Everglades is renowned for its distinctive water flow patterns. The Kissimmee River, its primary source of freshwater, meanders through the ecosystem, distributing water across the vast landscape. This water flows slowly through a mosaic of marshes, swamps, and sloughs, creating a complex network of aquatic habitats.
The Everglades also experiences seasonal flooding, which replenishes nutrients and supports the ecosystem’s productivity.The vegetation of the Everglades is equally diverse, ranging from sawgrass prairies to hardwood forests. Sawgrass, a tall, sharp-edged grass, dominates the open marshes, while cypress trees thrive in the deeper waters.
Hardwood forests, including mahogany, gumbo limbo, and live oak, provide shelter and nesting sites for a variety of animals.
Unique Characteristics
The Everglades ecosystem is characterized by several unique features that contribute to its ecological significance:
-
-*Water Flow Patterns
The slow-moving water and seasonal flooding create a mosaic of aquatic habitats that support a wide range of plant and animal species.
-*Vegetation
The diverse vegetation, including sawgrass prairies, cypress forests, and hardwood forests, provides habitat and food for numerous organisms.
-*Wildlife
The Everglades is home to a rich array of wildlife, including wading birds, alligators, crocodiles, and a variety of fish and invertebrate species.
Food Web Structure

The Everglades food web is a complex and interconnected system where organisms rely on each other for food and survival. The structure of the food web can be divided into different trophic levels, which represent the feeding relationships between organisms.
The four main trophic levels in the Everglades food web are:
Producers
- Plants, such as sawgrass, cattails, and algae
- These organisms use sunlight to produce their own food through photosynthesis and form the base of the food web.
Primary Consumers, Florida everglades food web
- Herbivores, such as grasshoppers, snails, and fish
- These organisms feed directly on producers.
Secondary Consumers
- Carnivores, such as snakes, birds, and raccoons
- These organisms feed on primary consumers.
Tertiary Consumers
- Top predators, such as alligators, crocodiles, and panthers
- These organisms feed on secondary consumers and are at the top of the food chain.
The different trophic levels are interconnected, and energy flows from one level to the next. Producers create the food that is consumed by primary consumers, which in turn are eaten by secondary consumers, and so on. Top predators play a crucial role in regulating the populations of their prey, ensuring the balance of the ecosystem.
Question Bank: Florida Everglades Food Web
What is the Everglades ecosystem?
The Everglades is a vast subtropical wilderness in southern Florida, covering an area of over 1.5 million acres. It is characterized by a unique combination of freshwater marshes, sawgrass prairies, and mangrove forests.
What are the different trophic levels in the Everglades food web?
The Everglades food web consists of four main trophic levels: producers (plants), primary consumers (herbivores), secondary consumers (carnivores), and tertiary consumers (apex predators).
What are some examples of keystone species in the Everglades food web?
Keystone species in the Everglades include alligators, wading birds, and native fish species. These species play a disproportionately large role in maintaining the stability and functioning of the ecosystem.
How have human activities impacted the Everglades food web?
Human activities such as land development, water diversion, and pollution have significantly impacted the Everglades food web. These impacts include habitat loss, changes in water flow patterns, and the introduction of invasive species.
What are some conservation efforts aimed at protecting the Everglades food web?
Conservation efforts aimed at protecting the Everglades food web include restoring wetlands, controlling invasive species, and reducing pollution. These efforts are essential for maintaining the long-term health and sustainability of the Everglades ecosystem.