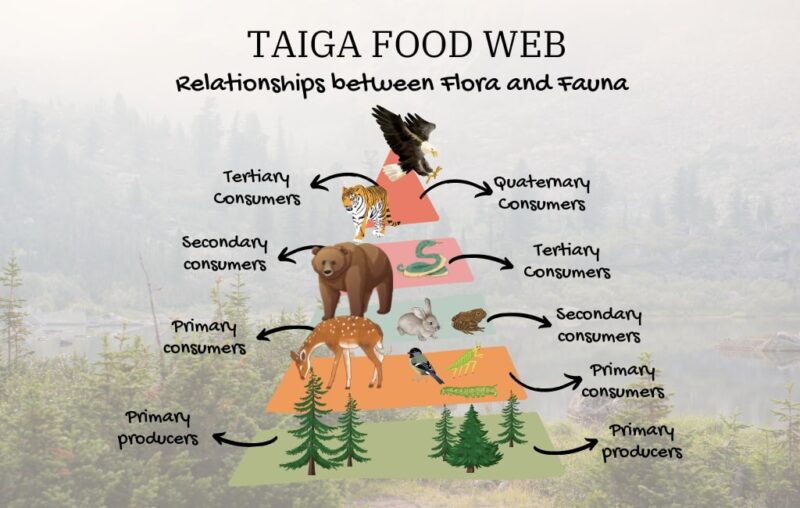
Delve into the intricate world of the taiga food web, a captivating tapestry of life that unfolds within the vast northern forests. From primary producers to apex predators, each organism plays a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of this ecosystem.
Within the taiga, a diverse array of flora and fauna interact in complex ways, forming a web of interconnected relationships. As energy flows through the food web, nutrients are cycled, and the ecosystem thrives.
Taiga Ecosystem
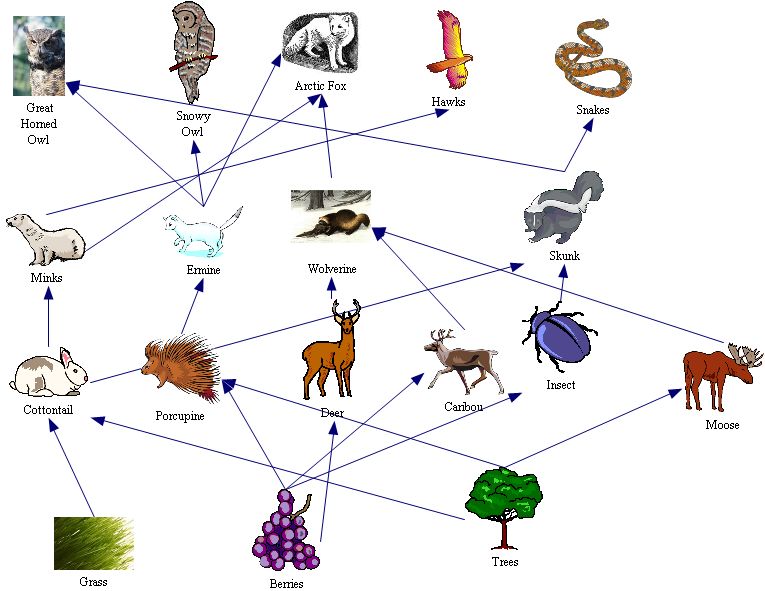
The taiga, also known as the boreal forest, is a vast and rugged ecosystem that encircles the globe in a broad belt across the northern latitudes. It is characterized by long, cold winters and short, warm summers. The taiga is home to a diverse array of plant and animal life, adapted to survive in this harsh climate.
The taiga is found in the northern regions of North America, Europe, and Asia. It covers an area of approximately 11 million square kilometers, making it the largest terrestrial biome on Earth. The climate of the taiga is characterized by long, cold winters with average temperatures below freezing for much of the year.
Summers are short and warm, with average temperatures ranging from 10 to 15 degrees Celsius. Precipitation is moderate, with annual totals ranging from 400 to 800 millimeters.
The taiga is a unique ecosystem with a rich and diverse flora and fauna. The vegetation is dominated by coniferous trees, such as spruce, fir, and pine. These trees are well-adapted to the cold climate, with thick bark and waxy leaves that help to prevent water loss.
The understory is typically composed of shrubs, mosses, and lichens.
The taiga is home to a variety of animals, including mammals, birds, and reptiles. Some of the most common mammals include moose, elk, wolves, and bears. Birds that are commonly found in the taiga include owls, hawks, and woodpeckers. Reptiles, such as snakes and lizards, are also found in the taiga, but they are less common.
The taiga is an important ecosystem that provides a number of benefits to humans. These benefits include:
- Timber: The taiga is a major source of timber, which is used to produce a variety of products, including lumber, paper, and furniture.
- Water: The taiga is a major source of water, which is used for drinking, irrigation, and hydroelectric power.
- Wildlife habitat: The taiga is home to a variety of wildlife, which provides opportunities for hunting, fishing, and other recreational activities.
- Carbon sequestration: The taiga plays an important role in carbon sequestration, which helps to mitigate climate change.
Question Bank: Taiga Food Web
What is the primary producer in the taiga food web?
Plants, particularly coniferous trees like spruce and fir, serve as the primary producers in the taiga ecosystem.
What is a keystone species in the taiga?
Keystone species in the taiga include wolves, which play a crucial role in regulating herbivore populations and maintaining ecosystem balance.
How does climate change impact the taiga food web?
Climate change can alter plant growth, disrupt predator-prey relationships, and affect the availability of resources, leading to shifts in the structure and dynamics of the taiga food web.