Natural food color, derived from nature’s bounty, is revolutionizing the food industry with its vibrant hues and wholesome appeal. Join us as we explore the world of natural food colors, their benefits, challenges, applications, and comparison to synthetic counterparts. Discover how nature’s palette enhances food products, promotes consumer well-being, and meets the growing demand for clean and sustainable ingredients.
Benefits of Using Natural Food Colors
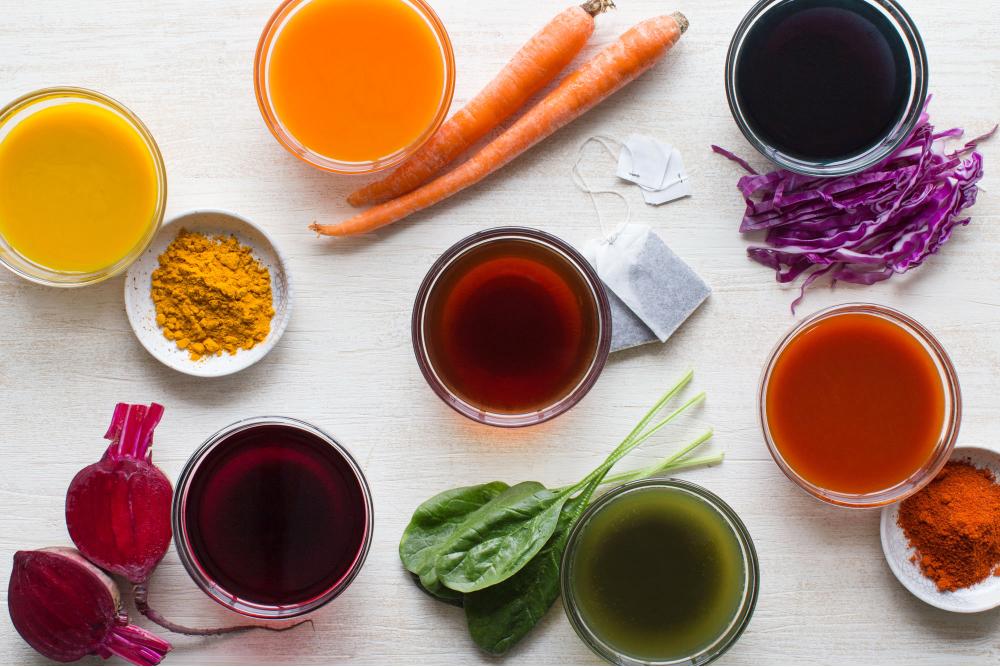

Incorporating natural food colors into food products offers a plethora of advantages over their synthetic counterparts. Not only do they enhance the visual appeal of food, but they also contribute significantly to consumer health and well-being.
Unlike synthetic food colors, which are often derived from petroleum or coal tar, natural food colors are extracted from plants, fruits, and vegetables. This makes them a more sustainable and environmentally friendly option.
Consumer Health and Well-being, Natural food color
Research suggests that natural food colors may possess health-promoting properties. For instance, anthocyanins, a type of natural food color found in berries and grapes, have been linked to reduced risk of cardiovascular disease and certain types of cancer.
Moreover, natural food colors are generally considered safe for consumption, as they are less likely to cause allergic reactions or other adverse health effects compared to synthetic food colors.
Evidence and Case Studies
A study published in the Journal of the American Dietetic Association found that consumers prefer food products made with natural food colors over those made with synthetic food colors. The study also showed that consumers are willing to pay a premium for food products that contain natural food colors.
Another study, conducted by the University of California, Davis, found that natural food colors can improve the shelf life of food products. The study showed that food products made with natural food colors had a longer shelf life than those made with synthetic food colors.
Challenges and Limitations of Natural Food Colors
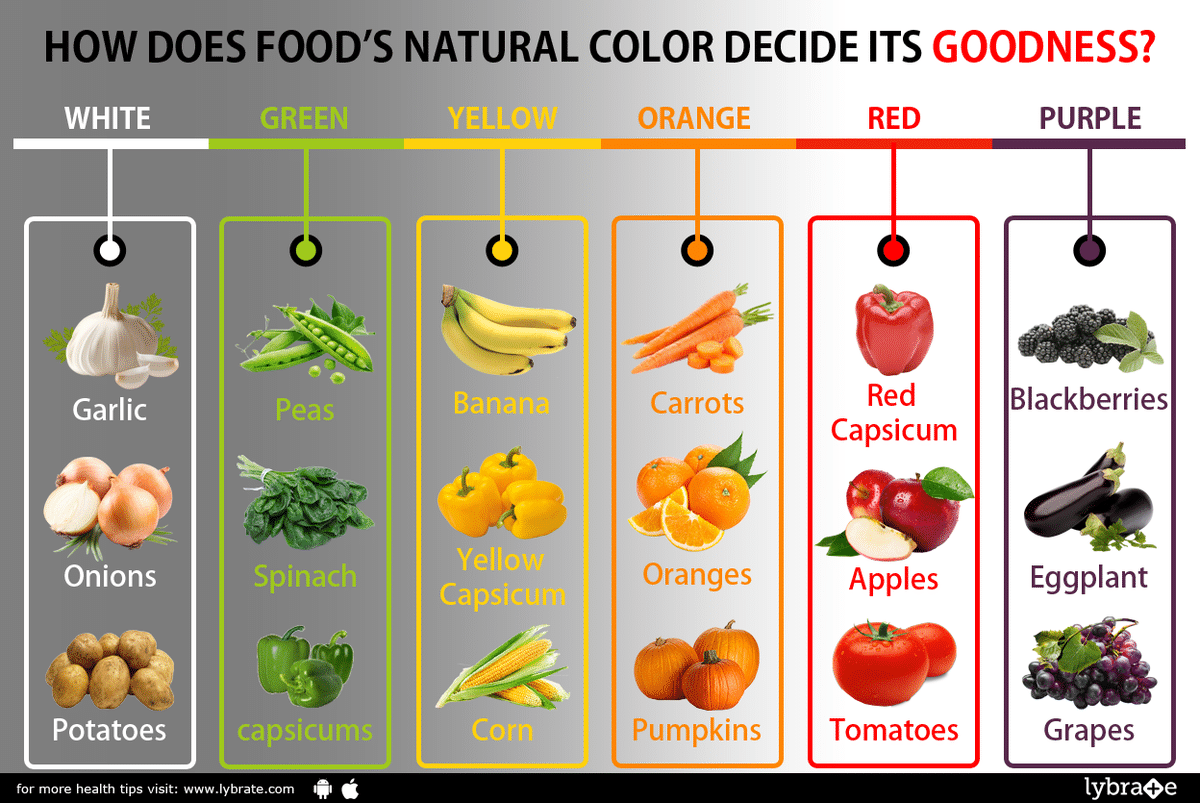
Incorporating natural food colors into food products poses several challenges and limitations. These aspects need careful consideration to ensure the desired color, stability, and cost-effectiveness.
One significant challenge lies in the stability of natural food colors. Unlike synthetic colors, which exhibit high stability under various conditions, natural colors may be susceptible to degradation caused by factors such as light, heat, pH, and enzymes. This instability can result in color fading or undesirable changes in hue over time.
Availability
Availability is another limitation associated with natural food colors. The production of natural colors often relies on specific plant or animal sources, which can be subject to seasonal variations, climatic conditions, and geographical constraints. This can lead to fluctuations in supply and potential shortages, affecting the consistency and availability of natural food colors.
Cost
Cost is a crucial factor to consider when using natural food colors. The production process for natural colors is generally more labor-intensive and requires specialized expertise compared to synthetic colors. This can result in higher production costs, which may impact the overall cost of food products.
To address these challenges, food manufacturers employ various strategies. For instance, they may utilize encapsulation techniques to improve the stability of natural colors, protecting them from degradation. Additionally, manufacturers can explore alternative natural sources or develop innovative extraction methods to enhance availability and reduce costs.
Applications of Natural Food Colors
Natural food colors are gaining popularity in the food industry due to their versatility and consumer demand for natural and clean-label products. They find applications in a wide range of food categories, enhancing the visual appeal and providing a natural alternative to synthetic colors.
The table below showcases the use of natural food colors in different food categories:
| Food Category | Natural Food Colors |
|---|---|
| Beverages | Anthocyanins (red, purple, blue), Curcumin (yellow), Chlorophyll (green) |
| Confectionery | Carotenoids (orange, yellow), Anthocyanins (red, purple), Curcumin (yellow) |
| Dairy | Beta-carotene (yellow), Annatto (orange), Turmeric (yellow) |
| Meat Products | Carmine (red), Paprika (orange, red), Beetroot (red) |
| Bakery Products | Caramel (brown), Saffron (yellow), Anthocyanins (purple, red) |
Emerging trends in the application of natural food colors include:
- Increasing use of plant-based colors derived from fruits, vegetables, and spices
- Development of new and improved extraction and processing techniques to enhance color stability and bioavailability
- Exploration of novel sources of natural colors, such as microalgae and edible flowers
Extraction and Production of Natural Food Colors
The production of natural food colors involves extracting pigments from natural sources, such as plants, animals, or minerals. These pigments are then processed and purified to obtain the desired color and stability.
Methods of Extraction
- Solvent Extraction:Using organic solvents like ethanol or hexane to dissolve and extract pigments from the source material.
- Aqueous Extraction:Employing water or aqueous solutions to extract water-soluble pigments.
- Enzymatic Extraction:Utilizing enzymes to break down plant cell walls and release pigments.
- Supercritical Fluid Extraction:Using supercritical fluids, such as carbon dioxide, to extract pigments under high pressure and temperature.
Factors Influencing Quality and Yield
- Source Material:Quality and availability of the natural source.
- Extraction Method:Efficiency and selectivity of the extraction process.
- Processing Conditions:Temperature, pH, and duration of processing can affect pigment stability.
- Storage and Handling:Proper storage conditions can preserve pigment quality and prevent degradation.
Sustainable Production
Sustainable production of natural food colors focuses on reducing environmental impact and promoting responsible practices. Challenges include:
- Resource Conservation:Minimizing the use of solvents and water in extraction processes.
- Waste Management:Proper disposal of extraction byproducts and wastewater.
- Organic Cultivation:Using organically grown source materials to avoid chemical residues.
- Fair Trade Practices:Ensuring fair compensation and working conditions for producers of natural source materials.
Opportunities for sustainability include:
- Innovative Technologies:Developing more efficient and eco-friendly extraction methods.
- Circular Economy:Utilizing byproducts from extraction processes as raw materials for other industries.
- Consumer Awareness:Promoting the use of natural food colors and educating consumers about their sustainability benefits.
Comparison with Synthetic Food Colors

Natural food colors and synthetic food colors each possess distinct characteristics and applications in the food industry. Understanding their advantages and disadvantages helps in making informed choices based on specific requirements.
Advantages of Natural Food Colors
- Consumer Preference:Consumers increasingly prefer natural ingredients over synthetic ones, leading to a growing demand for natural food colors.
- Health Concerns:Some synthetic food colors have been linked to potential health risks, while natural colors are generally considered safer.
- Regulatory Compliance:Natural food colors comply with stricter regulations and labeling requirements in many countries.
Disadvantages of Natural Food Colors
- Availability:The availability of natural food colors can be limited due to seasonal variations and sourcing challenges.
- Stability:Natural food colors may be less stable than synthetic ones, affecting their shelf life and color retention.
- Cost:Natural food colors are often more expensive than synthetic ones due to their limited availability and complex extraction processes.
Advantages of Synthetic Food Colors
- Consistency:Synthetic food colors provide consistent and vibrant hues, ensuring a standardized appearance of products.
- Stability:Synthetic food colors are highly stable, maintaining their color over a wide range of pH levels and temperatures.
- Cost-Effective:Synthetic food colors are generally less expensive than natural ones, making them a more affordable option.
Disadvantages of Synthetic Food Colors
- Health Concerns:Some synthetic food colors have been associated with potential health risks, such as allergies and hyperactivity.
- Regulatory Restrictions:The use of synthetic food colors is subject to strict regulations and labeling requirements in many countries.
- Consumer Perception:Consumers may perceive synthetic food colors as artificial and less desirable than natural ones.
Natural Food Colors and Consumer Concerns
The growing awareness of potential health risks associated with synthetic food additives has led to increased consumer demand for natural food colors. By using natural colors, manufacturers can address consumer concerns and cater to the growing preference for clean label products.
FAQ
What are the primary sources of natural food colors?
Natural food colors are derived from fruits, vegetables, plants, and minerals. Common sources include carotenoids from carrots and tomatoes, anthocyanins from berries and red cabbage, and chlorophyll from green leafy vegetables.
How do natural food colors compare to synthetic counterparts?
Natural food colors offer several advantages over synthetic colors, including their natural origin, potential health benefits, and consumer preference. Synthetic colors may have potential health concerns and can be perceived as less desirable by consumers.
What are the challenges associated with using natural food colors?
Natural food colors can be more expensive, less stable, and have limited availability compared to synthetic colors. Food manufacturers address these challenges through careful sourcing, extraction methods, and innovative formulations.
