The sweet potato food label holds a wealth of information that can empower you to make informed dietary choices. Dive into this comprehensive guide to decipher the nutritional content, cooking methods, and culinary versatility of this beloved root vegetable.
Sweet potatoes, a nutritional powerhouse, offer a rich source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. They rank among the top sources of vitamin A, providing an exceptional 438% of the daily recommended intake in a single serving.
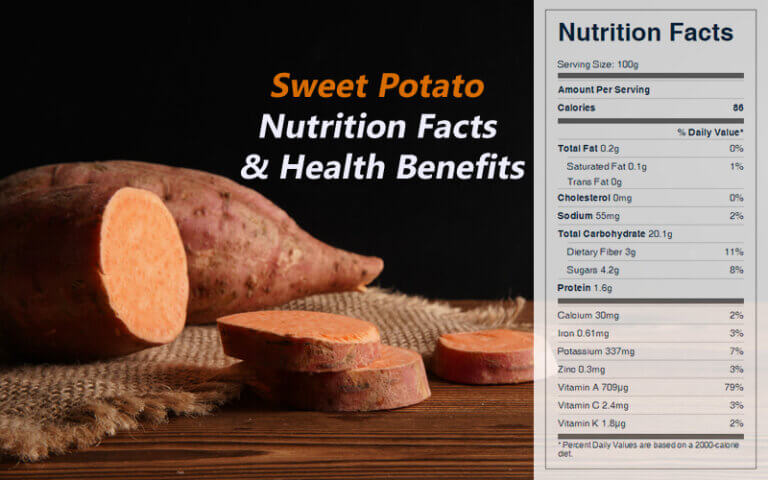
Nutritional Information

Sweet potatoes are a nutrient-rich root vegetable that offers a wide range of health benefits. They are a good source of calories, providing approximately 100 calories per 100 grams. They are also a good source of macronutrients, including carbohydrates, protein, and fiber.
Vitamins and Minerals
Sweet potatoes are an excellent source of vitamins and minerals, including vitamin A, vitamin C, potassium, and manganese. Vitamin A is essential for vision, immune function, and cell growth. Vitamin C is an antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage.
Potassium is an electrolyte that helps regulate blood pressure and muscle function. Manganese is a mineral that is involved in bone formation and metabolism.
Health Benefits, Sweet potato food label
The nutritional content of sweet potatoes contributes to a number of potential health benefits. Vitamin A helps protect against night blindness and other eye problems. Vitamin C helps boost the immune system and protect against infection. Potassium helps regulate blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Manganese helps promote bone health and reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
Comparison to Other Root Vegetables
Sweet potatoes compare favorably to other root vegetables in terms of nutritional value. They are a good source of calories, macronutrients, vitamins, and minerals. Compared to carrots, sweet potatoes have a higher content of vitamin A and potassium. Compared to beets, sweet potatoes have a higher content of vitamin C and fiber.
Food Label Analysis
Food labels provide crucial information about the nutritional content of packaged foods, enabling consumers to make informed dietary choices. Let’s delve into the components of a food label and explore how to interpret it effectively.
Sample Food Label
Consider a packaged sweet potato product with the following food label:
- Serving Size:1 medium potato (130g)
- Calories:100
- Total Fat:0g (0% DV)
- Saturated Fat:0g (0% DV)
- Cholesterol:0mg (0% DV)
- Sodium:0mg (0% DV)
- Total Carbohydrates:23g (8% DV)
- Dietary Fiber:3g (12% DV)
- Sugars:10g
- Protein:2g
- Vitamin A:10% DV
- Vitamin C:15% DV
Serving Size
The serving size indicates the recommended amount of food to consume in one serving. It is essential to note that this amount may not align with your actual portion size, so it’s crucial to be mindful of how much you’re eating.
Calorie Content
The calorie content represents the amount of energy provided by one serving of the food. It’s important to consider your daily calorie needs and adjust your intake accordingly.
Ingredient List
The ingredient list lists all the ingredients used in the product, in descending order of their quantity. This information can be helpful for individuals with allergies or specific dietary preferences.
Cooking Methods
Sweet potatoes offer versatility in the kitchen, with numerous cooking methods to choose from. Each method imparts unique flavors and textures, influencing the nutritional value of the dish.
Baking
Baking is a classic method that caramelizes the sugars in sweet potatoes, resulting in a tender and flavorful interior. Preheat your oven to 400°F (200°C). Scrub the potatoes clean, pierce them with a fork, and wrap them in foil. Bake for 45-60 minutes, or until tender when pierced with a fork.
Roasting
Roasting is another excellent method for achieving a crispy exterior and tender interior. Preheat your oven to 425°F (220°C). Cut the potatoes into wedges or cubes, toss them with olive oil, salt, and pepper, and spread them on a baking sheet.
Roast for 25-30 minutes, or until golden brown and tender.
Microwaving
Microwaving is a convenient method for quick and easy cooking. Scrub the potatoes clean and pierce them with a fork. Place them in a microwave-safe bowl with a splash of water. Microwave on high for 5-7 minutes per potato, or until tender when pierced with a fork.
Sweet Potato Varieties
The diverse world of sweet potatoes encompasses a captivating array of varieties, each boasting unique characteristics that enhance culinary experiences. These varieties differ in appearance, texture, and flavor profiles, influencing their suitability for various cooking methods and culinary applications.
Understanding the distinct attributes of each variety empowers home cooks and culinary professionals alike to optimize their culinary creations, unlocking the full potential of this versatile vegetable.
Appearance, Texture, and Flavor Profiles
The visual appeal of sweet potatoes varies significantly across varieties. Some possess a smooth, uniform skin, while others exhibit a rough, bumpy texture. The flesh of sweet potatoes can range from pale yellow to deep orange, with variations in intensity and vibrancy.
The texture of sweet potatoes also varies considerably. Certain varieties offer a firm, dense texture, while others are known for their soft, creamy consistency. The flavor profiles of sweet potatoes span a wide spectrum, encompassing sweet, earthy, and nutty notes.
The following table provides a comprehensive comparison of the key characteristics of different sweet potato varieties:
| Variety | Appearance | Texture | Flavor Profile |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beauregard | Deep orange skin, smooth texture | Firm, dense | Sweet, earthy |
| Garnet | Dark red skin, rough texture | Firm, dry | Sweet, nutty |
| Jewel | Light orange skin, smooth texture | Soft, moist | Sweet, slightly tart |
| Stokes Purple | Purple skin, white flesh | Soft, creamy | Sweet, earthy |
Influence on Cooking Methods and Culinary Applications
The unique characteristics of each sweet potato variety directly influence the most suitable cooking methods and culinary applications. Firm varieties, such as Beauregard, hold their shape well during roasting and baking, making them ideal for dishes that require a crisp exterior and tender interior.
Soft varieties, such as Jewel, are better suited for boiling and mashing, as their creamy texture lends itself to smooth, velvety preparations. The sweet flavor of certain varieties, like Stokes Purple, complements desserts and sweet dishes, while the earthy notes of others, like Garnet, enhance savory preparations.
Examples of Dishes that Showcase Unique Characteristics
- Beauregard:Roasted sweet potato wedges with a crispy exterior and fluffy interior
- Garnet:Sweet potato fries with a nutty flavor and crispy texture
- Jewel:Creamy sweet potato soup with a smooth, velvety texture
- Stokes Purple:Sweet potato pie with a vibrant purple hue and earthy sweetness
Culinary Applications: Sweet Potato Food Label

Sweet potatoes offer a culinary canvas that invites creativity and experimentation. Their versatility extends from savory to sweet dishes, making them a welcome addition to diverse cuisines.
From hearty soups and stews to tantalizing desserts, sweet potatoes seamlessly integrate into a myriad of culinary creations. Their ability to absorb flavors makes them an ideal companion for various herbs, spices, and sauces.
Savory Dishes
In the realm of savory dishes, sweet potatoes shine as a delectable ingredient. Whether roasted, mashed, or sautéed, they add a touch of sweetness and a vibrant hue to soups, stews, and casseroles. Their earthy flavor complements grilled meats, poultry, and fish, while their soft texture provides a comforting base for sauces and gravies.
- Roasted Sweet Potato Soup:A comforting and flavorful soup that combines roasted sweet potatoes, onions, garlic, and vegetable broth. Topped with crispy croutons or a drizzle of olive oil.
- Sweet Potato and Black Bean Tacos:A vibrant and flavorful taco filling made with mashed sweet potatoes, black beans, corn, onions, and spices. Served on warm tortillas with your favorite toppings.
- Sweet Potato and Lentil Curry:A hearty and satisfying curry that combines sweet potatoes, lentils, onions, tomatoes, and a blend of Indian spices. Served over rice or with naan bread.
Sweet Dishes
In the world of sweet treats, sweet potatoes take center stage as a delectable ingredient. Their natural sweetness and smooth texture make them a perfect choice for pies, cakes, and cookies. They can be paired with spices like cinnamon and nutmeg, or with fruits like apples and cranberries, to create a symphony of flavors.
- Sweet Potato Pie:A classic dessert that features a creamy sweet potato filling baked in a flaky crust. Topped with whipped cream or a dollop of ice cream.
- Sweet Potato Brownies:A fudgy and decadent brownie that incorporates sweet potatoes for a moist and flavorful texture. Studded with chocolate chips or nuts for added indulgence.
- Sweet Potato and Apple Muffins:A wholesome and comforting muffin that combines sweet potatoes, apples, cinnamon, and nutmeg. Perfect for breakfast or as a sweet snack.
Storage and Preservation
To maintain the quality and nutritional value of sweet potatoes, proper storage and preservation methods are crucial. This section will provide insights into effective storage techniques for both fresh and cooked sweet potatoes, along with tips on extending their shelf life and identifying spoilage indicators.
Fresh Sweet Potatoes
Fresh sweet potatoes should be stored in a cool, dark, and well-ventilated area. The ideal temperature range is between 55-60°F (13-16°C) with a relative humidity of 85-90%. Avoid storing sweet potatoes in direct sunlight or near heat sources, as this can accelerate spoilage.
Cooked Sweet Potatoes
Cooked sweet potatoes can be stored in the refrigerator for up to 3-4 days. Allow them to cool completely before placing them in an airtight container. For longer storage, cooked sweet potatoes can be frozen for up to 6 months.
Wrap them tightly in aluminum foil or freezer-safe bags to prevent freezer burn.
Extending Shelf Life
- Refrigeration:Refrigeration can extend the shelf life of fresh sweet potatoes for up to 2-3 weeks.
- Freezing:Freezing is an effective method for preserving sweet potatoes for up to 6 months.
- Canning:Canning is a traditional method of preserving sweet potatoes that involves sealing them in airtight jars and processing them in a boiling water bath.
Spoilage Indicators
Spoiled sweet potatoes may exhibit the following indicators:
- Soft, mushy, or wrinkled texture
- Discoloration or dark spots
- Mold growth
- Sour or unpleasant odor
If any of these signs are present, the sweet potatoes should be discarded immediately.
Question Bank
What are the key nutrients found in sweet potatoes?
Sweet potatoes are rich in vitamin A, vitamin C, potassium, and fiber.
How can I cook sweet potatoes to retain their nutritional value?
Baking or roasting sweet potatoes with the skin on helps preserve their nutrients.
What are some creative ways to incorporate sweet potatoes into my diet?
Sweet potatoes can be used in a variety of dishes, from savory casseroles to sweet pies.
