As A Foods takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with expertise and passion, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original. A Foods invites you to embark on a culinary journey that delves into the diverse and fascinating world of food.
From the nutritional value of different food types to the cultural significance of various cuisines, A Foods provides a comprehensive exploration of the many facets of food. This captivating guide offers insights into food production, preparation, consumption, and the ever-evolving food industry.
Food Industry
The food industry encompasses a vast and intricate network of businesses involved in the production, processing, distribution, and sale of food products. Major players in the industry include multinational corporations, small-scale farmers, and everything in between.
The food industry is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and regulatory shifts. These trends have a significant impact on the way food is produced, distributed, and consumed.
Technology
Technology has revolutionized the food industry in numerous ways. From precision agriculture to automated food processing, technology has improved efficiency, reduced costs, and increased food safety.
- Precision agricultureuses data and technology to optimize crop production, reducing the need for pesticides and fertilizers.
- Automated food processinghas increased efficiency and reduced the risk of contamination.
- Blockchain technologyis being used to track food products throughout the supply chain, improving transparency and traceability.
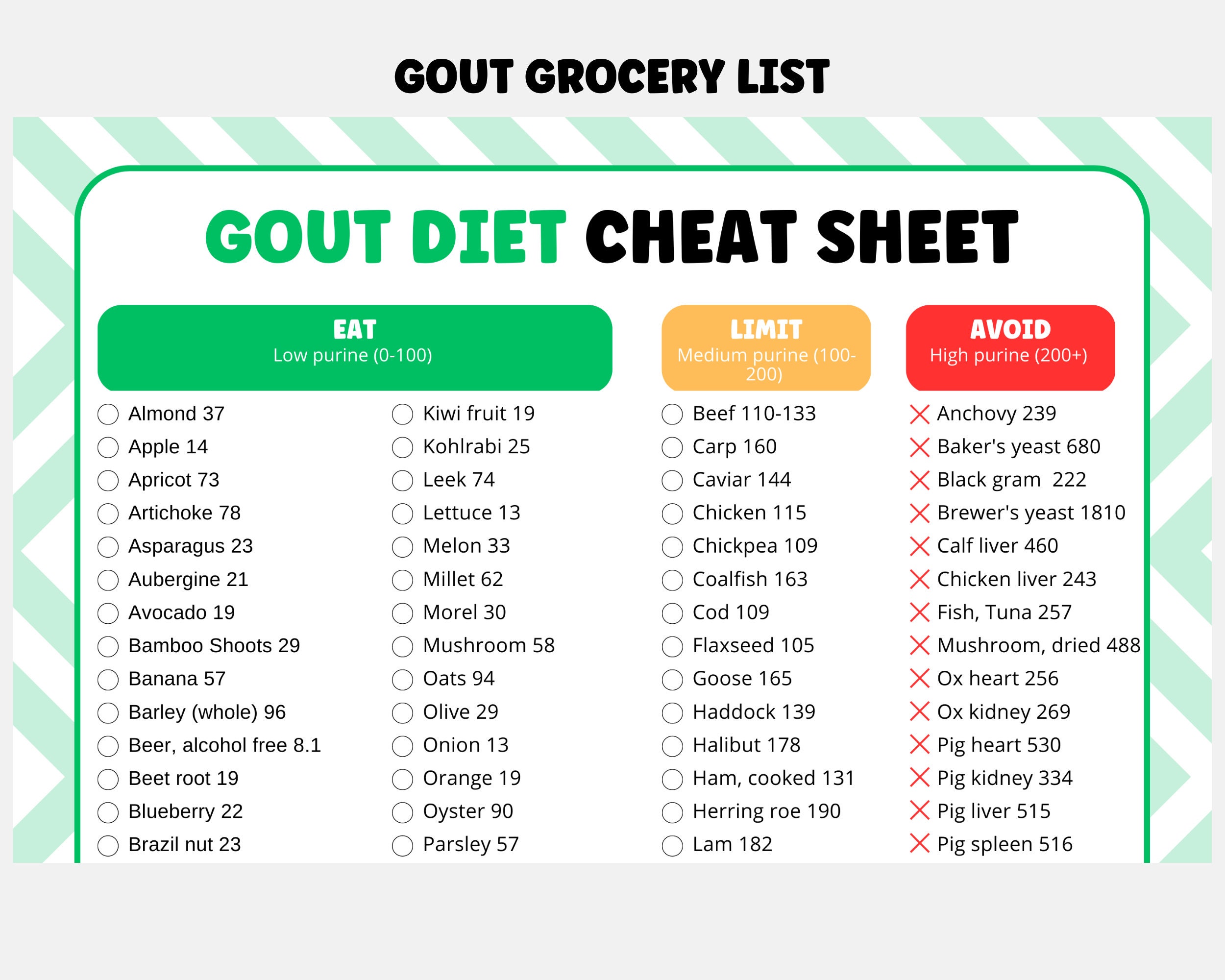
Ethics and Regulations, A foods
The food industry is heavily regulated to ensure food safety and quality. These regulations cover everything from food production to packaging and labeling.
- Food safety regulationsare designed to prevent foodborne illnesses and protect consumers.
- Environmental regulationsaim to minimize the environmental impact of food production.
- Consumer protection regulationsensure that consumers are provided with accurate information about food products.
Food Innovations

The food industry is constantly evolving, with new products and technologies emerging to meet the ever-changing needs of consumers. These innovations are driven by a number of factors, including the growing demand for healthy and convenient food, the increasing popularity of online grocery shopping, and the need to reduce food waste.
One of the most important areas of food innovation is the development of new food products that are healthier and more nutritious. This includes products that are low in fat, sugar, and sodium, as well as products that are fortified with vitamins and minerals.
These products are becoming increasingly popular as consumers become more aware of the importance of healthy eating.
Food Science and Biotechnology
Food science and biotechnology are playing a major role in the development of new food products and technologies. These disciplines allow scientists to understand the chemical and physical properties of food, and to develop new ways to process and preserve food.
This has led to the development of a number of innovative food products, such as shelf-stable milk, low-fat cheese, and fortified cereals.
Artificial Intelligence and Data Analytics
Artificial intelligence (AI) and data analytics are also having a major impact on the food industry. These technologies can be used to track consumer trends, identify new opportunities for product development, and optimize supply chains. For example, AI can be used to analyze data from online grocery shopping to identify which products are most popular, and to predict future demand.
This information can then be used to develop new products and marketing campaigns.
Food Waste and Sustainability: A Foods
Food waste is a global problem that has severe environmental and economic consequences. Approximately one-third of all food produced is wasted, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions, water scarcity, and soil degradation. Reducing food waste is crucial for creating a more sustainable and equitable food system.
Causes and Consequences of Food Waste
Food waste occurs at various stages of the food supply chain, including production, processing, distribution, retail, and consumption. Causes of food waste include:
Overproduction
Farmers may produce more food than is demanded, leading to surpluses that are often discarded.
Inefficient storage and transportation
Poor handling and inadequate storage conditions can damage food, making it unsafe or unappealing for consumption.
Consumer behavior
Consumers often purchase more food than they need, leading to spoilage and waste.
Query Resolution
What are the different types of food?
A Foods categorizes food into various types based on their nutritional composition, including carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals.
How is food produced?
A Foods explores the diverse methods of food production, such as farming, ranching, fishing, and aquaculture, highlighting the environmental impact and sustainable practices associated with each.
What are the key factors influencing food consumption?
A Foods analyzes the dietary habits and nutritional needs of different population groups, considering social, cultural, and economic factors that shape food consumption patterns.
