Welcome to the fascinating world of food web maker, where we delve into the intricate tapestry of ecological relationships that shape the natural world. A food web maker is an indispensable tool for ecologists, educators, and anyone curious about the interconnectedness of species within an ecosystem.
Food webs are complex networks that depict the feeding relationships between organisms in a community. They provide insights into the flow of energy and nutrients, the stability of ecosystems, and the impact of human activities on the environment.
Food Web Dynamics
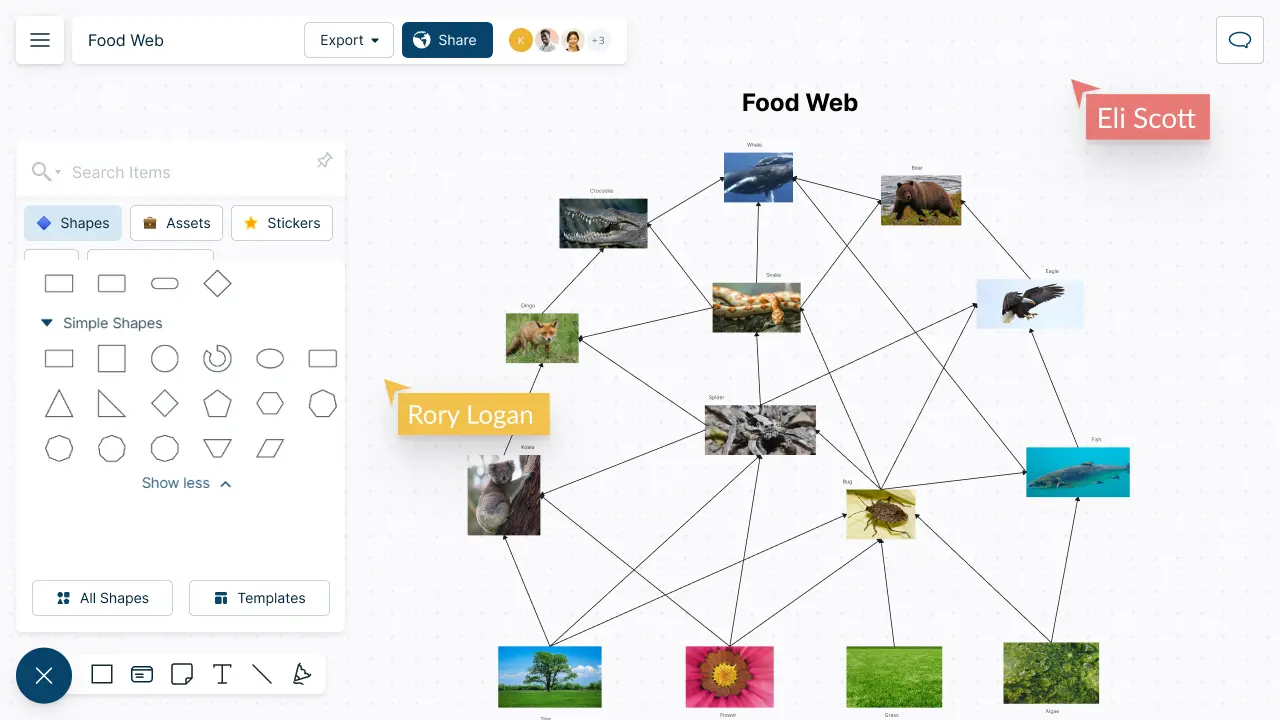
Food webs are intricate networks of interconnected food chains that illustrate the feeding relationships within an ecosystem. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for comprehending the stability and resilience of ecological communities.
Role of Producers, Consumers, and Decomposers
In a food web, producers (typically plants) utilize sunlight and nutrients to create organic matter through photosynthesis. Primary consumers (herbivores) feed on producers, while secondary consumers (carnivores) feed on primary consumers. Higher-level consumers may exist, forming complex food chains. Decomposers (such as bacteria and fungi) break down dead organisms, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycling, Food web maker
Energy flows unidirectionally through a food web, from producers to consumers and ultimately to decomposers. At each trophic level, approximately 10% of the energy is transferred to the next, resulting in an energy pyramid. Nutrients, on the other hand, are recycled within the ecosystem through decomposition and waste products, maintaining the availability of essential elements for life.
Effects of Disturbances
Disturbances, such as species introductions or extinctions, can significantly impact food web dynamics. Invasive species may compete with native species for resources, alter food chains, and disrupt nutrient cycling. Extinctions can lead to trophic cascades, where the loss of a species affects multiple other species within the food web.
Food Web Representation: Food Web Maker
Food webs are complex networks that depict the feeding relationships among species within an ecosystem. To understand and analyze these intricate systems, scientists employ various representation methods, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Diagrams
Diagrams are the most intuitive and commonly used method for visualizing food webs. They represent species as nodes connected by arrows that indicate the direction of energy flow. Diagrams provide a clear overview of the structure and connectivity of the food web, allowing for easy identification of key species and trophic levels.
However, diagrams can become cluttered and difficult to interpret when the food web contains numerous species. Additionally, they may not accurately reflect the strength or frequency of interactions between species.
Matrices
Matrices are tabular representations of food webs, where species are listed in rows and columns. The cells of the matrix indicate the presence or absence of a feeding relationship between the corresponding species. Matrices are concise and provide a comprehensive view of the food web’s structure.
However, matrices can be challenging to interpret, especially for large food webs. They also do not provide information about the strength or frequency of interactions.
Mathematical Models
Mathematical models use mathematical equations to represent the dynamics of food webs. These models can simulate the flow of energy and nutrients through the system, allowing for predictions about the effects of disturbances or changes in environmental conditions.
Mathematical models are powerful tools for analyzing complex food webs. However, they require detailed data and can be computationally intensive. Additionally, their accuracy depends on the assumptions and simplifications made in the model.
The choice of representation method depends on the specific research question and the availability of data. Diagrams are suitable for visualizing the structure of small to medium-sized food webs. Matrices provide a comprehensive view of the food web’s structure but may be challenging to interpret.
Mathematical models are powerful tools for analyzing complex food webs but require detailed data and computational resources.
Food Web Tools and Resources
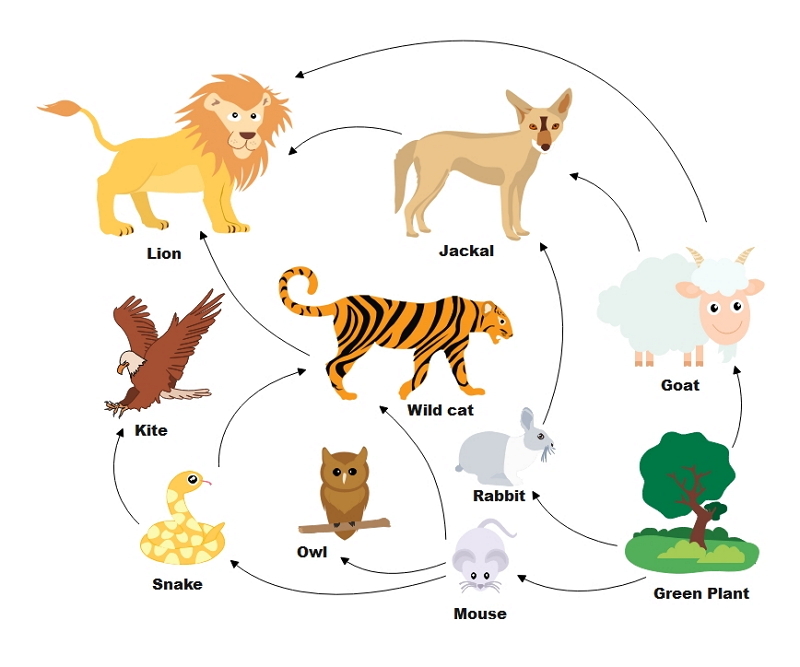
The analysis and construction of food webs have been greatly aided by the availability of a range of computational tools and resources. These tools provide a variety of features and capabilities that can assist researchers in various fields, including ecology, conservation, and agriculture.
Available Tools and Resources
Numerous software programs and online platforms are available for creating and analyzing food webs. Some of the most commonly used tools include:
- Food Web Builder (FWB): A user-friendly software program that allows users to create and visualize food webs, calculate food web metrics, and perform simulations.
- EcoWeb: An online platform that provides a comprehensive suite of tools for food web analysis, including network visualization, metric calculation, and statistical analysis.
- Network3D: A software program that allows users to create and visualize 3D food webs, providing a more immersive and interactive experience.
Features and Capabilities
These tools offer a wide range of features and capabilities that can enhance the process of food web analysis. These features include:
- Data import and export:Tools allow users to import data from various sources, such as field surveys, literature databases, and online repositories.
- Food web visualization:Tools provide options for visualizing food webs in various formats, including network diagrams, matrices, and 3D representations.
- Food web metrics calculation:Tools can calculate a variety of food web metrics, such as connectance, trophic levels, and species richness, which provide insights into the structure and dynamics of food webs.
- Simulation and modeling:Some tools allow users to simulate and model food web dynamics, which can help predict the effects of disturbances or changes in environmental conditions.
Applications in Various Fields
Food web tools and resources have found applications in a variety of fields, including:
- Ecology:Food web analysis can help ecologists understand the structure and function of ecosystems, identify key species, and assess the impacts of environmental changes.
- Conservation:Food web tools can be used to identify vulnerable species and ecosystems, prioritize conservation efforts, and develop management strategies.
- Agriculture:Food web analysis can help agricultural scientists understand the dynamics of pest and beneficial species, develop integrated pest management strategies, and improve crop yields.
FAQ Compilation
What is a food web?
A food web is a graphical representation of the feeding relationships between multiple species in an ecosystem.
What are the different types of food web structures?
Food webs can vary in complexity, from linear chains to intricate networks with multiple trophic levels and interconnected species.
How do food webs help us understand ecosystems?
Food webs provide insights into the flow of energy and nutrients, the stability of ecosystems, and the potential impacts of disturbances.
What tools are available for creating and analyzing food webs?
Various software and online platforms offer tools for constructing, visualizing, and analyzing food webs.
