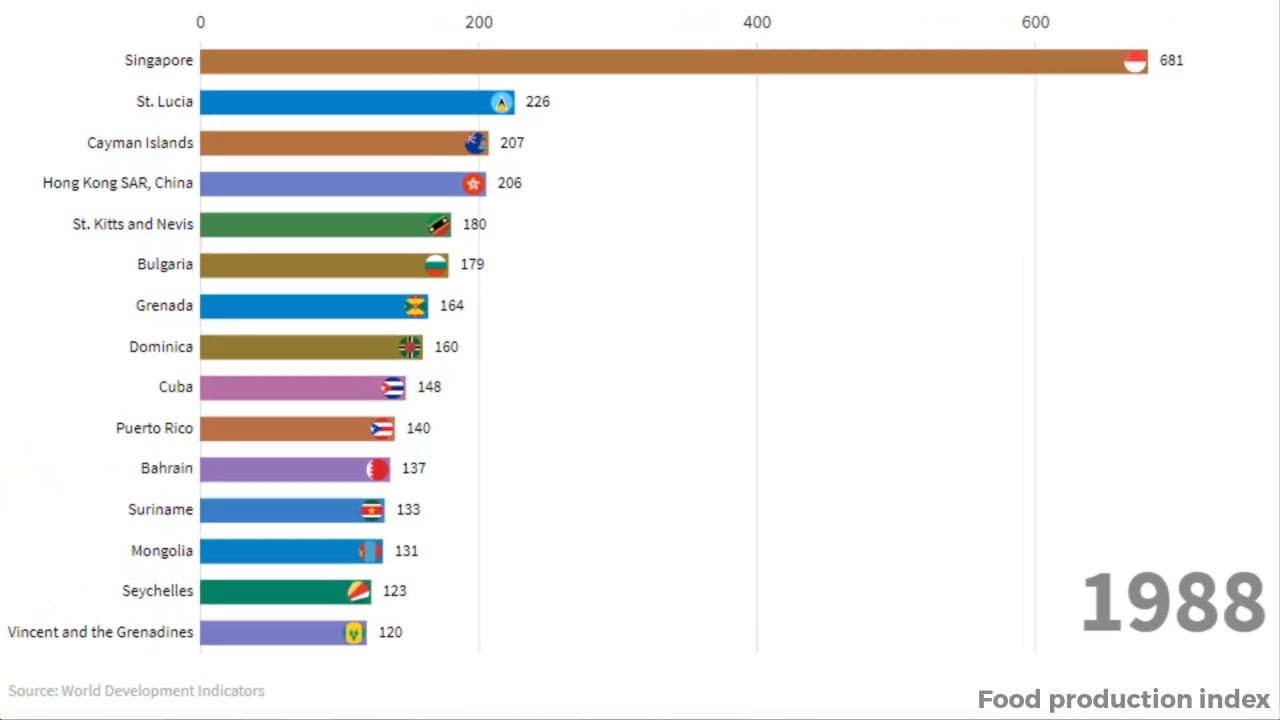
Food production index explained: a comprehensive overview of the index that measures the global food supply, its components, and its significance in understanding food security and global food systems.
The Food Production Index (FPI) is a crucial indicator of the world’s food supply, providing insights into production trends, factors influencing food availability, and the challenges and opportunities in ensuring global food security.
Food Production Index Definition and Overview
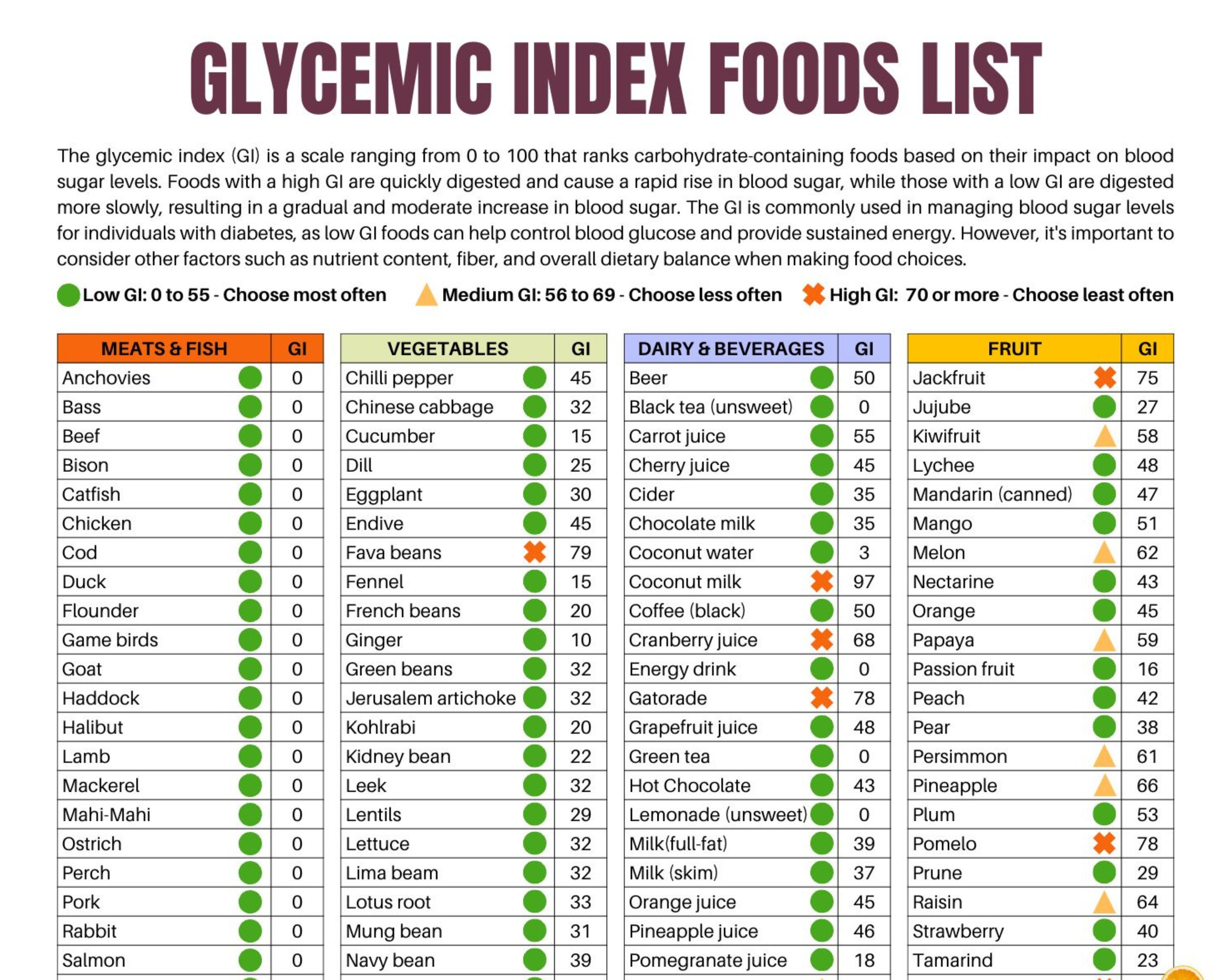
The Food Production Index (FPI) is a measure of the physical volume of agricultural production. It tracks changes in the output of crops and livestock over time. The FPI is an important indicator of the performance of the agricultural sector and can be used to assess food security and inflation risks.
The FPI is calculated by dividing the current volume of agricultural production by the volume of production in a base year and multiplying the result by 100. The base year is typically set to a year when agricultural production was relatively stable.
This allows for easy comparison of production levels over time.
Purpose and Significance
The FPI is used by governments, businesses, and investors to make informed decisions about food production and consumption. It can be used to:
- Assess the performance of the agricultural sector
- Identify trends in food production
- Forecast future food prices
- Make decisions about food imports and exports
- Develop policies to support the agricultural sector
Components and Calculation of the FPI
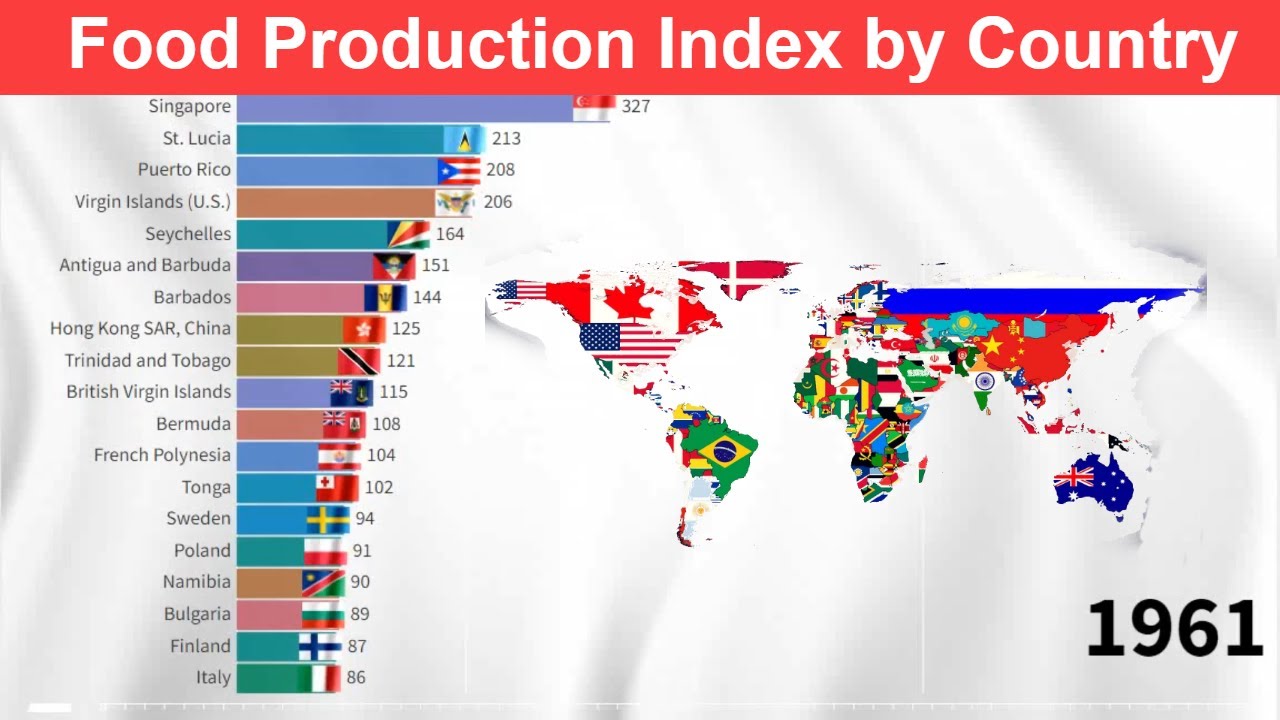
The Food Production Index (FPI) is a composite indicator that measures the changes in the volume of food production. It is calculated using a combination of data on crop production, livestock production, and fisheries production.
The FPI is calculated using a Laspeyres index formula, which means that the weights used to aggregate the individual components are fixed over time. The base period for the FPI is 2004-2006, and the index is published monthly by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations.
Data Sources, Food production index explained
The data used to calculate the FPI come from a variety of sources, including national statistical offices, international organizations, and private sector companies. The FAO collects and harmonizes this data to ensure that it is consistent and comparable across countries and over time.
Methodology
The FPI is calculated by first calculating a production index for each of the three main components: crop production, livestock production, and fisheries production. These component indices are then aggregated using fixed weights to produce the overall FPI.
The weights used to aggregate the component indices are based on the average share of each component in total food production during the base period. For example, if crop production accounted for 60% of total food production during the base period, then the weight for the crop production index would be 0.6.
Example
The following table shows an example of how the FPI is calculated.
| Component | Weight | Production Index ||—|—|—|| Crop production | 0.6 | 105 || Livestock production | 0.3 | 110 || Fisheries production | 0.1 | 120 |
The overall FPI for this example would be calculated as follows:
“`FPI = (0.6
- 105) + (0.3
- 110) + (0.1
- 120) = 107.7
“`
Q&A: Food Production Index Explained
What is the Food Production Index?
The Food Production Index (FPI) is a measure of the global food supply, calculated based on the production of major food commodities such as cereals, meat, and dairy products.
How is the FPI calculated?
The FPI is calculated using data on production, population, and trade of major food commodities, weighted by their nutritional value and importance in global food systems.
What factors influence the FPI?
The FPI is influenced by various factors, including weather conditions, technological advancements, economic conditions, and government policies.