As food colors take center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world of vibrant hues and delectable delights, where the interplay of science, art, and consumer preferences shapes the visual appeal of our culinary creations.
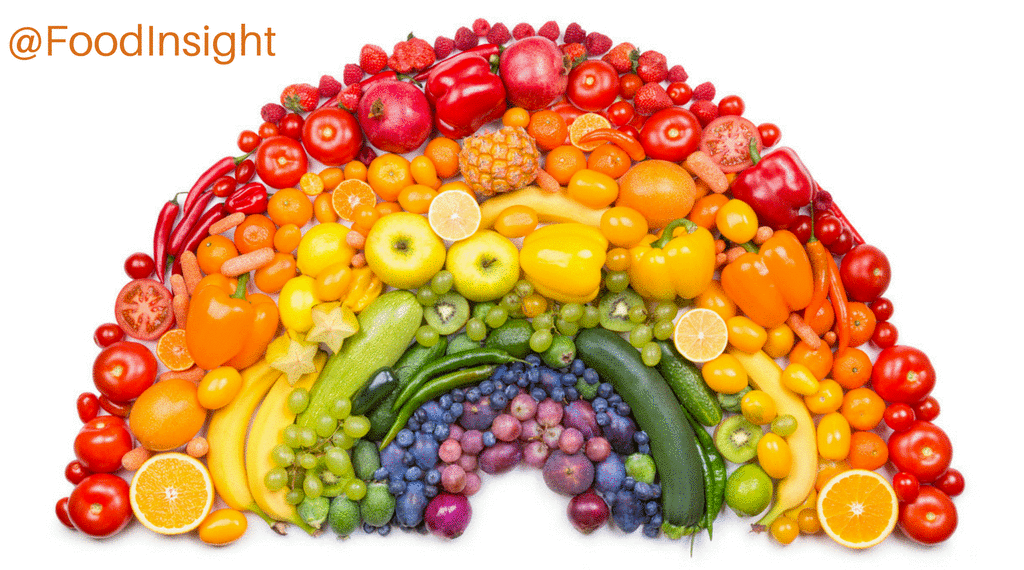
From the vibrant reds of tomatoes to the verdant greens of spinach, food colors have long played a captivating role in our culinary experiences. Whether natural or artificial, these pigments not only enhance the visual appeal of our meals but also impact our perceptions, preferences, and even our health.
Natural Food Colors
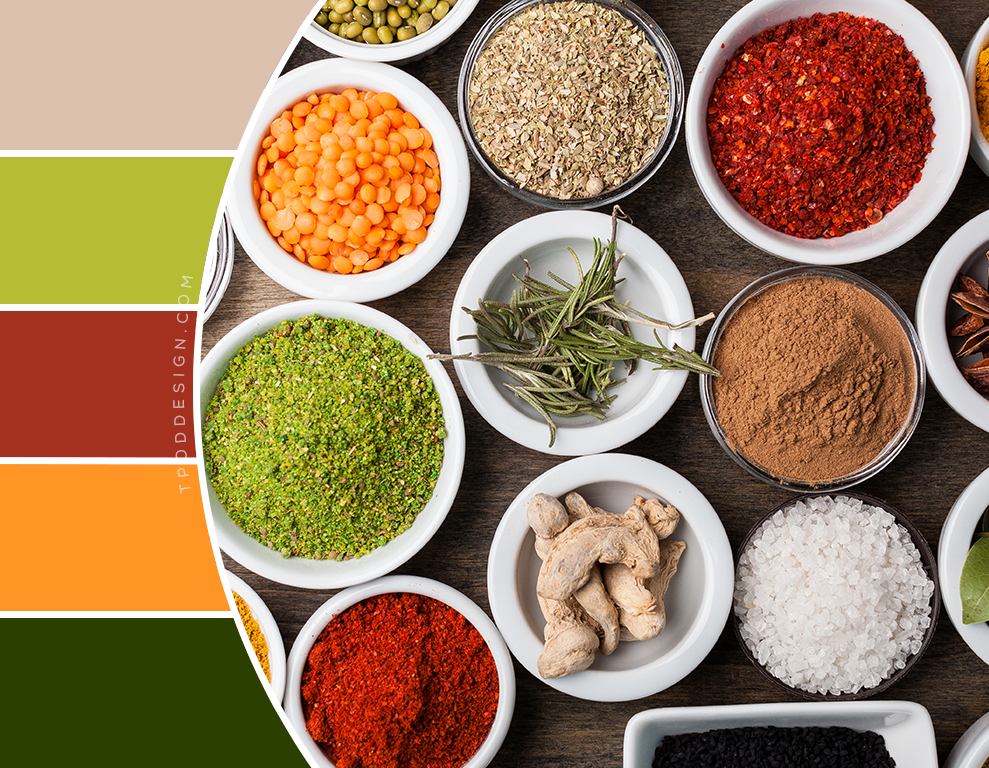

Natural food colors are derived from plants, animals, or minerals and have been used for centuries to enhance the visual appeal of food and beverages. They are generally considered safer and healthier than artificial food colors, as they do not contain synthetic chemicals that may pose health risks.
Sources and Chemical Structures
- Carotenoids: Found in fruits, vegetables, and algae, carotenoids are responsible for yellow, orange, and red colors. They include beta-carotene, lycopene, and astaxanthin.
- Anthocyanins: Found in berries, grapes, and red cabbage, anthocyanins produce red, purple, and blue colors. They are sensitive to pH and can change color depending on the acidity of the food.
- Chlorophyll: Found in green plants, chlorophyll is a green pigment that absorbs blue and red light. It is often used as a natural food coloring in products like spinach pasta and green tea.
- Betalains: Found in beets and Swiss chard, betalains produce red, pink, and purple colors. They are stable over a wide pH range and heat-resistant.
- Curcumin: Found in turmeric, curcumin is a yellow pigment that has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of natural food colors:
- Generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by regulatory agencies
- May have health benefits due to their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties
- Consumers perceive them as healthier and more natural
Disadvantages of natural food colors:
- Can be more expensive than artificial food colors
- May not be as stable or resistant to light, heat, or pH changes
- Can have a limited color range compared to artificial food colors
Regulatory Aspects, Food colors
The use of natural food colors is regulated by various government agencies around the world. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approves and monitors the use of food colors, including both natural and artificial ones. Natural food colors must meet certain safety and purity standards to be approved for use in food.
Applications in the Food Industry
Natural food colors are widely used in the food industry to enhance the appearance of a variety of products, including:
- Beverages (fruit juices, sports drinks, sodas)
- Confectionery (candy, chocolate, ice cream)
- Dairy products (yogurt, cheese, milk)
- Processed foods (sauces, soups, snacks)
- Baked goods (breads, pastries, cakes)
Artificial Food Colors

Artificial food colors are synthetic dyes used to enhance the appearance of food and beverages. They are derived from petroleum or coal tar and have been widely used in the food industry for decades.
Commonly Used Artificial Food Colors
| Color | Chemical Structure | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Red 40 | Candy, soft drinks, baked goods | |
| Yellow 5 | Candy, pudding, cheese | |
| Blue 1 | Sports drinks, candy, ice cream | |
| Green 3 | Candy, pickles, olives | |
| Orange B | Orange juice, candy, baked goods |
Potential Health Concerns
The use of artificial food colors has raised concerns about potential health risks. Some studies have suggested that certain artificial colors may be linked to hyperactivity, allergies, and even cancer. However, the evidence is inconclusive, and the safety of artificial food colors remains a subject of ongoing debate.
Impact on Consumer Behavior
Artificial food colors have a significant impact on consumer behavior. They make food appear more appealing and desirable, which can lead to increased consumption. This can have both positive and negative consequences. On the one hand, it can encourage people to eat more fruits and vegetables that have been artificially colored.
On the other hand, it can also contribute to overconsumption of unhealthy foods that are high in sugar and calories.
Food Color Measurement: Food Colors
Food color measurement is a crucial aspect of the food industry, as it helps ensure product quality, consistency, and consumer appeal. Several methods are employed to measure food color, including spectrophotometry and colorimetry.
Spectrophotometry
Spectrophotometry is a technique that measures the amount of light absorbed or reflected by a sample at specific wavelengths. In food color measurement, a spectrophotometer is used to analyze the light spectrum of a food sample and determine its color characteristics.
The spectrophotometer generates a graph known as a “spectral curve,” which shows the absorbance or reflectance of the sample at different wavelengths. This curve provides detailed information about the sample’s color, including its hue, saturation, and lightness.
Colorimetry
Colorimetry is another technique used to measure food color. Unlike spectrophotometry, which measures the entire light spectrum, colorimetry focuses on specific color coordinates, such as L* (lightness), a* (redness-greenness), and b* (yellowness-blueness).
A colorimeter measures these coordinates by comparing the sample’s color to a standard reference. The resulting values are used to calculate the sample’s color in the L*a*b* color space, providing a quantitative representation of its color.
Importance of Color Measurement
Color measurement plays a vital role in the food industry, serving various purposes:
- Quality Control:Color is an indicator of food quality. By measuring color, manufacturers can ensure that products meet desired specifications and reject batches that do not conform.
- Consistency:Color consistency is essential for maintaining brand identity and consumer expectations. Color measurement helps manufacturers maintain consistent color across different batches and production lines.
- Consumer Appeal:Color is a key factor in consumer perception of food. By measuring color, manufacturers can optimize the appearance of their products to enhance their appeal to consumers.
Challenges and Emerging Technologies
Food color measurement faces several challenges, including:
- Sample Variability:Natural food products exhibit variability in color due to factors such as growing conditions and processing methods.
- Environmental Factors:Lighting conditions and temperature can affect color measurements.
- Human Subjectivity:Visual assessment of color can be subjective and inconsistent.
To address these challenges, emerging technologies are being developed to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of food color measurement. These include:
- Hyperspectral Imaging:This technique captures a wide range of wavelengths, providing more detailed spectral information.
- Computer Vision:Machine learning algorithms are used to analyze images and extract color information.
- Portable Colorimeters:These handheld devices allow for on-site color measurements.
Food Color Design
Food color design is a crucial aspect of food product development, influencing consumer preferences and enhancing the visual appeal of food items. It encompasses the principles of color theory, color harmony, and color psychology.
Color Theory and Color Harmony
Color theory provides the foundation for understanding how colors interact and create visual effects. The color wheel, a circular representation of the primary, secondary, and tertiary colors, serves as a guide for creating harmonious color combinations. Complementary colors, located opposite each other on the color wheel, create striking contrasts, while analogous colors, adjacent to each other, produce a cohesive and visually pleasing effect.
Color Psychology and Food Color Design
Color psychology explores the emotional and psychological associations evoked by different colors. Warm colors, such as red, orange, and yellow, are known to stimulate appetite and evoke feelings of warmth and energy. Cool colors, such as blue, green, and purple, have a calming effect and are often associated with freshness and health.
Food Color Design in Branding and Packaging
Food color plays a significant role in branding and packaging design. It helps establish brand recognition and differentiate products in the marketplace. Colors can convey the brand’s personality, values, and target audience. For example, green is often used to convey freshness and health, while red is associated with boldness and excitement.
Food Color Trends
The food industry is constantly evolving, and with it, the trends in food color usage. In recent years, there has been a growing demand for natural and sustainable colors, as consumers become more aware of the potential health risks associated with artificial colors.
Social media and food photography have also had a significant impact on food color trends. With the rise of platforms like Instagram and Pinterest, consumers are now more exposed to visually appealing food than ever before. This has led to a demand for foods that are not only delicious but also visually appealing.
Natural and Sustainable Colors
The demand for natural and sustainable colors is being driven by a number of factors, including consumer concerns about the health risks associated with artificial colors, the growing popularity of clean eating, and the increasing availability of natural colorants.
Artificial colors have been linked to a number of health problems, including hyperactivity, allergies, and cancer. As a result, many consumers are now looking for foods that are made with natural colors.
Clean eating is a trend that emphasizes eating whole, unprocessed foods. Natural colors are a key component of clean eating, as they are derived from fruits, vegetables, and other natural sources.
The increasing availability of natural colorants is also making it easier for food manufacturers to use natural colors in their products. In the past, natural colorants were often more expensive and less stable than artificial colors. However, advances in technology have made natural colorants more affordable and easier to use.
Social Media and Food Photography
Social media and food photography have had a significant impact on food color trends. With the rise of platforms like Instagram and Pinterest, consumers are now more exposed to visually appealing food than ever before.
This has led to a demand for foods that are not only delicious but also visually appealing. Food manufacturers are now using color to create foods that are more likely to be shared on social media.
For example, many food manufacturers are now using bright, vibrant colors in their products. These colors are more likely to catch the eye of consumers and make them want to share the food on social media.
Future of Food Color
The future of food color is bright. As consumers become more aware of the health risks associated with artificial colors, the demand for natural and sustainable colors will continue to grow.
Social media and food photography will also continue to play a major role in food color trends. As consumers continue to share photos of their food on social media, food manufacturers will need to use color to create foods that are more visually appealing.
Emerging technologies may also revolutionize the way we color food. For example, 3D printing could be used to create foods with complex and intricate colors.
Key Questions Answered
What are the most common natural food colors?
Some of the most common natural food colors include turmeric (yellow), paprika (red), annatto (orange), beetroot (red), and spinach (green).
What are the advantages of using natural food colors?
Natural food colors are generally considered to be healthier than artificial food colors, as they are derived from natural sources and do not contain synthetic chemicals. They are also less likely to cause allergic reactions.
What are the disadvantages of using natural food colors?
Natural food colors can be more expensive than artificial food colors, and they may not be as stable or vibrant. They can also be more difficult to work with, as they may require special handling or storage conditions.
