Best foods for dysphagia offer a safe and nutritious solution for individuals with swallowing difficulties. Dysphagia, a condition that affects the ability to swallow, presents unique nutritional challenges that require specialized dietary modifications. This comprehensive guide explores the best foods for dysphagia, providing valuable insights into their nutritional value, benefits, and preparation techniques.
Understanding the specific food texture modifications and nutrient requirements for dysphagia patients is crucial for ensuring optimal nutrition and well-being. By embracing these modifications and incorporating a variety of recommended foods into their diet, individuals with dysphagia can maintain a balanced and satisfying eating experience.
Nutritional Needs of Dysphagia Patients
Dysphagia patients face unique nutritional challenges due to difficulty swallowing. This can lead to inadequate intake of essential nutrients, resulting in malnutrition and other health complications. Understanding their specific nutrient requirements is crucial for developing appropriate dietary plans.
Nutrient Requirements
Dysphagia patients require increased nutrient intake compared to healthy individuals due to:
- Increased energy expenditure from compensatory swallowing techniques
- Reduced food intake and absorption
- Altered metabolism
Specific nutrient requirements include:
- Calories: 1,500-2,000 kcal/day
- Protein: 1.2-1.5 g/kg body weight/day
- Carbohydrates: 4-6 g/kg body weight/day
- Fat: 1-1.5 g/kg body weight/day
- Vitamins and minerals: As per recommended daily intake guidelines
Note: Individual requirements may vary based on age, weight, and underlying medical conditions.
Recommended Daily Nutrient Intake
| Nutrient | Recommended Daily Intake |
|---|---|
| Calories | 1,500-2,000 kcal |
| Protein | 1.2-1.5 g/kg body weight |
| Carbohydrates | 4-6 g/kg body weight |
| Fat | 1-1.5 g/kg body weight |
| Vitamin A | 700-900 mcg |
| Vitamin C | 75-90 mg |
| Vitamin D | 600 IU |
| Vitamin E | 15 mg |
| Calcium | 1,000-1,200 mg |
| Iron | 8-18 mg |
Food Texture Modifications for Dysphagia: Best Foods For Dysphagia
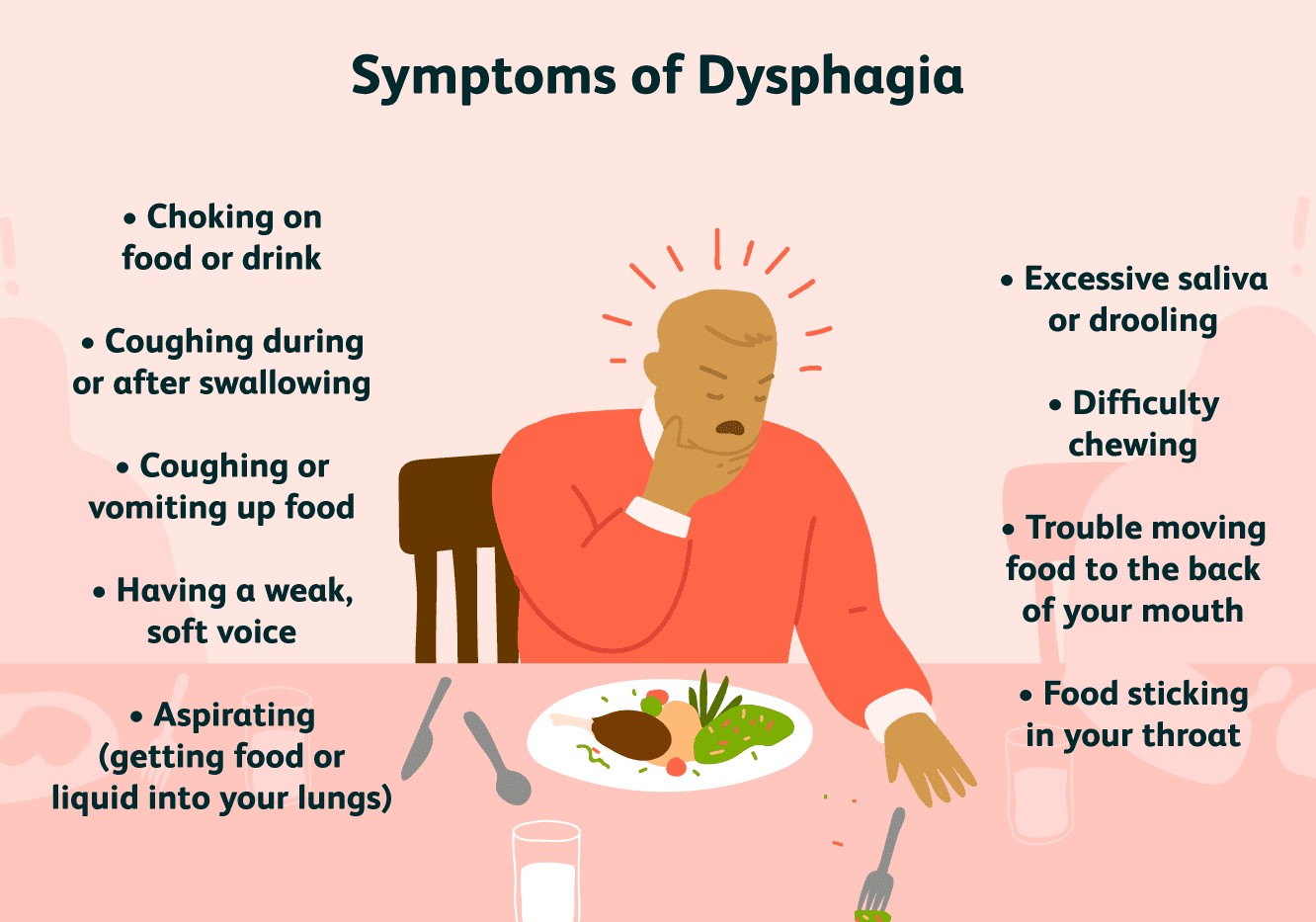
Modifying food textures is crucial for individuals with dysphagia, as it enhances their ability to swallow safely and effectively. These modifications involve altering the consistency, thickness, and form of foods to meet the specific needs of each patient.
When it comes to dysphagia, choosing the right foods is crucial. For a delectable culinary experience that caters to this condition, look no further than Brattleboro, VT . Its renowned restaurants offer a diverse selection of soft, easy-to-swallow dishes that won’t compromise on flavor.
So, whether you’re managing dysphagia or simply seeking a delightful meal, Brattleboro has got you covered.
Pureed Foods
Pureed foods are smooth and homogeneous, resembling a thick liquid. They are suitable for individuals with severe dysphagia who have difficulty managing solid foods. Pureeing eliminates the need for chewing and allows for easy swallowing.
- Examples: Pureed fruits, vegetables, meats, and soups
Mechanically Altered Foods, Best foods for dysphagia
Mechanically altered foods are softened or ground to reduce their toughness and make them easier to chew and swallow. This modification is appropriate for individuals with moderate dysphagia who can manage some solid foods.
- Examples: Ground meats, mashed potatoes, soft-cooked vegetables
Thickened Liquids
Thickened liquids are modified to increase their viscosity, making them easier to control during swallowing. This modification is beneficial for individuals who have difficulty controlling the flow of thin liquids, which can lead to aspiration.
- Examples: Nectar-thick liquids (e.g., thickened juices, soups), honey-thick liquids (e.g., pudding, yogurt)
Semi-Solid Foods
Semi-solid foods are a transition between pureed and solid foods. They have a soft, cohesive texture that is easy to form into bite-sized pieces. This modification is suitable for individuals who are progressing from pureed foods to solid foods.
- Examples: Soft fruits (e.g., bananas, berries), cooked pasta, soft cheeses
Best Foods for Dysphagia
Dysphagia patients require foods that are easy to swallow and meet their nutritional needs. These foods should be soft, moist, and free of lumps or fibers that can cause choking.
The nutritional value of foods recommended for dysphagia patients varies depending on the type of texture modification. Pureed foods, for example, provide a similar nutritional profile to their original form, but with a smoother consistency. Thickened liquids, on the other hand, may have a higher calorie content due to the addition of thickeners.
Pureed Foods
- Fruits: applesauce, bananas, peaches, pears
- Vegetables: mashed potatoes, carrots, green beans, peas
- Meats: ground beef, chicken, fish
- Dairy: yogurt, pudding, custard
Mechanically Altered Foods, Best foods for dysphagia
- Fruits: canned fruits, soft berries
- Vegetables: cooked vegetables, canned vegetables
- Meats: tender meats, fish, poultry
- Dairy: soft cheeses, cottage cheese
Thickened Liquids
- Water
- Juice
- Soup
- Milk
Food Preparation and Presentation
Preparing and presenting food in a way that is suitable for dysphagia patients requires careful consideration of their specific needs and limitations. Dysphagia can make it difficult to swallow, so foods must be modified to make them easier to eat and prevent choking.
Visual Appeal and Presentation
Visual appeal is important for all diners, but it is especially important for dysphagia patients. Food that is visually appealing is more likely to be eaten, and it can help to make the dining experience more enjoyable. There are several ways to make food more visually appealing for dysphagia patients, including:
- Using bright colors and contrasting textures
- Arranging food in an attractive way on the plate
- Garnishing food with fresh herbs or fruit
Tips for Making Food More Visually Appealing and Appetizing
Here are some additional tips for making food more visually appealing and appetizing for dysphagia patients:
- Use a variety of colors and textures in each meal.
- Cut food into small pieces or puree it to make it easier to eat.
- Add sauces or gravies to moisten food and make it more flavorful.
- Use cookie cutters to cut food into fun shapes.
- Garnish food with fresh herbs or fruit to add color and flavor.
Meal Planning for Dysphagia
Meal planning for dysphagia patients involves creating balanced and nutritious meals that meet their specific dietary needs and texture modifications. It is essential to consider variety, balance, and portion control to ensure adequate intake of essential nutrients.
Variety
Offering a wide variety of foods from all food groups helps ensure that dysphagia patients receive the full range of nutrients they need. This includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and dairy or fortified plant-based alternatives. Variety also helps prevent boredom and encourages patients to eat.
Balance
A balanced diet provides the body with the proper proportions of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. For dysphagia patients, it is important to focus on nutrient-rich foods that are easy to swallow and digest. This may include pureed soups, soft-cooked vegetables, and ground meat.
Portion Control
Dysphagia patients may have difficulty eating large meals, so it is important to offer smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day. This helps prevent overeating, which can lead to discomfort and aspiration. Portion sizes should be adjusted based on the patient’s individual needs and tolerance.
Sample Meal Plans
Sample meal plans tailored to different texture modifications: Pureed Diet:
Breakfast
Pureed oatmeal with mashed banana and cinnamon
Lunch
Pureed vegetable soup with soft bread
Dinner
Pureed chicken with mashed potatoes and pureed carrots Mechanical Soft Diet:
Breakfast
Scrambled eggs with soft toast
Lunch
Grilled cheese sandwich with tomato soup
Dinner
Baked fish with steamed vegetables and rice Regular Diet with Modifications:
Breakfast
Yogurt with fruit and granola
Lunch
Salad with grilled chicken and soft vegetables
Dinner
Roasted chicken with mashed potatoes and broccoli
Final Summary
In conclusion, best foods for dysphagia provide a foundation for safe and nutritious eating for individuals with swallowing difficulties. By following the recommended food texture modifications, nutritional guidelines, and meal planning principles Artikeld in this guide, dysphagia patients can enjoy a variety of delicious and nourishing foods that support their overall health and well-being.
