The Amazon River food web is a captivating and complex ecosystem that teems with life and interconnections. From the microscopic producers at the base to the apex predators that dominate the river’s surface, each organism plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of this aquatic realm.
Delving into the intricacies of this food web reveals a fascinating story of adaptation, competition, and cooperation. Primary consumers graze on the abundant plant life, while secondary and tertiary consumers hunt and scavenge, forming intricate webs of predator-prey relationships. Decomposers complete the cycle, breaking down organic matter and returning nutrients to the system.
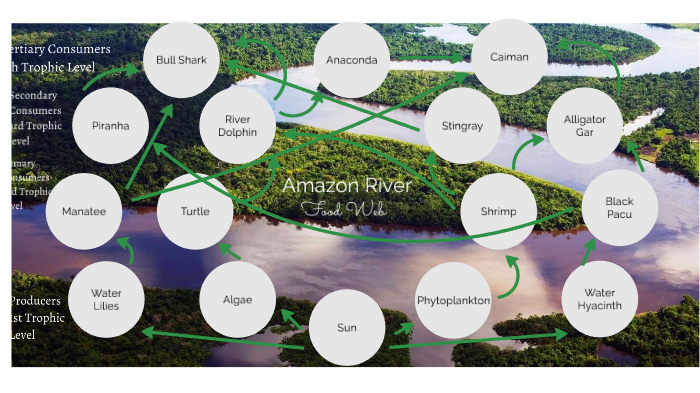
Amazon River Food Web Overview
The Amazon River, the largest river in the world, supports a complex and diverse food web. A food web is a graphical representation of the feeding relationships between different species in an ecosystem. It shows how energy and nutrients flow through the ecosystem from producers to consumers.
The Amazon River food web is unique in several ways. First, it is one of the most diverse food webs on Earth. Over 10,000 species of fish, birds, mammals, reptiles, and amphibians have been identified in the Amazon River basin.
Second, the Amazon River food web is very productive. The warm, nutrient-rich waters of the river support a high biomass of organisms. Third, the Amazon River food web is highly interconnected. There are many different feeding relationships between the different species in the ecosystem.
Trophic Levels, Amazon river food web
The different species in the Amazon River food web can be divided into different trophic levels. Trophic levels are based on the source of an organism’s food. Producers are organisms that can make their own food from inorganic matter. Consumers are organisms that cannot make their own food and must eat other organisms to obtain energy.
There are three main types of consumers: primary consumers, secondary consumers, and tertiary consumers.
- Producers:Producers are the foundation of the Amazon River food web. They include plants, algae, and some bacteria. These organisms use sunlight and nutrients from the water to produce food through photosynthesis.
- Primary Consumers:Primary consumers are organisms that eat producers. They include herbivores, such as fish, turtles, and monkeys. These organisms consume plants and algae.
- Secondary Consumers:Secondary consumers are organisms that eat primary consumers. They include carnivores, such as jaguars, caimans, and eagles. These organisms consume herbivores.
- Tertiary Consumers:Tertiary consumers are organisms that eat secondary consumers. They include apex predators, such as anacondas, harpy eagles, and humans. These organisms consume carnivores.
Ending Remarks: Amazon River Food Web
Understanding the Amazon River food web is essential for preserving the health and biodiversity of this vital ecosystem. Human activities, such as deforestation and pollution, pose significant threats to the delicate balance of this aquatic world. By unraveling the intricate connections within this food web, we gain valuable insights into the challenges it faces and the strategies needed to protect its future.
The Amazon River food web is a complex and interconnected system that supports a vast array of species. From the tiny microorganisms that form the base of the food chain to the large predators that dominate the river’s apex, each organism plays a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of this ecosystem.
However, the Amazon River food web is not immune to the pressures of human activity. Pollution, overfishing, and deforestation are all taking their toll on this fragile ecosystem. As a result, it is more important than ever to understand the Amazon River food web and to take steps to protect it.
We can all make a difference by supporting sustainable practices and by educating ourselves about the importance of this vital ecosystem. If you’re looking for a great way to learn more about the Amazon River food web, I recommend checking out the 476 food district grand junction . This website provides a wealth of information on the Amazon River food web, as well as other environmental issues.
By learning more about the Amazon River food web, we can all help to protect this vital ecosystem.
