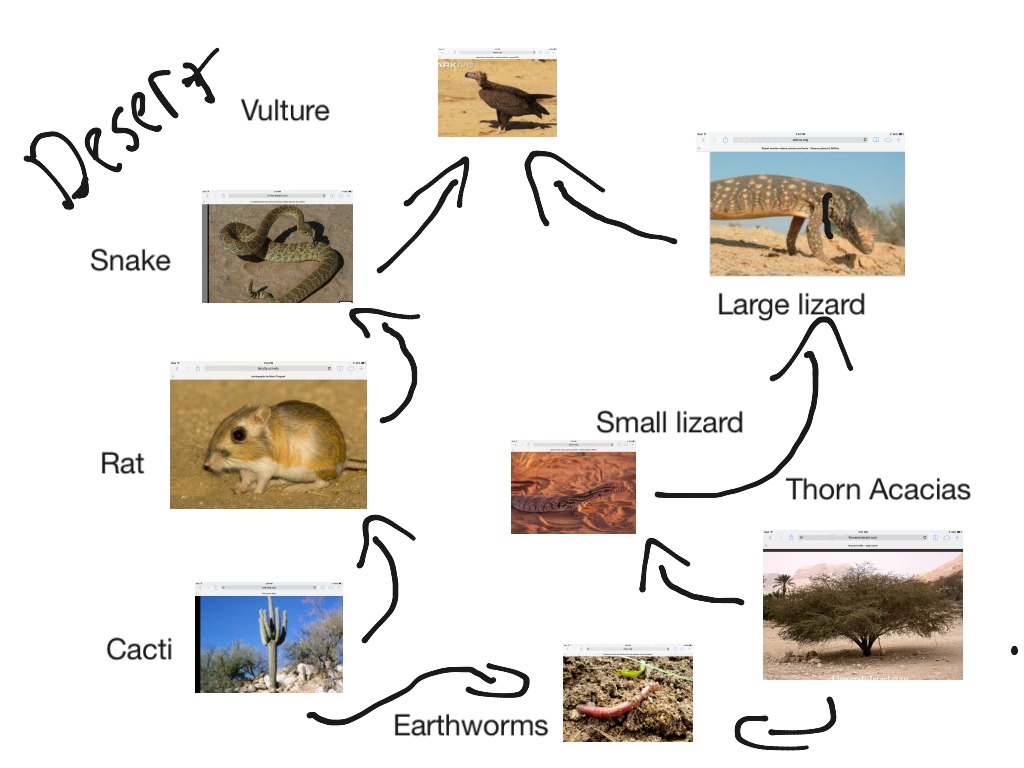
Embark on a culinary adventure as we delve into the intricacies of dessert food webs, where sweet treats take center stage in a complex tapestry of ecological interactions.
Dessert food webs paint a vibrant picture of the interconnectedness of species, from the tiniest ants to the majestic birds that soar above.
Human Impacts on Dessert Food Webs
Human activities have a profound impact on dessert food webs, altering the delicate balance and stability of these ecosystems. From habitat destruction to pollution and climate change, human actions pose significant threats to the survival and health of dessert food webs.
Habitat Destruction
Habitat destruction is one of the most direct and devastating impacts of human activities on dessert food webs. The conversion of natural desert landscapes into urban areas, agricultural fields, or mining sites fragments and destroys habitats, reducing the availability of food and shelter for desert organisms.
- Loss of vegetation: Clearing of desert vegetation removes a primary food source for herbivores, leading to population declines and cascading effects throughout the food web.
- Habitat fragmentation: Fragmentation of habitats isolates populations, making it difficult for organisms to find mates, food, and shelter, increasing their vulnerability to extinction.
- Introduction of invasive species: Habitat destruction can create opportunities for invasive species to establish, outcompeting native species for resources and disrupting the natural balance of the ecosystem.
Pollution, Dessert food web
Pollution from human activities, such as industrial emissions, agricultural runoff, and plastic waste, can contaminate desert ecosystems and harm organisms at all trophic levels.
- Water pollution: Contamination of water sources with pollutants like pesticides and heavy metals can poison organisms, disrupt aquatic food webs, and alter nutrient cycling.
- Plastic pollution: Plastic waste can entangle and kill wildlife, leach harmful chemicals into the environment, and disrupt the natural breakdown of organic matter.
li>Air pollution: Air pollutants, such as smog and ozone, can damage plant tissues, reducing their productivity and affecting the entire food web.
Climate Change
Climate change is a major threat to dessert food webs, as it alters temperature, precipitation patterns, and the availability of resources.
- Rising temperatures: Increased temperatures can lead to heat stress, dehydration, and increased evapotranspiration, reducing plant productivity and affecting water availability for organisms.
- Changes in precipitation: Altered precipitation patterns, such as droughts or extreme rainfall events, can disrupt plant growth, reduce water availability, and affect the abundance and distribution of organisms.
- Phenological shifts: Climate change can alter the timing of life cycle events, such as flowering and migration, disrupting interactions between species and affecting the stability of the food web.
Strategies for Minimizing Human Impacts
Minimizing human impacts on dessert food webs requires a multifaceted approach that involves conservation, restoration, and sustainable practices.
- Protected areas: Establishing and maintaining protected areas, such as national parks and wildlife refuges, helps preserve critical habitats and reduce habitat destruction.
- Habitat restoration: Restoring degraded habitats through reforestation, revegetation, and invasive species removal can improve food availability and shelter for organisms.
- Pollution reduction: Implementing pollution control measures, such as reducing industrial emissions, promoting sustainable agriculture, and managing waste effectively, can mitigate the negative effects of pollution on desert food webs.
- Climate change mitigation: Addressing climate change through reducing greenhouse gas emissions, investing in renewable energy, and promoting sustainable land use practices is crucial for the long-term preservation of dessert food webs.
By understanding the impacts of human activities on dessert food webs and implementing effective strategies to minimize these impacts, we can help ensure the survival and resilience of these unique and fragile ecosystems.
Questions Often Asked
What are the key components of a dessert food web?
Producers, consumers, and decomposers form the foundation of dessert food webs, each playing a vital role in the flow of energy and nutrients.
How does energy flow through a dessert food web?
Energy enters the food web through photosynthesis and is passed along through trophic levels as organisms consume each other.
What are the threats to dessert food webs?
Habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change pose significant threats to the stability and resilience of dessert food webs.