Delving into the realm of foods that contain isoleucine, this comprehensive guide unveils a treasure trove of nutritional insights, exploring the sources, benefits, and considerations of this essential amino acid. From its role in protein synthesis to its impact on muscle growth and energy production, discover the significance of incorporating isoleucine-rich foods into a balanced diet.
Embark on a culinary journey as we uncover a diverse array of plant-based and animal-based sources of isoleucine, empowering you to make informed choices that support your nutritional well-being.
Overview of Isoleucine

Isoleucine, a branched-chain amino acid (BCAA), is an essential nutrient that plays a vital role in various bodily functions. It has a molecular formula of C6H13NO2 and is structurally characterized by its side chain, which consists of a three-carbon aliphatic group.
Isoleucine’s chemical properties include its nonpolar nature, making it hydrophobic and soluble in organic solvents.
Role in Protein Synthesis and Metabolism
Isoleucine is a key component of protein synthesis, as it is one of the 20 amino acids that form the building blocks of proteins. It is involved in the initiation and elongation stages of protein synthesis and contributes to the structural integrity and functionality of proteins.
Moreover, isoleucine participates in energy metabolism, serving as a source of energy for muscles during exercise. It is also involved in the regulation of glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity.
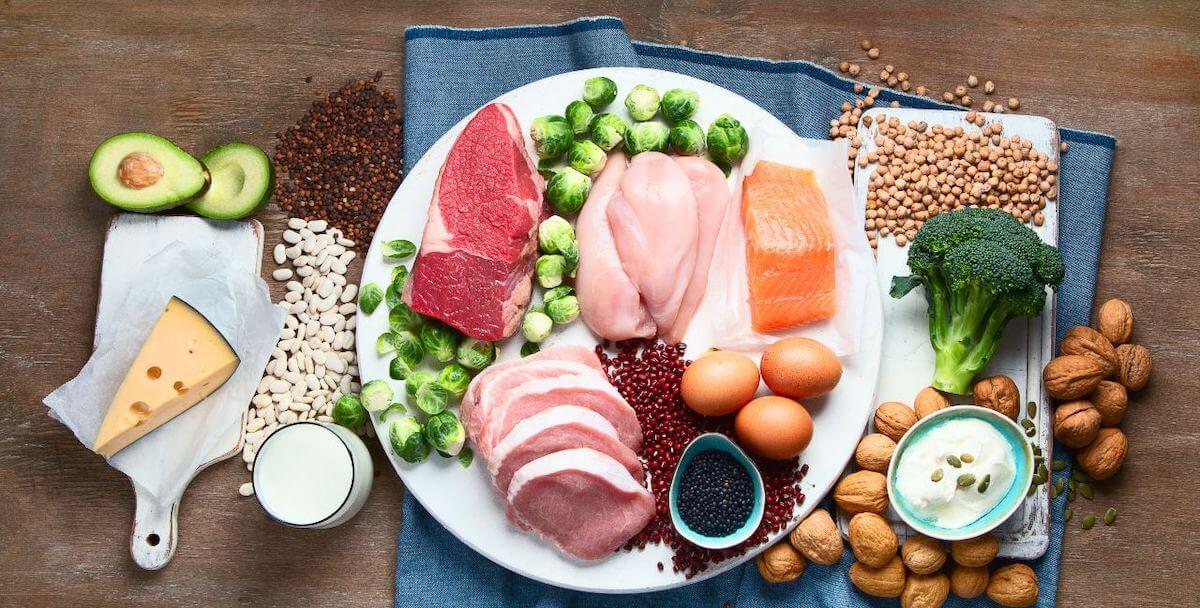
Dietary Sources of Isoleucine
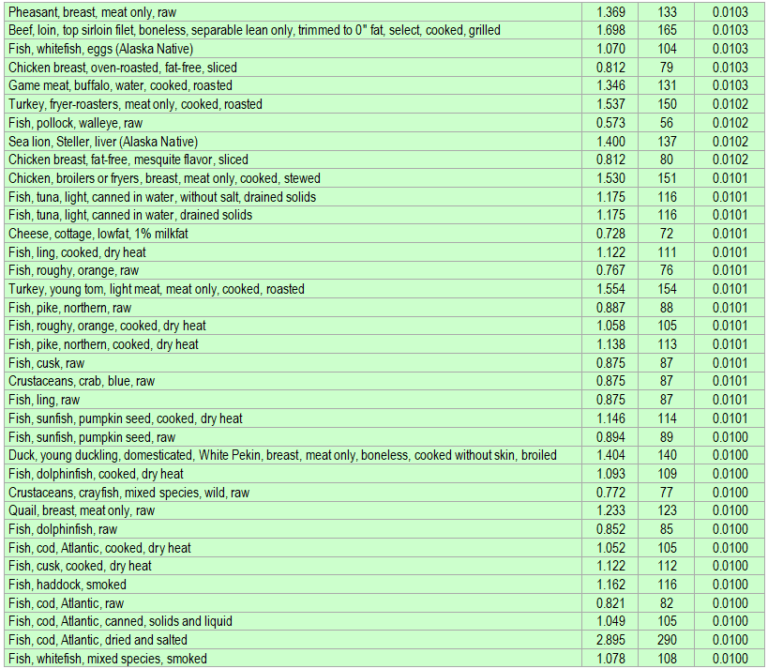
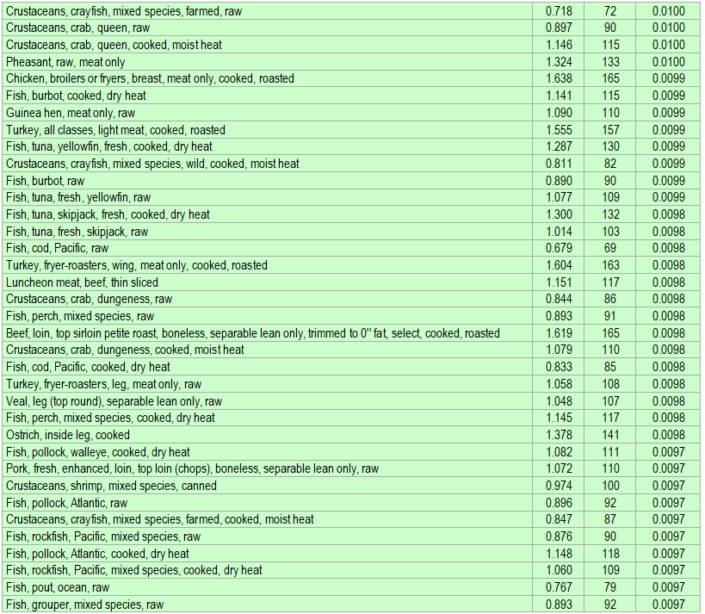
Isoleucine is an essential amino acid that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions. It can be obtained through dietary sources, including both plant-based and animal-based foods. This section provides a comprehensive list of foods rich in isoleucine, organized in an HTML table for easy reference.
List of Isoleucine-Rich Foods
| Food | Isoleucine Content (mg per 100g) | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Soybean | 565 | Plant-based |
| Chicken Breast | 435 | Animal-based |
| Tuna | 426 | Animal-based |
| Beef | 420 | Animal-based |
| Lentils | 407 | Plant-based |
| Pork | 395 | Animal-based |
| Eggs | 394 | Animal-based |
| Almonds | 386 | Plant-based |
| Milk | 383 | Animal-based |
| Quinoa | 379 | Plant-based |
This table highlights a diverse range of foods rich in isoleucine, allowing individuals to incorporate this essential amino acid into their diets through various dietary choices.
Benefits of Consuming Isoleucine
Isoleucine offers a range of potential health benefits, contributing to overall well-being and supporting various bodily functions. Consuming adequate amounts of isoleucine may provide advantages such as:
Muscle Growth and Recovery, Foods that contain isoleucine
Isoleucine plays a crucial role in muscle growth and repair. As one of the three branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), isoleucine stimulates protein synthesis and reduces muscle breakdown, promoting muscle development and recovery after exercise.
Energy Production
Isoleucine serves as a source of energy for the body, particularly during prolonged physical activity. It undergoes metabolism to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of cells, providing the fuel needed for muscle contractions and other energy-demanding processes.
Immune Function
Isoleucine supports a healthy immune system. It enhances the production of lymphocytes, white blood cells that fight infection, and promotes the synthesis of antibodies, proteins that recognize and neutralize foreign invaders.
Recommended Intake and Safety Considerations: Foods That Contain Isoleucine
Determining the optimal isoleucine intake depends on various factors, including age, activity level, and overall health status. The recommended daily intake (RDI) for isoleucine varies based on these individual needs:
Children (0-18 years):10-30 mg/kg of body weight
Adults (19+ years):10-20 mg/kg of body weight
Athletes and individuals engaged in strenuous physical activity:20-30 mg/kg of body weight
Potential Side Effects and Interactions
Excessive isoleucine consumption may lead to potential side effects or interactions, especially when taken in supplement form or through high-protein diets. These include:
- Nausea and vomiting:High doses of isoleucine can cause gastrointestinal upset, leading to nausea and vomiting.
- Headaches:Some individuals may experience headaches as a side effect of excessive isoleucine intake.
- Kidney stones:Individuals with a history of kidney stones should be cautious, as high isoleucine levels can increase the risk of stone formation.
- Drug interactions:Isoleucine supplements may interact with certain medications, such as antibiotics and antidepressants. It’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional before taking isoleucine supplements if you’re on any medications.
Isoleucine Deficiency and Supplementation
Isoleucine deficiency is a rare condition that can occur due to inadequate dietary intake or impaired absorption. Symptoms may include fatigue, muscle weakness, impaired wound healing, and cognitive issues.
Causes of Isoleucine Deficiency
- Inadequate dietary intake: This can occur in individuals with restrictive diets or those who consume a limited variety of foods.
- Impaired absorption: Conditions such as celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, or short bowel syndrome can interfere with the absorption of isoleucine from food.
Potential Benefits of Isoleucine Supplementation
- Improved muscle function: Isoleucine is essential for muscle protein synthesis and can help improve muscle strength and endurance.
- Enhanced recovery from exercise: Isoleucine supplementation may reduce muscle soreness and promote faster recovery after intense exercise.
- Boosted immune function: Isoleucine plays a role in immune cell function and may help strengthen the immune system.
Considerations for Isoleucine Supplementation
- Dosage: The recommended daily intake of isoleucine for adults is 10-20 mg per kg of body weight.
- Safety: Isoleucine is generally considered safe for most individuals. However, excessive intake may cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Consult a healthcare professional: Before taking isoleucine supplements, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage and to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
Conclusion
Isoleucine, an essential amino acid, plays a vital role in various bodily functions. Incorporating foods rich in isoleucine into a balanced diet is crucial for optimal health. However, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and to avoid excessive intake, as this may lead to potential health concerns.
Remember, a balanced and varied diet that includes a range of isoleucine-containing foods is the key to maintaining adequate levels of this essential nutrient.
FAQ Guide
What are the best plant-based sources of isoleucine?
Legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains are excellent plant-based sources of isoleucine.
Can excessive isoleucine consumption have negative effects?
Yes, excessive isoleucine intake may lead to gastrointestinal issues, skin problems, and potential interactions with certain medications.
Is isoleucine supplementation necessary for everyone?
Generally, a balanced diet provides sufficient isoleucine for most individuals. Supplementation may be considered for those with specific dietary restrictions or intense physical activity.
