Microgreens whole foods, a nutritional powerhouse, have emerged as culinary and health enthusiasts’ favorites. These tiny, nutrient-packed greens offer a world of flavors and textures, promising a transformative culinary experience while boosting overall well-being.
From their nutritional value to their diverse culinary applications, this guide explores the fascinating world of microgreens whole foods, uncovering their potential to revolutionize our diets and redefine the food landscape.
Nutritional Value

Microgreens are packed with nutrients, often exceeding the nutritional value of their mature counterparts. They contain high levels of vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and phytonutrients, providing numerous health benefits.
Comparison to Mature Greens
The table below compares the nutritional content of microgreens to mature greens:
| Nutrient | Microgreens | Mature Greens |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C | 25-40 times higher | – |
| Vitamin E | 10-20 times higher | – |
| Beta-carotene | 5-10 times higher | – |
| Iron | 2-3 times higher | – |
| Calcium | 4-5 times higher | – |
Unique Nutrients
Microgreens contain unique nutrients not typically found in mature greens, such as:
- Sulforaphane: A potent antioxidant linked to cancer prevention
- Lutein and zeaxanthin: Antioxidants that protect eye health
- Anthocyanins: Antioxidants with anti-inflammatory and anti-aging properties
Types of Microgreens
Microgreens, the tiny edible greens harvested within a few weeks of germination, come in a wide variety of types, each with its unique flavor and nutritional profile. These variations stem from the different plant species used, as well as the growing conditions employed.
Flavor profiles range from mild and sweet to peppery and tangy, while textures can vary from tender and succulent to slightly crunchy. These characteristics are influenced by the specific microgreen variety, as well as factors such as light exposure, temperature, and nutrient availability.
Flavor Profiles, Microgreens whole foods
- Mild and Sweet:Alfalfa, Broccoli, Clover, Pea Shoots
- Peppery:Arugula, Cress, Mustard, Radish
- Tangy:Beetroot, Cabbage, Kale, Spinach
Textures
- Tender and Succulent:Alfalfa, Broccoli, Clover
- Slightly Crunchy:Arugula, Cress, Pea Shoots, Radish
Growing Conditions
The growing conditions under which microgreens are cultivated can also impact their taste and appearance. Factors such as light exposure, temperature, and nutrient availability influence the production of flavor compounds and the development of chlorophyll, which gives microgreens their characteristic green color.
For example, microgreens grown under high-light conditions tend to have more intense flavors and higher concentrations of antioxidants. Conversely, those grown in cooler temperatures may exhibit slower growth and milder flavors.
Cultivation Methods: Microgreens Whole Foods
Cultivating microgreens at home is a rewarding and accessible way to enjoy fresh, nutrient-rich greens. Here’s a step-by-step guide to growing microgreens:
Materials
- Microgreen seeds
- Growing medium (e.g., soil, coconut coir)
- Shallow trays or containers
- Spray bottle
- Light source (e.g., grow light, sunlight)
Step 1: Preparing the Growing Medium
Fill shallow trays or containers with a well-draining growing medium, such as soil, coconut coir, or a mix of both. Moisten the medium but avoid overwatering.
Step 2: Sowing the Seeds
Sprinkle the microgreen seeds evenly over the growing medium. Avoid overcrowding as this can lead to poor growth and disease.
Step 3: Providing Light
Microgreens require plenty of light to thrive. Place the trays under a grow light or in a location that receives bright, indirect sunlight for 12-16 hours per day.
Step 4: Watering and Humidity
Water the microgreens regularly using a spray bottle to keep the growing medium moist but not soggy. Maintain high humidity by covering the trays with a clear lid or plastic wrap.
Step 5: Harvesting
Microgreens are typically ready to harvest within 7-14 days, depending on the variety. Use scissors to cut the greens just above the soil line, leaving the roots intact.
The method of harvesting can affect the quality of the microgreens. Harvesting the greens with scissors preserves their delicate texture and freshness, while harvesting with a knife or pulling them up by the roots can damage the greens and reduce their nutritional value.
Culinary Applications
Microgreens are not only nutritious but also add a burst of flavor and visual appeal to various dishes. Their versatility allows them to be incorporated into a wide range of culinary creations, enhancing both the taste and presentation.
From salads and sandwiches to soups and entrees, microgreens offer a vibrant and flavorful addition to any meal. Their delicate textures and diverse flavor profiles make them perfect for garnishing and enhancing dishes, adding a touch of freshness and sophistication.
As Garnishes
- Microgreens’ vibrant colors and delicate textures make them ideal for garnishing soups, salads, and entrees.
- They add a touch of elegance and freshness to any dish, enhancing its visual appeal.
- Use microgreens like pea shoots, sunflower shoots, or radish sprouts to create a colorful and flavorful garnish.
In Salads
- Microgreens add a burst of flavor and nutrients to salads, making them more vibrant and nutritious.
- Combine microgreens with other leafy greens, vegetables, and fruits to create a colorful and flavorful salad.
- Microgreens like arugula, broccoli, or kale add a peppery or bitter flavor to salads, balancing the sweetness of other ingredients.
In Sandwiches
- Microgreens add a touch of freshness and crunch to sandwiches, making them more satisfying and nutritious.
- Use microgreens as a flavorful and healthy alternative to lettuce or sprouts in your favorite sandwiches.
- Microgreens like alfalfa, clover, or radish sprouts provide a peppery or tangy flavor that complements meats, cheeses, and vegetables.
In Soups
- Microgreens can be added to soups to enhance their flavor and nutritional value.
- Stir microgreens into soups just before serving to preserve their delicate texture and flavor.
- Microgreens like cilantro, dill, or parsley add a fresh and herbaceous flavor to soups, balancing the richness of the broth.
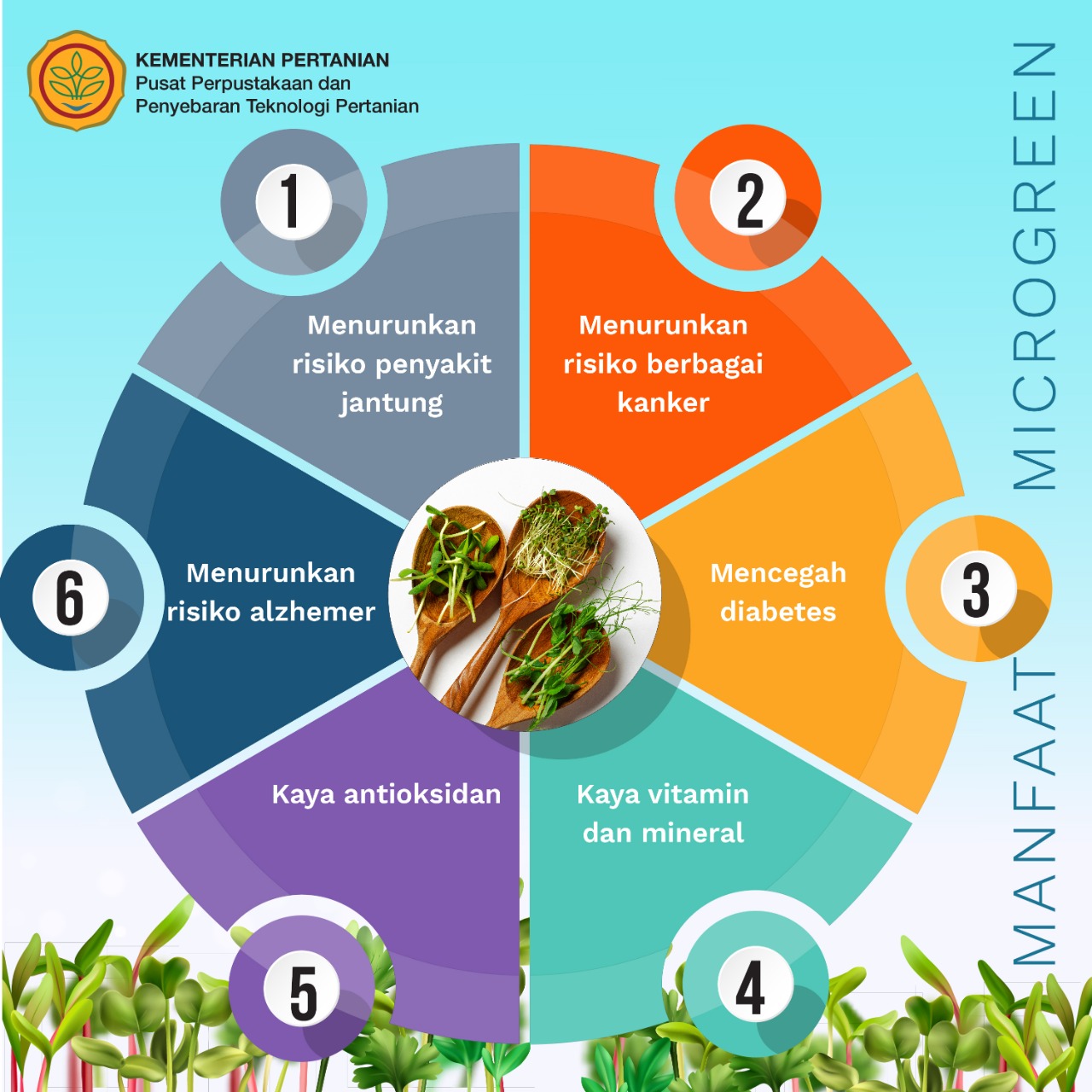
Health Benefits
Microgreens offer an array of health benefits due to their high nutrient content. Studies have shown that consuming microgreens may contribute to:
- Enhanced antioxidant capacity, protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals.
- Reduced inflammation, thanks to the presence of anti-inflammatory compounds.
- Improved immune function, supporting the body’s natural defenses against infections.
Antioxidant Properties
Microgreens are rich in antioxidants, including vitamins C and E, beta-carotene, and flavonoids. These compounds neutralize free radicals, unstable molecules that can damage cells and contribute to chronic diseases. Research has shown that microgreens may help protect against oxidative stress, which is linked to conditions such as heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders.
Anti-inflammatory Effects
Microgreens contain anti-inflammatory compounds such as sulforaphane and kaempferol. These compounds have been found to reduce inflammation in the body, which may benefit conditions like arthritis, asthma, and inflammatory bowel disease. Studies suggest that regular consumption of microgreens may help lower inflammatory markers in the blood.
Immune-Boosting Properties
Microgreens are a good source of vitamins and minerals essential for a healthy immune system. Vitamin C, for example, supports the production of white blood cells, which fight off infections. Microgreens also contain zinc, which plays a crucial role in immune function.
Research indicates that consuming microgreens may help boost the immune system and reduce the risk of infections.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact

Microgreens cultivation offers significant environmental benefits. Their small size and rapid growth cycle reduce water consumption and minimize the need for extensive land use.
Water Efficiency
Microgreens require minimal water compared to traditional crops. Their shallow root systems and short growing period allow them to thrive with limited water input. This water efficiency makes them suitable for arid regions or areas facing water scarcity.
Space Efficiency
Microgreens can be grown vertically in trays or containers, maximizing space utilization. This vertical farming technique enables higher crop yields per square foot compared to traditional field cultivation. It reduces the need for large-scale land conversion, preserving natural ecosystems.
Contribution to Sustainable Food Systems
- Local Production:Microgreens can be grown locally, reducing transportation distances and associated carbon emissions.
- Year-Round Availability:Indoor cultivation allows microgreens to be produced year-round, ensuring a consistent supply and reducing seasonal dependency.
- Nutrient Density:Microgreens are nutrient-rich, providing essential vitamins and minerals. Their high nutritional value can contribute to healthy diets and reduce the environmental impact of producing nutrient-dense foods.
Market Trends and Availability
Microgreens have gained significant traction in the food industry, driven by their nutritional value, versatility, and aesthetic appeal. The demand for microgreens is steadily increasing as consumers become more health-conscious and seek nutrient-rich, flavorful ingredients.
Microgreens are widely available in various markets and distribution channels, including supermarkets, farmers’ markets, and online retailers. They are often sold in small containers or bags, making them convenient for home use. Some restaurants and food service establishments also incorporate microgreens into their dishes to enhance presentation and nutritional content.
Future Growth Potential
The microgreens market is projected to experience continued growth in the coming years. Factors contributing to this growth include the increasing popularity of healthy eating, the expansion of the food service industry, and the growing awareness of the environmental benefits of microgreens.
FAQ
What are microgreens?
Microgreens are young, edible seedlings of various vegetables, herbs, and grains, harvested within 10-14 days of germination.
Are microgreens more nutritious than mature greens?
Yes, microgreens typically contain higher concentrations of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants compared to their mature counterparts.
How can I incorporate microgreens into my diet?
Microgreens can be added to salads, sandwiches, wraps, smoothies, soups, and various other dishes as a nutritious and flavorful garnish or ingredient.
