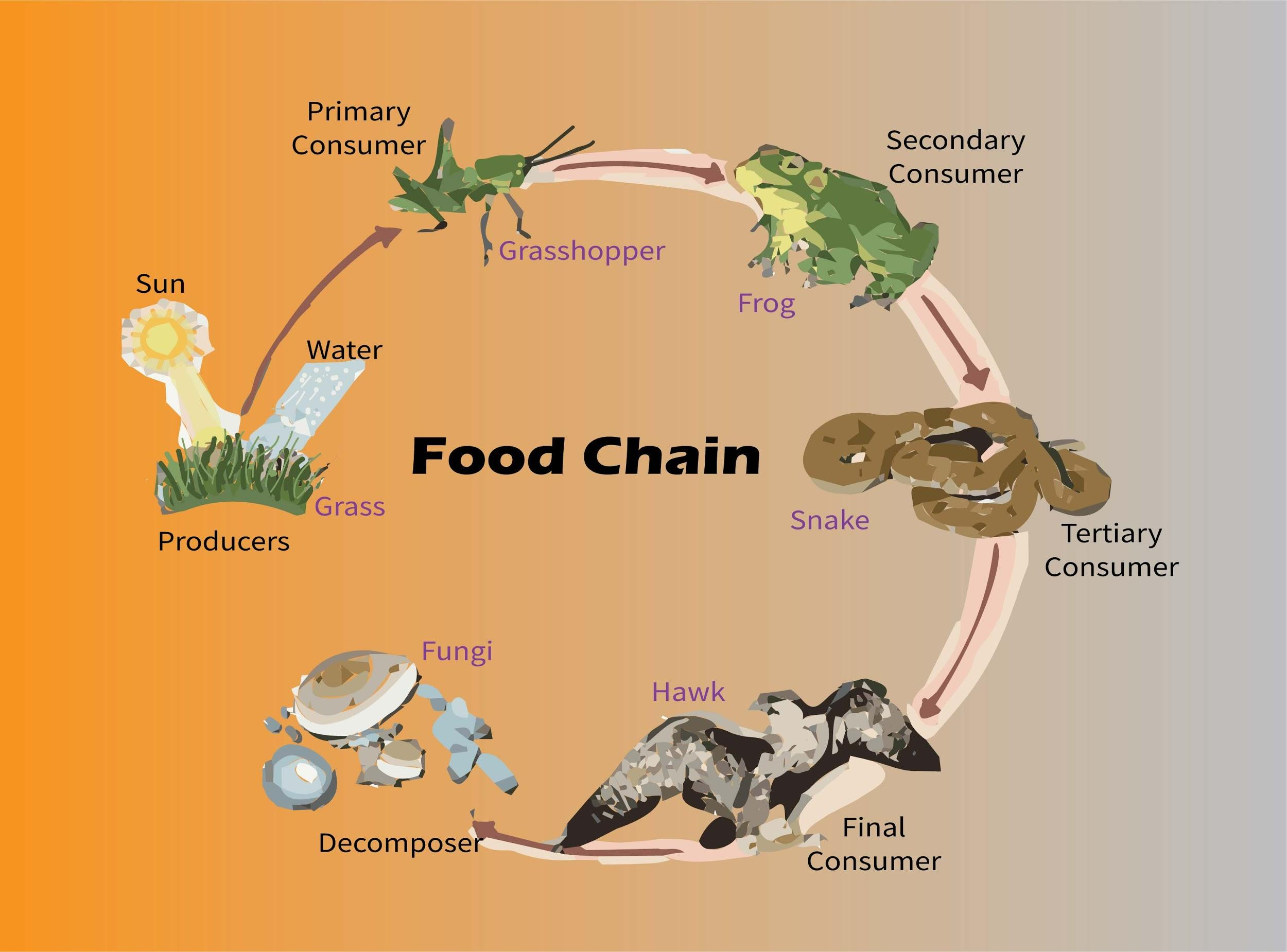
Embark on an exploration of the grasslands food web, a captivating tapestry of interconnected species that weaves together the intricate fabric of this vibrant ecosystem. From the primary producers that harness the sun’s energy to the apex predators that dominate the food chain, each organism plays a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of this thriving natural community.
Grasslands, with their vast expanses of waving grasses and diverse flora and fauna, offer a fascinating glimpse into the intricate workings of nature’s food webs. As we delve deeper into this topic, we will unravel the complex relationships between producers, consumers, and decomposers, uncovering the hidden dynamics that govern this dynamic ecosystem.
Grassland Ecosystem

Grasslands are vast ecosystems characterized by the dominance of grasses and other herbaceous plants, forming a continuous ground cover. These ecosystems exhibit unique structural and functional attributes, supporting a diverse array of flora and fauna.
Structure and Characteristics
Grasslands are typically open, treeless landscapes with a distinct vertical structure. The herbaceous layer, composed of grasses and forbs (non-grassy flowering plants), is the most prominent feature. Grasses possess narrow, elongated leaves that facilitate efficient photosynthesis, while forbs contribute to floral diversity and provide nectar and pollen for pollinators.
The soil in grasslands is typically deep and fertile, with a well-developed root system that stabilizes the soil and facilitates water and nutrient uptake. Grasslands often have a high rate of primary productivity, producing a substantial amount of plant biomass that supports herbivores and other organisms.
Types of Grasslands
Grasslands can be classified into different types based on their geographical location, climate, and vegetation composition. Some notable types include:
- Temperate grasslands: Found in regions with moderate temperatures and precipitation, these grasslands are dominated by tall grasses such as bluestem and switchgrass.
- Tropical grasslands: Occur in warm, humid regions and are characterized by a mix of tall grasses and broad-leaved plants. Savannas are a type of tropical grassland with scattered trees or shrubs.
- Subpolar grasslands: Located in cold, high-latitude regions, these grasslands are dominated by short, hardy grasses that can withstand harsh conditions.
Notable Grasslands Worldwide, Grasslands food web
Grasslands are found on every continent except Antarctica. Some notable examples include:
- Serengeti National Park, Tanzania: A vast savanna ecosystem renowned for its abundant wildlife, including lions, elephants, and wildebeest.
- Great Plains, North America: A vast temperate grassland that extends from Canada to Texas, known for its rich agricultural lands.
- Pampas, South America: A fertile temperate grassland region that supports extensive cattle ranching.
Helpful Answers: Grasslands Food Web
What is a food web?
A food web is a diagram that shows the feeding relationships between different species in an ecosystem. It illustrates who eats whom and how energy flows through the system.
What is the role of producers in a food web?
Producers are organisms that can make their own food from inorganic matter. They are the foundation of the food web and provide energy for all other organisms.
What is the role of consumers in a food web?
Consumers are organisms that cannot make their own food and must eat other organisms to obtain energy. They are classified as herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores based on their diet.
What is the role of decomposers in a food web?
Decomposers are organisms that break down dead organisms and recycle their nutrients back into the ecosystem. They play a crucial role in nutrient cycling and ecosystem health.