Delving into the world of food safety auditor jobs, we uncover a critical role that safeguards the quality and safety of our food supply. These auditors are the guardians of food safety, ensuring that food production and handling practices adhere to industry standards and regulations.
Food safety auditors play a pivotal role in protecting public health by identifying and mitigating potential food safety hazards throughout the food chain, from farm to fork. They conduct rigorous audits, assess food safety management systems, and provide valuable guidance to food businesses to enhance their food safety practices.
Reporting and Corrective Actions

Food safety auditors play a crucial role in reporting audit findings to management and other stakeholders. These findings provide valuable insights into areas where food safety practices can be improved.
The audit report typically includes a detailed account of the findings, along with supporting evidence and recommendations for corrective actions.
Types of Corrective Actions
- Immediate actions:These are actions that must be taken immediately to address critical food safety hazards that pose an imminent threat to public health.
- Short-term actions:These actions are required to address less severe food safety issues that do not pose an immediate threat but require prompt attention.
- Long-term actions:These actions involve systemic changes to food safety practices and procedures to prevent future non-conformances.
Follow-up on Corrective Actions
Food safety auditors are responsible for following up on corrective actions to ensure that they are implemented effectively and that compliance is maintained.
- Verification:Auditors may conduct follow-up audits to verify that corrective actions have been implemented as planned.
- Re-evaluation:If necessary, auditors may re-evaluate corrective actions to ensure their effectiveness and make adjustments as needed.
- Continuous monitoring:Auditors may establish ongoing monitoring programs to ensure that food safety practices remain compliant and that corrective actions continue to be effective.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities: Food Safety Auditor Jobs
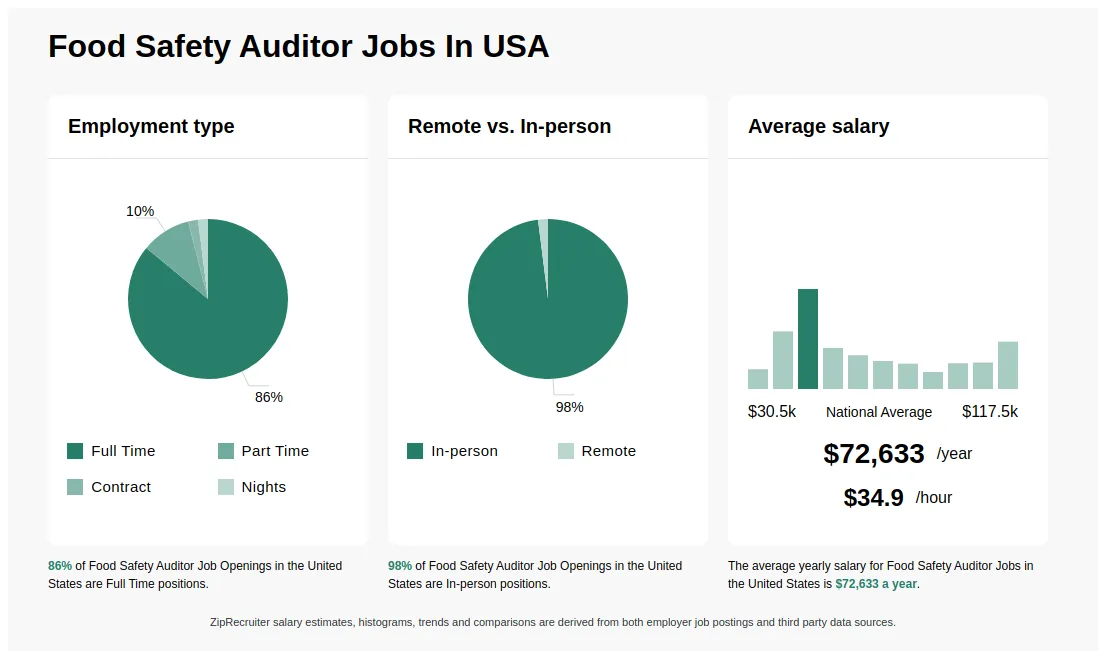
A career as a food safety auditor offers a well-defined path for professional growth and advancement. Individuals typically start as entry-level auditors and gradually progress through various levels of responsibility and expertise.
Advancement Opportunities, Food safety auditor jobs
- Senior Auditor:With experience and proven competence, auditors can advance to senior roles, where they lead audit teams and oversee complex projects.
- Lead Auditor:Lead auditors are responsible for managing and directing audit programs, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and industry best practices.
- Managerial Positions:Auditors with exceptional leadership and management skills can move into managerial roles, such as Quality Assurance Manager or Food Safety Director, where they oversee the entire food safety program.
- Consulting and Training:Experienced auditors can also pursue careers in consulting and training, providing expertise and guidance to food businesses on food safety management.
Professional Development Opportunities
To stay current with industry standards and best practices, food safety auditors have access to various professional development opportunities, including:
- Conferences and Seminars:Industry conferences and seminars offer opportunities for auditors to learn about the latest food safety trends, regulations, and technologies.
- Training Programs:Specialized training programs can enhance auditors’ skills in specific areas, such as auditing techniques, risk assessment, and HACCP implementation.
- Certifications:Auditors can obtain professional certifications, such as the Certified Food Safety Auditor (CFSA) or Certified Professional Food Safety Manager (CP-FSP), to demonstrate their expertise and commitment to the field.
FAQ
What are the key responsibilities of a food safety auditor?
Food safety auditors are responsible for conducting food safety audits, evaluating food safety management systems, identifying potential food safety hazards, and providing guidance to food businesses to enhance their food safety practices.
What qualifications are required to become a food safety auditor?
Typically, food safety auditors possess a bachelor’s degree in food science, microbiology, or a related field, along with relevant experience in food safety or quality assurance.
What are the career advancement opportunities for food safety auditors?
Food safety auditors can advance their careers by pursuing leadership roles within food safety departments, becoming food safety consultants, or specializing in specific areas of food safety, such as HACCP or foodborne illness investigations.

