The kelp forest food web, an intricate tapestry of marine life, unfolds in a captivating dance of interdependence and resilience. Immerse yourself in the verdant depths of this underwater wonderland, where towering kelp forests sway gently in the ocean currents, providing sustenance and shelter to a myriad of creatures.
From microscopic plankton to majestic sea otters, each organism plays a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of this thriving ecosystem.
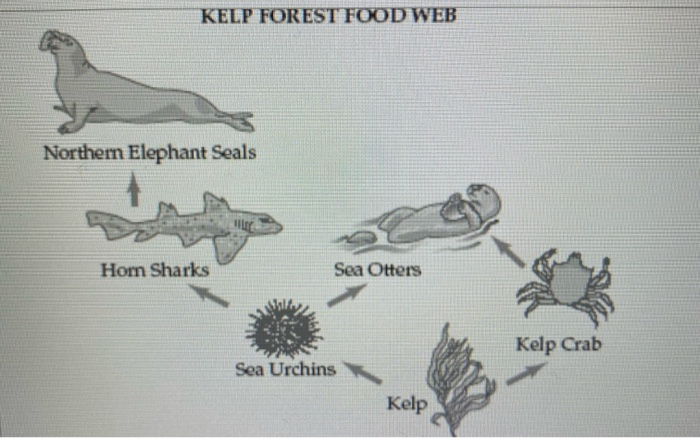
Kelp Forest Ecosystem: Kelp Forest Food Web
Kelp forests are unique and productive marine ecosystems that are found in cold, temperate waters around the world. They are characterized by dense stands of giant kelp ( Macrocystis pyrifera), which can grow up to 100 feet in length. Kelp forests provide food and shelter for a wide variety of marine life, including fish, invertebrates, and mammals.
Types of Kelp, Kelp forest food web
There are several different types of kelp that are found in kelp forests. The most common type is giant kelp, but other types include bull kelp ( Nereocystis luetkeana), sugar kelp ( Laminaria saccharina), and ribbon kelp ( Laminaria digitata).
Physical Structure and Vertical Zonation
Kelp forests have a distinct physical structure and vertical zonation. The canopy is the uppermost layer of the kelp forest, and it is formed by the floating blades of the kelp plants. The understory is the layer below the canopy, and it is made up of smaller kelp plants and other algae.
The bottom layer of the kelp forest is the benthos, which is the seafloor.
Kelp Forest Food Web Structure

The kelp forest food web is a complex and interconnected system of organisms that rely on each other for survival. The primary producers in the kelp forest are the giant kelp, which are large brown algae that provide food and shelter for a variety of other organisms.
The primary consumers in the kelp forest are herbivores, such as sea urchins and snails, which feed on the kelp. These herbivores are in turn preyed upon by carnivores, such as fish and seals. The kelp forest food web is a delicate balance, and any disruption to one level of the food web can have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem.
Trophic Levels within the Kelp Forest Food Web
The kelp forest food web can be divided into several trophic levels. The first trophic level consists of the primary producers, which are the giant kelp. The second trophic level consists of the primary consumers, which are the herbivores. The third trophic level consists of the secondary consumers, which are the carnivores.
The fourth trophic level consists of the tertiary consumers, which are the top predators in the ecosystem.
Interdependence of Organisms within the Kelp Forest Ecosystem
The organisms in the kelp forest ecosystem are all interdependent on each other. The giant kelp provides food and shelter for the herbivores, which in turn provide food for the carnivores. The carnivores help to keep the herbivore population in check, which prevents the herbivores from overgrazing the kelp.
The kelp forest ecosystem is a delicate balance, and any disruption to one level of the food web can have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem.
Kelp Forest Food Web Dynamics
Kelp forests are highly productive ecosystems that support a diverse array of marine life. The dynamics of these ecosystems are driven by a complex interplay of factors, including light availability, herbivory, and predation.
Light Availability
Light is essential for kelp growth. Kelp plants use sunlight to photosynthesize, producing food for themselves and the entire food web. Light availability is influenced by a variety of factors, including water depth, turbidity, and canopy cover. In general, kelp forests are found in shallow waters where there is sufficient light for photosynthesis.
However, kelp can also grow in deeper waters if there is enough sunlight available.
Herbivory
Herbivores are animals that eat plants. In kelp forests, the primary herbivores are sea urchins and fish. Sea urchins graze on kelp blades, while fish eat kelp fronds and stipes. Herbivory can have a significant impact on kelp abundance and forest structure.
When herbivore populations are high, they can reduce kelp growth and abundance, creating a “barrens” ecosystem. However, when herbivore populations are low, kelp can flourish, creating a dense forest ecosystem.
Predation
Predators are animals that eat other animals. In kelp forests, the primary predators are fish, sea otters, and sea lions. Predators can have a significant impact on herbivore populations. When predator populations are high, they can reduce herbivore abundance, allowing kelp forests to flourish.
However, when predator populations are low, herbivore populations can increase, leading to a decline in kelp abundance.
Human Impacts on Kelp Forest Food Webs
Human activities can significantly disrupt kelp forest ecosystems and the delicate balance of their food webs. Understanding these impacts is crucial for conservation and management efforts.
Direct threats to kelp forests include overfishing, pollution, and coastal development. Indirect threats arise from climate change, which alters water temperature, nutrient availability, and ocean acidification.
Overfishing
Excessive fishing of kelp-eating animals, such as sea urchins and abalone, can lead to an overabundance of these herbivores. This, in turn, can result in overgrazing of kelp, reducing its abundance and creating barren “urchin barrens.” Overfishing also disrupts the food chain, as predators that rely on these herbivores for sustenance may decline in population.
Question Bank
What are the primary producers in a kelp forest food web?
Kelp, a type of brown algae, are the primary producers in a kelp forest food web, utilizing sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose through photosynthesis.
How does light availability affect the kelp forest food web?
Light availability is crucial for kelp growth, as it provides the energy needed for photosynthesis. Changes in light availability, such as those caused by cloud cover or sediment runoff, can impact the abundance of kelp and subsequently affect the entire food web.
What is the role of predators in the kelp forest food web?
Predators, such as sea otters and fish, play a vital role in regulating herbivore populations and maintaining kelp forest health. By consuming herbivores, predators prevent overgrazing of kelp, allowing the kelp forest to thrive.
