The cube theory of food, a groundbreaking concept, takes center stage as an innovative approach to understanding the complexities of food. This theory provides a comprehensive framework that encompasses the nutritional, preparation, and cultural dimensions of food, offering a holistic perspective on its multifaceted nature.
By delving into the nutritional dimension, the cube theory empowers us to assess the nutrient composition of different foods, enabling informed dietary choices. The preparation dimension sheds light on the impact of various cooking methods on nutritional value, guiding us towards optimizing meal preparation for maximum nutritional benefit.
Preparation Dimension: Cube Theory Of Food
The preparation dimension of the cube theory focuses on the various methods used to prepare food and their impact on its nutritional value. Understanding these preparation techniques empowers us to make informed choices that maximize the nutritional benefits of our meals.
Preparation methods can significantly alter the nutrient composition of food. For instance, boiling vegetables can leach out water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C, while steaming or roasting preserves them better. Similarly, frying foods in excessive oil adds unhealthy fats and calories, whereas grilling or baking promotes healthier cooking practices.
Optimizing Nutritional Value
The preparation dimension provides valuable insights into optimizing the nutritional value of our meals. By selecting appropriate preparation methods, we can retain essential nutrients and minimize the loss of beneficial compounds:
- Preserving Vitamins:Steaming, roasting, or microwaving vegetables helps retain heat-sensitive vitamins like vitamin C and folate.
- Minimizing Fat Absorption:Grilling, baking, or roasting meats and poultry allows excess fat to drain away, reducing saturated fat intake.
- Enhancing Nutrient Absorption:Soaking legumes and grains overnight before cooking improves nutrient bioavailability and digestibility.
Cultural Dimension

Culture plays a pivotal role in shaping our food habits and preferences. It influences our choice of ingredients, cooking techniques, and dining rituals. The cube theory provides a framework for analyzing the cultural significance of different foods by considering their preparation, sensory, and cultural dimensions.
The cultural dimension encompasses the beliefs, values, and traditions that shape our foodways. It includes factors such as religion, ethnicity, geography, and history. These factors influence our perceptions of what is considered edible, desirable, and taboo. For example, in some cultures, pork is considered unclean and forbidden, while in others, it is a staple food.
Cultural Significance of Food
Food can serve as a symbol of cultural identity and heritage. It can be used to express cultural values, commemorate special occasions, and strengthen social bonds. For example, in many Asian cultures, rice is not just a food but a symbol of prosperity and fertility.
It is often used in religious ceremonies and festivals.
Promoting Cultural Understanding and Tolerance
Understanding the cultural dimension of food can help promote cultural understanding and tolerance. By learning about the different ways that people eat, we can gain insights into their cultures and perspectives. This can help break down stereotypes and foster respect for diversity.
For example, a study found that people who had eaten a meal with someone from a different culture were more likely to have positive attitudes towards that culture.
Applications of the Cube Theory
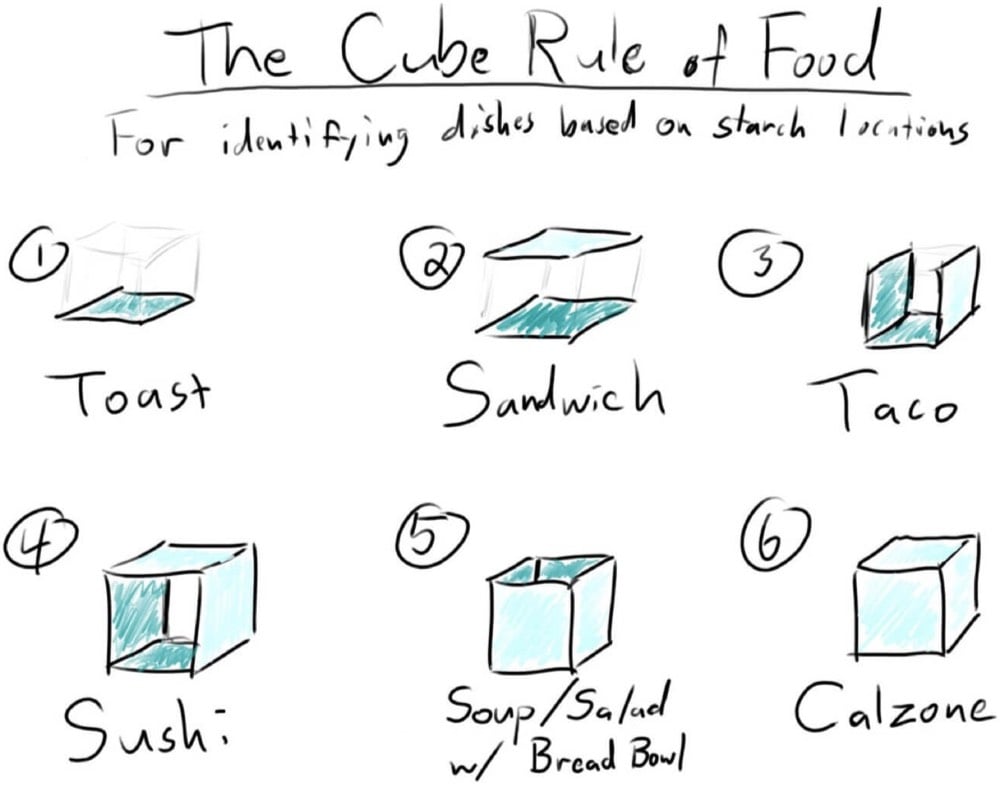
The cube theory is a versatile tool that can be applied in various settings to enhance our understanding and interaction with food. Its multifaceted nature allows for its utilization in fields such as nutrition education, food policy, and culinary arts.
Nutrition Education
The cube theory can be an effective tool for nutrition educators to convey complex nutritional information in a simplified and engaging manner. By utilizing the three dimensions of the cube, educators can illustrate the interplay between food components, preparation methods, and cultural influences.
This holistic approach helps students develop a comprehensive understanding of the factors that shape their food choices.
For instance, the cube theory can be used to demonstrate the impact of different cooking techniques on the nutritional value of foods. By comparing the nutrient content of raw, steamed, and fried vegetables, students can learn how cooking methods can affect the availability and absorption of essential nutrients.
Food Policy
The cube theory can inform food policy development by providing a framework for considering the multiple dimensions of food systems. Policymakers can use the cube to analyze the impact of proposed policies on food production, distribution, and consumption. This comprehensive approach ensures that policies are aligned with the goal of promoting healthy and sustainable food systems.
For example, the cube theory was used in the development of the 2015-2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans. The guidelines incorporated the cube’s dimensions to provide evidence-based recommendations on healthy eating patterns that consider cultural diversity and the availability of foods.
Culinary Arts, Cube theory of food
The cube theory can inspire culinary innovation and creativity. Chefs can use the cube to explore new flavor combinations and textures by experimenting with different ingredients, preparation methods, and cultural influences. This approach can lead to the development of innovative dishes that appeal to diverse palates.
For instance, the cube theory was used by chef Ferran Adrià in the creation of his groundbreaking molecular gastronomy dishes. Adrià’s experiments with different ingredients, such as foams and gels, and his use of innovative cooking techniques resulted in the development of unique and unforgettable culinary experiences.
Conclusion

The cube theory of food provides a comprehensive framework for analyzing and understanding food from multiple perspectives. It highlights the complex interplay between preparation, culture, and applications, offering valuable insights into the multifaceted nature of food.
The implications of the cube theory are far-reaching. It has the potential to enhance our understanding of food systems, inform decision-making related to food production, distribution, and consumption, and promote interdisciplinary collaboration in food research.
Directions for Future Research
The cube theory opens up numerous avenues for future research. Some promising directions include:
- Exploring the relationship between preparation and nutritional value.
- Investigating the impact of cultural factors on food choices and dietary patterns.
- Developing practical applications of the cube theory in food product development and marketing.
- Examining the role of the cube theory in addressing food security and sustainability challenges.
Question & Answer Hub
What are the key dimensions of the cube theory of food?
The cube theory of food comprises three key dimensions: nutritional, preparation, and cultural.
How can the cube theory be used to improve dietary choices?
The cube theory provides a framework for assessing the nutritional value of different foods, enabling individuals to make informed dietary choices that meet their specific needs and preferences.
What role does the preparation dimension play in the cube theory?
The preparation dimension emphasizes the impact of cooking methods on the nutritional value of food, guiding individuals towards optimizing meal preparation for maximum nutritional benefit.
