The socialization process of food is a captivating exploration into the intricate web of cultural influences, social norms, and personal experiences that shape our food choices and eating habits. From the earliest moments of our lives, we are immersed in a world of food-related practices and beliefs that mold our preferences and behaviors.
This enthralling narrative delves into the historical evolution of food socialization, examining how societal and cultural changes have influenced our relationship with food.
Culture plays a pivotal role in shaping our food preferences and habits. Different cultures have unique norms and values that dictate what foods are considered acceptable, desirable, or even taboo. These cultural influences extend beyond individual choices, influencing the availability and accessibility of certain foods within communities.
Historical Evolution of Food Socialization
Food socialization, the process by which individuals learn about food and eating behaviors, has undergone significant transformations throughout history. Cultural and societal shifts have profoundly influenced our relationship with food, shaping our preferences, habits, and rituals.
In ancient societies, food socialization was primarily a familial affair. Children learned about food preparation and consumption through observation and participation in family meals. Food played a central role in social bonding and cultural identity.
Influence of Religion
Religion has played a significant role in shaping food socialization practices. Dietary restrictions and observances associated with religious beliefs have influenced food choices and meal patterns. For example, the Jewish kosher laws and the Islamic halal dietary guidelines have guided food consumption within these communities for centuries.
Industrialization and Globalization
The Industrial Revolution and subsequent globalization have had a profound impact on food socialization. Mass production and distribution of food products led to the availability of a wider variety of foods, altering dietary habits and preferences. Globalization has introduced new cuisines and ingredients, broadening our culinary horizons.
Role of Media and Technology
The advent of mass media and technology has revolutionized food socialization. Television shows, cookbooks, and social media platforms have become influential sources of food-related information and inspiration. Digital technologies have also facilitated the sharing of recipes, food experiences, and dietary advice, further shaping our food socialization practices.
Cultural Influences on Food Socialization

Culture plays a pivotal role in shaping our food preferences and habits. Cultural norms, values, and traditions influence what we eat, how we eat it, and the meanings we attach to food.
Socialization of Food in Different Cultures
Cultural socialization of food varies widely across different cultures. For example:
- In many Western cultures, meat is a central part of the diet, while in some Eastern cultures, vegetables and rice are more prevalent.
- In some cultures, it is considered rude to eat with your hands, while in others, it is the preferred way to eat.
- Certain foods may have religious or symbolic significance in some cultures, while they may be considered ordinary in others.
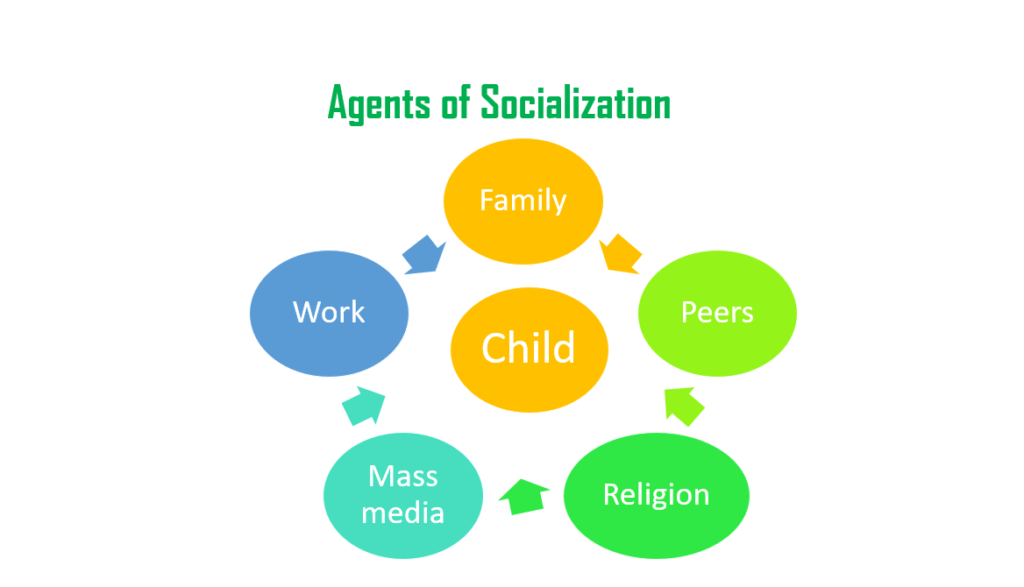
Socialization Agents in Food Consumption

Food socialization is a lifelong process that begins in infancy and continues throughout adulthood. It involves learning about food, its preparation, and its consumption. A variety of agents influence food socialization, including family, peers, and media.
The family is the primary agent of food socialization. Parents and other caregivers teach children about food through their own eating habits, food preparation practices, and conversations about food. Children learn about the foods that are considered acceptable and desirable within their culture, as well as the rules and rituals surrounding food consumption.
Peers
Peers also play an important role in food socialization. Children and adolescents often learn about new foods and eating habits from their friends. They may also be influenced by the food preferences of their peers, and they may adopt these preferences in order to fit in.
Media
The media also has a significant impact on food socialization. Food advertising, cooking shows, and other media content can influence people’s food choices and eating habits. The media can promote certain foods and diets, and it can also shape people’s perceptions of food and its role in society.
Food Socialization in Different Contexts
Food socialization is not limited to the family setting. It occurs in various contexts, each with its unique influences on food choices and eating habits.
Family Meals, Socialization process of food
Family meals provide a structured and consistent environment for food socialization. Parents model eating behaviors, introduce new foods, and establish family food traditions. Studies have shown that children who regularly participate in family meals have healthier eating habits and lower rates of obesity.
School Cafeterias
School cafeterias offer a different context for food socialization. Students are exposed to a wider variety of foods and may interact with peers from diverse backgrounds. Cafeterias can promote healthy eating by providing nutritious options and encouraging students to try new foods.
Restaurants
Restaurants provide a more social and interactive setting for food consumption. Diners can engage in conversations, share meals, and experience different cuisines. Restaurants can influence food choices by offering a wide range of options, creating a positive dining atmosphere, and providing opportunities for social interaction.
The Impact of Food Socialization on Health and Well-being
Food socialization profoundly influences dietary outcomes and overall health. Socialization practices can either promote healthy eating habits or contribute to health issues.
Positive Impact: Promoting Healthy Eating Habits
Food socialization can positively impact health by fostering:
- Balanced Diet:Exposure to a variety of foods through socialization events encourages individuals to develop a well-rounded and diverse diet, providing essential nutrients.
- Mindful Eating:Social meals promote mindful eating practices, where individuals pay attention to hunger cues and enjoy food without distractions, promoting healthy eating habits.
- Cooking Skills:Food socialization often involves cooking and preparing meals together, developing culinary skills and encouraging home-cooked meals, which are generally healthier than processed foods.
Negative Impact: Contributing to Health Issues
In contrast, food socialization can also contribute to health issues when it:
- Unhealthy Food Preferences:Social pressure and modeling can lead individuals to adopt unhealthy food preferences, such as excessive consumption of processed foods, sugary drinks, or unhealthy fats.
- Emotional Eating:Food socialization can reinforce emotional eating patterns, where individuals turn to food for comfort or stress relief, leading to overeating and weight gain.
- Disordered Eating Behaviors:In extreme cases, food socialization can contribute to the development of disordered eating behaviors, such as anorexia nervosa or bulimia nervosa.
Interventions to Promote Healthy Food Socialization
Encouraging healthy food socialization practices is crucial for promoting optimal health and well-being. Various strategies can be implemented to achieve this, involving education, policy changes, and community initiatives.
Role of Education
Educational programs play a vital role in shaping food-related behaviors. School-based interventions can introduce children to healthy eating habits, cooking skills, and nutrition knowledge. By integrating food socialization concepts into curricula, students can develop positive attitudes towards healthy food choices and learn how to navigate social situations involving food.
Policy Changes
Government policies can create supportive environments for healthy food socialization. Regulations on food advertising, labeling, and school nutrition standards can influence the availability and accessibility of healthy food options. Additionally, policies that promote breastfeeding and reduce sugar-sweetened beverage consumption can contribute to healthier food socialization practices.
Community Initiatives
Community-based initiatives can engage families and individuals in promoting healthy food socialization. Community gardens, cooking classes, and food-sharing programs provide opportunities for people to connect over food, learn about nutrition, and develop positive food habits. By fostering a sense of community around food, these initiatives can create supportive environments for healthy food socialization.
Successful Interventions
Several successful interventions have demonstrated the positive impact of promoting healthy food socialization practices. For instance, the “5-a-Day for Better Health” campaign increased fruit and vegetable consumption among children and adults. The “Eat Smart, Play Smart” program in New York City improved the nutritional quality of food served in schools and led to healthier eating habits among students.
Helpful Answers: Socialization Process Of Food
What is the primary goal of food socialization?
The primary goal of food socialization is to transmit cultural values, norms, and beliefs related to food and eating practices from one generation to the next.
How does food socialization impact health outcomes?
Food socialization can significantly influence health outcomes by shaping dietary choices and eating habits. Unhealthy food socialization practices can contribute to the development of chronic diseases such as obesity, heart disease, and diabetes.
What are some effective strategies to promote healthy food socialization?
Effective strategies to promote healthy food socialization include nutrition education programs, policy changes that support healthy food choices, and community initiatives that encourage healthy eating habits.
